Research Approach
In the field of science different researchers may assign different meanings for the team research approach. In some publications you may see that research approach may imply methods of data collection and data analysis in general and differences between qualitative and quantitative methods in particular.
However, in our view research approach is best seen as a general plan and procedure for conducting the study. Accordingly, approach for the research can be divided into three categories:
The relevance of hypotheses to the study is the main distinctive point between deductive and inductive approaches. Deductive approach tests the validity of assumptions (or theories/hypotheses) in hand, whereas inductive approach contributes to the emergence of new theories and generalizations. Abductive research, on the other hand, starts with ‘surprising facts’ or ‘puzzles’ and the research process is devoted their explanation.[1]
The following table illustrates the major differences between deductive, inductive and abductive research approaches in terms of logic, generaliability, use of data and theory.[2]
| Deduction | Induction | Abduction | |
| Logic | In a deductive inference,
when the premises are true, the conclusion must also be true |
In an inductive inference, known premises are used
to generate untested conclusions |
In an abductive inference, known
premises are used to generate testable conclusions |
| Generalizability | Generalising from the general to the specific | Generalising from the specific to the general | Generalising from the interactions between the specific and the general |
| Use of data | Data collection is used to
evaluate propositions or hypotheses related to an existing theory |
Data collection is used to
explore a phenomenon, identify themes and patterns and create a conceptual framework |
Data collection is used to explore a phenomenon, identify themes and patterns, locate these in a conceptual framework
and test this through subsequent data collection and so forth |
|
Theory
|
Theory falsification or verification | Theory generation and building | Theory generation or modification;
incorporating existing theory where appropriate, to build new theory or modify existing theory |
Differences between deductive, inductive and abductive approaches
Discussion of research approach is a vital part of any scientific study regardless of the research area. Within the methodology chapter of your dissertation, you need to explain the main differences between inductive, deductive and abductive approaches. Also, you need to specify the approach you have adopted for your research by breaking down your arguments into several points.
Let me explain the research approach for a following study:
Effects of labour migration within the EU on the formation of multicultural teams in Dutch private sector organizations
Deductive Approach
If you have formulated a set of hypotheses for your dissertation that need to be confirmed or rejected during the research process you would be following a deductive approach. In deductive approach, the effects of labour migration within the EU are assessed by developing hypotheses that are tested during the research process.
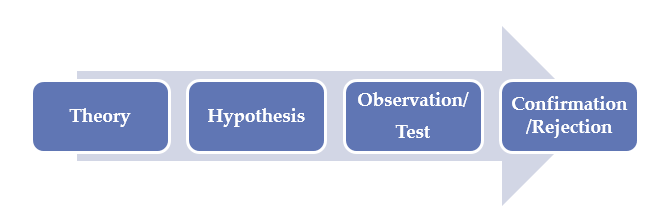
Dissertations with deductive approach follow the following path:
Deductive process in research approach
The following hypotheses can be developed in order to assess the effects of labour migration within the EU on the formation of multicultural teams in Dutch private sector organizations using a deductive approach:
Hypothesis: Labour migration within the EU contributes to the formation of multicultural teams in Dutch private sector organizations
The whole research process will be devoted to testing this hypothesis. The hypothesis will be proved right or wrong by the end of the research process.
Inductive Approach
Alternatively, inductive approach does not involve formulation of hypotheses. It starts with research questions and aims and objectives that need to be achieved during the research process.
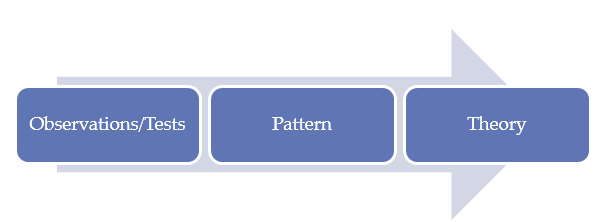
Inductive studies follow the route below:
Inductive process in research approach
Referring to the example above, the effects of labour migration within the EU on the formation of multicultural teams in Dutch private sector organizations can be assessed through finding answers to the following research questions:
Research question: How does labour migration within the EU effect the formation of multicultural teams in Dutch private sector organizations?
The research process will focus on finding answer to this research question. Answer to the research question to be found by the end of the research process will imply generating a new theory related to the research problem.
Abductive Approach
In abductive approach, the research process is devoted to explanation of ‘incomplete observations’, ‘surprising facts’ or ‘puzzles’ specified at the beginning of the study. Referring to the same research topic, you may observe that labour migration within the EU was actually decreasing the extent of cross-cultural differences within teams in Dutch private sector organizations.
In this case your study can be devoted to the explanation of this phenomenon by using qualitative and/or quantitative methods of data collection and data analysis in an integrated manner.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance contains discussions of theory and application of research approaches. The e-book also explains all stages of the research process starting from the selection of the research area to writing personal reflection. Important elements of dissertations such as research philosophy, research design, methods of data collection, data analysis and sampling are explained in this e-book in simple words.
John Dudovskiy
[1] Bryman A. & Bell, E. (2015) “Business Research Methods” 4th edition, Oxford University Press, p.27
[2] Source: Saunders, M., Lewis, P. & Thornhill, A. (2012) “Research Methods for Business Students” 6th edition, Pearson Education Limited