
Scott and Wang (2006) state that there are several sources of finance available for SMEs in China. However, types of finance that are both available and obtainable differ for SMEs in different life cycle of the enterprises. They mentioned the following sources of finance available for SMEs in China: 1. Personal savings This form of financing is usually preferred if it is available as it does not require any interest payments in a fixed nature. Therefore, due to difficulties in finding and obtaining loan at the start-up stage, most owners of the small enterprises usually invest their own savings. 2. Loan from immediate friends and relatives This is another source of finance for SMEs in China as majority SMEs are organized and opened with the help of this type of financing. Due to strong family culture in China, the access to this type of financing is easier than it can be found in EU or theUS. 3. Trade credits Zhuo (2001) stated that trade credits is one of the financing sources for SMEs in China as it gives them the privilege of paying back to their suppliers later. This is also considered to be a good form of financing methods as small and medium sized enterprises usually struggle with cash at the early stage of their business operations. However, getting a trade credit also requires SMEs to provide healthy and strong cash flow statements, where in many cases it is impossible. 4. Bank loans Banks loans are crucial sources if financing any business in most countries due to the length and lower interest rates than the equity. However, obtaining a bank loan is another obstacle in financing SMEs in China. This is due to the fact that most of the banks are state-owned commercial banks that…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Finance

The capital structure model was promoted by Modigliani and Miller (also known as MM) (1958) which indicated that the value of the company is unchanged by the alternative mix of capital structure, namely the structure of the capital is irrelevant to the value of the firm assuming that no tax and all profit are apportioned as dividends. However, Gray et al (2007) stated that such a perfect capital market does not exist in real life. Jensen and Meckling’s (1976) (cited in Gregory et al, 2005) agency theory provides insight into the financial management of capital structure where it states that a contract is made where a principal (owner) hires and agent (directors) to run the company on their behalf by delegating the responsibilities and pays them for it. However, in the case of SMEs, majority directors of the businesses are owners of them too. Cassar and Holmes (2003) mentioned about the pecking order model by (Myers, 1984), which suggests that firms have a particular preference order to finance their businesses. He indicated that due to the information asymmetry between the firm and the potential investors, the agents (managers) know more about the firm, its potential value and future prospects than the new investors. Therefore, managers know what form of financing is available to the business at any given stage. From this point of view managers usually try to obtain the financing that they think is obtainable for them. This sometimes leads to a situation where managers have not tried other available sources of financing as they assumed that the source of finance they obtained has been the best and only choice for them. Many researchers have researched the capital structure decision form the perspectives of small firms (Gregory et al, 2005, Cassar and Holmes, 2003, Coleman, 1998, Berger and Udell,…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Finance

Employee rewards can be divided into two categories: tangible and intangible. Tangible employee rewards include financial incentives, presents, holidays, various perks etc. According to Woods (2009) intangible rewards include the following points: i) Communication between management and employees. Management should ensure the intensive level of communication with the workforce discussing with them the various aspects of the business. Moreover, engaging employees in decision making processes will positively contribute to the level of their job-satisfaction and will increase their loyalty. ii) Opportunities for career development. Some of the highly qualified professionals value the opportunity for personal and professional growth, and display willingness to join a company where such opportunities exist, even if the payment package is not so competitive. This fact should not be ignored by management, and accordingly opportunities for personal and professional growth should be provided for employees that would be highly beneficial for both, employees, as well as the company. iii) Assisting with employee work/life balance. Management should assist its employees with maintaining their work and life balance by providing opportunities of job sharing, working from home etc so, and in this way the company can dramatically increase its value in view of a potential job applicant. iv) Recognition of employee contribution. Each single occasion of positive employee contribution should be recognised by management by sending appreciation letters, verbal appreciation, and announcement and through other means. v) Providing coaching at work. Some potential applicants hesitate to apply for a vacancy because they would not feel confident if they could do the job. The management should organise coaching for each new employee joining the company, so that people with necessary qualifications would feel confident to apply for a position with the company. Moreover, according to Price (2004), as taken from Naidoo and Wills (2000) promoting health and safety in the workplace companies…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: HRM

Banking profitability. Ramlall (2009, p.2) divides the determinant factors of banking profitability into two groups: 1. External factors. They can be divided into further two categories: macroeconomic environment and market/industry characteristics. 2. Internal factors that is characteristics which are bank-specific. Dividing banking profitability in such groups is an efficient way of studying the issue, because it differentiates the factors affecting it according to its characteristics. According to Anthanasoglu (2005) studies dealing with internal profitability determinants employ such variables as size, capital, risk management and expenses management. However, the authors fail to mention external profitability determinants in greater details as compared to the internal factors, despite the fact that external factors are important as well. 1. Mergers as a Measure to Increase Banking Profitability A study undertaken by Akhvein et al (1997) was focused on examining the efficiency and price effects of mergers by the use of frontier profit function. The result of their study indicated that merged banks enjoyed an average of 16 per cent increase on profit efficiency compared to other banks due to the range of factors including shifting outputs from securities to loans and improvements on higher value product range. While examining the effect on banking profitability and rate of return on capital on changes in interest rates, Hancock (1985), made three assumptions: 1. Banking profitability depend on interest rates for asset and liability items, which is not the same for one market interest rate. 2. Banking profitability depend on the user costs of all financial items, and user costs depend on service charges, service premium costs and deposit insurance premiums, as well as on interest rates. 3. The relative price changes between financial and non-financial items is taken into account. Berg et al. (1993) concluded Swedish banks being generally more efficient than Norwegian and Finnish banks. 2.…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Finance

