Samsung PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool used to assess the impact of external factors on businesses. Samsung PESTEL analysis involves critical analysis of political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors affecting the multinational electronics company.
Political Factors in Samsung PESTEL Analysis
A set of political factors such as political stability in the country, government attitude towards the industry and the company, home market lobbying and pressure groups, international pressure groups, risk of military invasion of the country and others affect revenue and long-term growth prospects of Samsung Electronics in direct and indirect ways.
Samsung Electronics is found to be involved in a number of political scandals in its home market in South Korea. Lee Kwang-jae, Uri Party representative working for South Korean President Roh Moo-hyun officially admitted the receipt of 50 to 60 billion KRW from Samsung Group in the forms of bonds to be used in the presidential campaign in 2002. Moreover, the prosecution found that the company has also funded the opposition, Grand National Party via 2.47 billion KRW before the election.[1] The instance mentioned above represents an attempt by the company to achieve positive impact of political factors via illegal means and methods with potentially severe detrimental impact on Samsung brand image.
In August 2017, Jay Y. Lee, the former de facto head of the Samsung conglomerate, was given 5-year jail term for his role in bribery and embezzlement, part of a series of scandals that led to the ouster of Park Geun-hye, South Korea’s first female president.[2] As it is illustrated in figure below, Samsung has increased the amount of its political lobbying significantly starting from 2012. It can be argued that these spending included controversial payments as discussed above.
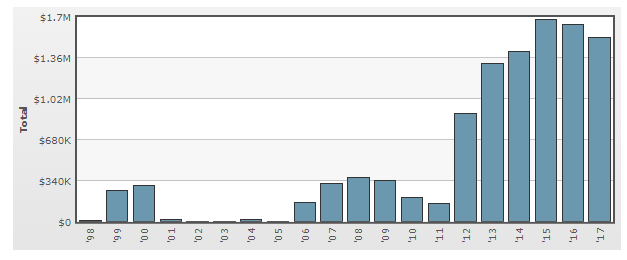
Annual lobbying by Samsung Group[3]
Economic Factors in Samsung PESTEL Analysis
Strong Korean currency is one of the major economic factors that proved to have a detrimental impact on Samsung revenues. Specifically, Won appreciation has been named by the company as one of the main reasons for the decline of the second quarterly profits in 2014 by 25% to 7.2trn won.[4] Moreover, profit of the business can be immensely affected by economic crisis, as it was the case with the global economic and financial crisis of 2007- 2009. As it is illustrated in figure below, Samsung’s quarterly operating profits halved in the third quarter of 2008, as a direct consequence of the global economic and financial crisis.
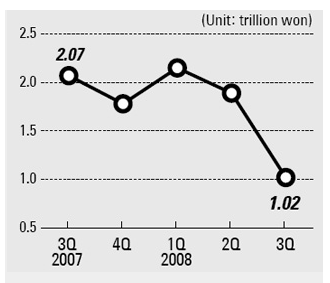
Changes in Samsung Electronics quarterly operating profits
Additional range of economic factors that can impact Samsung include levels of taxation and interest rates, inflation rate, changes in the costs of labour and other resources and others. Tax rates in particular have proved to have direct and significant effects on Samsung’s financial performance. For example, due to tax regulations in Korea, although domestic sales accounted for only 10% over the past three years, the percentage of tax paid in Korea by Samsung rose up to 67% in 2016.[5]
Samsung Group Report contains a full version of Samsung PESTEL analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung business strategy, leadership, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Samsung marketing strategy and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Ji-Young, K. (2010) The Korea Herald, Available at: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20051216000027
[2] Stone, B., Kim, S. & King, I. (2017) “Summer of Samsung: A Corruption Scandal, a Political Firestorm—and a Record Profit” Bloomberg, Available at: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/features/2017-07-27/summer-of-samsung-a-corruption-scandal-a-political-firestorm-and-a-record-profit
[3] Samsung Group (2017) Open Secrets, Available at: https://www.opensecrets.org/lobby/clientsum.php?id=D000042406
[4The New Economy (2014) Available at: http://www.theneweconomy.com/technology/samsungs-profits-fall-again-as-smartphone-market-declines
[5] Herh, M. (2017) “Despite 10% Sales Portion Samsung Electronics’ Local Tax Payment Covers 67% of Its Total Tax Paid” Business Korea, Available at: http://www.businesskorea.co.kr/english/news/industry/18755-despite-10-sales-portion-samsung-electronics%E2%80%99-local-tax-payment-covers-67-its