Banking profitability. One of the fundamental functions of any bank is its profitability. There is no doubt that recent global financial crisis negatively affected on the profitability of many banks around the globe. Some of them are starting to recover due to efficient measures from bank management and help from their governments. However, many European banks are still struggling to regain strong position in marketplace which they used to hold only a few years ago. And many of them are still not too far from the verge of bankruptcy. The problem of assessing the profit efficiency of banking industry is of paramount importance for local governments and economic theorists. Therefore, the important point is if government is striving to assist for the performance of banks to be improved, it is crucial to know how far a bank is able to increase its profit by increasing its efficiency, not using new resources for the purpose. The study on profitability of banks is especially important at this point of time. As in summer of 2012, the lowest point of global economic crises is past; however the banks and financial system in many countries and in many industries are still vulnerable to various shocks. The main important point is that problems within banking system are going to affect all other businesses as well. Because businesses have a close relationship with banks and most of them are financed by banks. This fact makes it necessary to study all the causes of the recent economic crisis in detail, giving extra attention to its affect to banks and to work on making banks less vulnerable to such external shocks. Studies into banking profitability Kumbhakar and KnoxLovell (2000, p.8) inform that Christensen, Jorgensen and Lau were the first researchers to estimate a flexible profit function in…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Finance

Employee training and development. The following purposes of training and development as proposed by Beardwell et al (2004): a) Maximising productivity and service provision for the company b) Developing the adaptability for the workforce c) Developing an organisation as a whole d) Increasing job satisfaction, motivation and morale of workforce e) Improving standards and safety at work f) Promoting the Better utilisation of other resources g) Standardisation of work practices and procedures Wood (2009) divides trainings methods into two categories: traditional training methods, and electronic training methods. Traditional training methods include lectures, on-the-job training, apprenticeship training, offside training, programmed learning, informal learning, job instruction training, and training stimulated by audiovisual tools. As a traditional training method, on-the-job training includes job rotation, coaching, and action learning, whereas the main elements of off-the-job training (offside training) are case-study, games, external seminars, Internet-based seminars and conferences, university-related programs, role-playing, behavioural modelling, Internet educational portals, and behavioural modelling. The main elements of electronic training are computer-based training, video-conferencing, electronic performance support systems, tele-training, learning portals and others. Paauwe (2004) specifies task analysis to be a detailed study of the job to be undertaken in order to identify skills required for the job. Performance analysis, on the other hand, as Shermon (2004) informs, examine individual and collective performances within organisations in order to identify deficiencies, then training and development programs can be devised in order to eliminate these performance deficiencies. Moreover, Behaviour Modelling has also been identified as an important element of training and development programs and Dessler (1984) informs that behaviour modelling includes three following components: a) Showing trainees the right (or “model”) method of performing a task b) Giving opportunities to trainees to perform in this way c) Giving feedback on the trainees’ performance. Strengths of behaviour modelling as an element of training and development scheme is…

According to Goodhart and Xu (1996, p.24) China had a dual exchange rate system: official artificially high value of RMB, and its lower value in the swap market, and these two markets were unified on January 1, 1994. The analysis by Goldstein (2003) regarding China’s currency regime resulted in five conclusions: Chinese RMB is under-valued within 15-25 percent range. This is resulted by China maintaining controls on capital outflows, running surpluses on overall current and capital accounts in its balance of payments and accumulating international reserves in large amounts. The revaluation of RMB will benefit China and the global economy, otherwise net capital inflows and the large accumulation of international reserves will continue. Adopting a flexible exchange rate and opening its capital market will benefit China, but the economy is not ready for this. China should be persuaded to change its exchange rate policy, and trade measures should be imposed against China’s exports by United States. The effect of medium-size revaluation of RMB within external accounts of US must not be exaggerated. Wu (2006, p.3) argues that before revaluation of RMB 2 per cent in 2005 The People Bank of China had four options to consider as its short-term policy options: Option 1: Increasing the supply of money without revaluing the RMB. This option would have contradicted the macroeconomic objectives of The People’s Bank of China Option 2: Waiting for the tightening of the Federal Reserve without revaluing the RMB. Option 3: Aiming to lower revaluation expectations tightening macroeconomic environment, without revaluing RMB. Option 4: Revaluing the RMB Marsh and Diaz (2008, pp.2-4) suggest following forecast methods to forecast the exchange rate of a currency for a future period: Technical forecast method. This method involves analysing relevant historical data with the aim of forecasting…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Economics

A vast amount of literature reviewed recognize following factors as determinants of the strengths of currency exchange rate: Inflation If the inflation rate is low in a country the value of its currency and its purchasing power towards other currencies rises, meaning its currency becomes stronger. Alternatively, countries with high inflation rate experience their currency depreciating against the currency of countries they trade with. The relationship between inflation and the exchange rate is that fixed interest regime can be practiced by countries with the aim of controlling the inflation rate. Initially it was done on the basis of Bretton Woods agreement before it was annulled in early 1970’s, which allowed other countries to fix their currencies against US dollars. Although fixed interest rate regime does help governments to control their inflation it has negative sides as well in the forms of vulnerability to the speculation and inability of undertaking domestic monetary policy. Interest rates Interest rates and exchange rates are correlated. Higher interest rates cause the exchange rates to increase, because higher interest rates would generate more profit for lenders, at the same time, attracting foreign capital. Conversely, if interest rate in a country is lower, exchange rates tend to be lower as well. Speculation According to Economicshelp (online, 2010), a fixed exchange rate can be a victim of speculation if the following three conditions apply: The currency is at the wrong market value .The Government doesn’t have sufficient reserves to protect the currency. People have no Confidence in the government intervention. Relative strength of other currencies For obvious reasons the relative strength of other currencies are going to affect the exchange rate of a currency of a country. If the strength of any other country currency increases for various range of reasons the exchange rate of…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Economics

Recruitment and selection of new team members need to be undertaken with the primary aim that “the required numbers of employees with required talent are available when needed” (Bratton and Gold, 2001, p.13), in our case the required number of employees are seven team members with special characteristics and talents specified as above. It is important to have a clear understanding about the differences between recruitment and selection. The primary aim of recruitment is searching for and obtaining potential job candidates in sufficient numbers and quality in order for the organization to be able to select the most appropriate people to satisfy its job needs. (Dowling and Schuler, 1990).Selection, on the other hand, involves selecting candidates among recruited pool of candidates in order to hire for the job. (Hackett, 1991) The primary aim of recruitment is considered to be “to obtain at minimum cost the number and quality of employees required to satisfy the human resource needs of the company” (Armstrong, 2001, p.385) In order to employ the members of the team for the roles specified above the following recruitment strategy is going to be followed as proposed by Beardwell et al (2004): Firstly, each individual vacancy within the team, and their roles and responsibilities are going to be specified. Secondly, all available recruitment methods are going to be critically analysed in order to identify the most suitable ones taking into account the specifications and objectives of the team. Thirdly, recruitment advertisements are going to be undertaken in accordance with the chosen specific recruitment method(s). Fourthly, employment documentations are going to be dealt with as regards to each person recruited. Fifthly, recruitment monitoring and evaluation is going to take place taking advantage of previous experiences regarding this matter. Sixthly, recruited candidates are going to be shortlisted in order to proceed…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: HRM
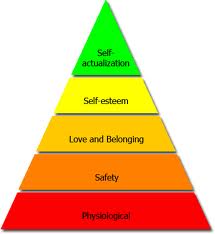
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. The nature of initial studies on motivation can be summarised in the idea that “early and modern approaches to motivation are based on the premise that increasing the amount of time and effort that an individual devotes to a task (i.e. task motivation) will result in higher levels of individual performance and increased productivity for the organisation” (Landy and Conte, 2010, p.368). Arguably the most prominent author on the topic of motivation is Abraham Maslow. Maslow states (1943, p.372) that employees have five levels of needs: 1. The Physiological needs. This is the basic needs for living, which includes oxygen water, protein, salt, sugar, calcium, and other minerals and vitamins. They are also known as the “Biological necessities”. They also include the needs to be active, to rest, and to sleep. These needs are the strongest because a person needs to have the factors above in order to survive. In business environment it means good payment, and good environment for working. 2. The safety and security needs. When physiological needs are reached, the second need comes into place, which for employees means finding the safe circumstances, stability, and protection. 3. The belonging needs. When the both satisfactions are reached, belonging needs layer would arise. Employees might begin to feel the needs of friendships, affectionate relationships in general, or even a sense of community. 4. The esteem needs. Maslow has divided esteem needs into two parts: lower and higher self-esteem needs. The lower one is the need for respects for others, whereas the higher one requires self-respect, which includes the sense of confidence, achievement, independence, and freedom. 5. Self-actualization needs. This is the level, when employees satisfy all their needs, including the four needs above. In business sense it means the opportunities for developing new skills, scope to meet challenges and room to perform…
