Customer Services

The literature review has established viewpoints of other authors about unique characteristics of tourism industry. Literature review has revealed the following unique characteristics of tourism industry as summarised by TSA project in 2008: Firstly, the tourism is not an industry. The rationale behind this viewpoint relates to the idea that tourism comprises a wide range of individual businesses in a wide range of areas such as catering, transportation, entertainment, manufacturing and others. However, this viewpoint is not shared by all authors and many prominent authors in the area of tourism such as Webb (2009), Solomon and Rabolt (2009) and Rajagopal (2010) still refer to tourism as an industry. Secondly, in tourism consumers come to products. It is not possible to import tourism products and services or to provide them to customers through other channels and this point can be specified as an important distinctive feature of tourism industry from other industries. Thirdly, in tourism location is a part of the product. In tourism industry it is difficult to make a clear distinction between the value of a tourism destination and a wide range of products and services offered in this destination. In other words, tourism interconnects many separate businesses into a single entity (Schiffman et. al., 2012). Moreover, according to literature review findings there are range of systems that can be applied in order to characterise tourism destinations. For example, a system proposed by Pearce (2005) identifies six different labels in tourism industry and explains characteristics of each label. Label Emphasis Characteristics and examples of the system Activities Physical Listings, profiles, GIS approach Settings Physical Public management agencies use of zones using a biophysical basis Facilities Physical Micro-environments and service escapes: the immediate physical features of the tourist space Service Social Personnel: the characteristics of personnel in the service…

Gap Model of Service Quality consists of the following gaps: Gap 1: customer expectation – management perception gap: the difference between the service the customer expects and the service level the supplier thinks that customer wants. Gap 2: management perception-service standard gap: the difference between the service specification that is set and the supplier management assessment of customer service requirements. Gap 3: service standard-service delivery gap: the difference between the actual service that is provided and the planned level of service based on the service specification that has been set. Gap 4: service delivery-external communication gap: the difference between the actual service that is provided and the promised level of service that was communicated to the customer. Gap 5: actual service – perceived service gap: the difference between the service that the supplier is providing and the service that the customer thinks is being received.

According to Grigoroudis and Siskos (2009) as taken by Oliver (1997) “satisfaction is the consumer’s fulfilment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product or service itself, provided (or is providing) a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfilment, including levels of under-or overfulfillment” (Grigoroudis and Siskos, 2009, p.4) The Business Dictionary (online, 2013) defines private sector as a part of national economy that consists of private enterprises including personal sector (households) and corporate sector (companies). The definition of the public sector is suggested by The Free Dictionary (2011) as “the part of an economy that consists of state-owned institutions, including nationalised industries and services provided by local authorities” (The Free Dictionary, online, 2011). Although the term ‘quality’ on its own is widely known and does not require further elaboration, some authors have offered their viewpoints regarding the definition of the term within the context of customer services. Specifically, it has been stated that, “quality of the delivered products or services is essential to achieving customer satisfaction. The quality concept embraces how to meet all customers’ requirements, including how they are greeted on the telephone or at the counter, the speed with which a query is responded, providing new services when required, and ensuring the delivered services satisfy the community needs” (Nagel, 2000, p.47). Introduction According to Grigoroudis and Siskos (2009) the advantages of private sector organisations over the public sector organisations include better level of the service, more information about various aspects of customer services, better management, market testing and rewarding performance. Secondary data authors (Murley, 1997) argue that a part of the issue of effective customer service provision within public sector relates to the identification of customers in public sector in the first place. Discussing police services specifically, the author reasons that “their customers…

Customer relationship management has been defined as “a business approach that integrates people, processes, and technology to maximise relationships with customers” Goldenberg (2008, p.3). Moreover, it has been stated that customer relationship management “characterises a management philosophy that is a complete orientation of the company toward existing and potential customer relationships” (Raab et al, 2008, p.6) Mueller (2010) characterises customer relationship management aspect of the business as a highly dynamic, and convincingly argues that businesses have to adopt a proactive approach in devising relevant programs and initiatives in order to remain competitive in their industries. Sinkovics and Ghauri (2009) relate the necessity for engaging in customer relationship management to high cost of direct sales, highly intensifying level of competition in the global level, and need for information about various aspects of the business in general, and consumer behaviour in particular, that can be used to increase the levels of sales. According to Peppers and Rogers (2011), there is global tendency in customer relationship management that relates to the shift from transactional model towards the relationship model. In other words, Peppers and Rogers (2011) argue that satisfying customer needs as a result of on-time transaction is not sufficient today in order to ensure the long-term growth of the businesses. Instead, businesses have to strive to maintain long-term relationships with their customers in order to maintain flexibility to adopt their increasing expectations and thus achieving their life-long loyalty. Peppers and Rogers (2011) further stress that, businesses that refuses to acknowledge this tendency in the global marketplace would be risking their market share and growth prospects in the future. One of the most critical sources for the research is the book “Relationship Marketing and Customer Relationship Management” authored by Brink and Berndt (2009). The book offers an in-depth discussion of the concept of…

Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction: case study of London Underground and National Rail Services
There are many factors that affect the level of satisfaction of both product and service customers equally, and some of these factors have been discussed in detail earlier. However, there are also some factors that affect the level of satisfaction of service customers alone, and not necessarily customers satisfaction levels of people buying products. The most common factors proposed by authors that effect the customer satisfaction levels of service customers can be summarized into following points: First, non-verbal behaviour of service provider greatly affects the level of customer satisfaction of service customers (Gabbot, 2000). Due to the fact that most of the services are provided by people, service customers are more sensitive and critical towards behaviour, including nonverbal behaviour of people offering these services. However, this statement is less relevant to services provided by London Underground and National Rail Services, due to the fact that although they operate in service sector, nevertheless, human aspect of their operations that has a direct contact with customers are less intensive compared to many other types of services like teaching and hairdressing. Second, in service sector the quality of service and customer satisfaction level may depend on the competency of a single employee (Barnard, 2000) In cases of London Underground and National Rail Services this statement is especially true which can be illustrated by the role of train operators in cases of trains being held between two stations. London Underground and National Rail Services trains being held between two stations for signal failures and other occasions are not rare occurrences. However, some train operators positively contribute to the level of customer satisfaction by repeatedly apologizing and explaining the reasons of delays, while others damage the customer satisfaction level even more by keeping customers ‘in dark’ in such an unpleasant circumstances. Third, customers’ own involvement…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Customer Services

Factors Influencing Customer Expectations Factors that influence the level of customer expectations have been specified by Rai (2008) as the following: Firstly, benchmarks specified by service competitors. Competitors’ service benchmark influence customer expectations in a way that the higher the benchmarks, the higher customer expectations will be. Secondly, individual psychology. As it has been discussed above the role of individual differences find greater reflection in the level of customer satisfaction in the service sector compared to the level of customer satisfaction in products. Therefore, most of the service companies strive to adopt individual approach taking into account expectations and characteristics of each individual customer (Barnard, 2002) Thirdly, individual background. As it has been identified that individual psychology plays a great role on the service expectations from that individual; individual background as one of the main determinants of individual psychology also plays an important role in customer service expectations. Fourthly, previous service records of the company. When potential consumers approach a service company they will have their expectations according to various characteristics of the company, including its previous service records. Accordingly consumer expectations will be high in companies with reputable service records, and vice-versa. Issues in Customer Expectations As it has been well established in business world, one of the important conditions of ensuring long-time profitability of the business is meeting or exceeding customer expectations at all times. However, even with the willingness of the company to exceed customer expectations and with relevant skills and capabilities achieving this objective can prove to be challenging due to the following reasons specified by Rai (2008): Firstly, customer expectations may be unrealistic. The issue of customer expectations being unrealistic have been raised by several authors including Miller (1995), James (2004), and Hayes (2008). The common practice for service companies in such a scenario…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Customer Services
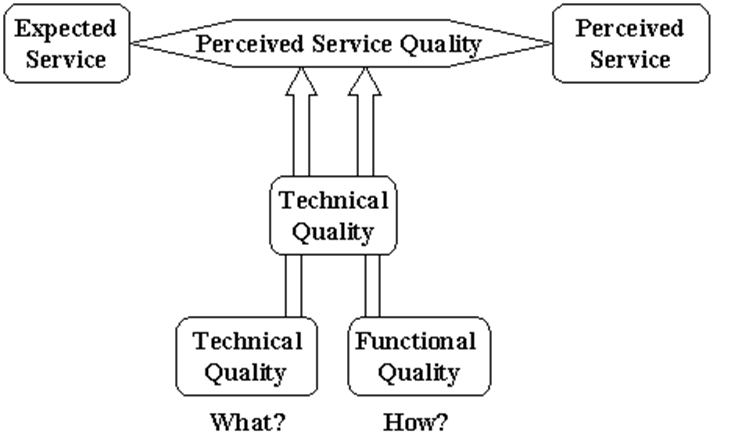
Service Quality Model pioneered by Gronroos (1982) states that customer’s perception of quality, and ultimately customer satisfaction depends on customer’s perception of two dimensions of the service: technical quality and functional quality. Technical quality dimension of the service concentrates on what the customer receives, focusing on the technical outcome of the process. Functional quality, on the other hand, concentrates on how the consumer receives the technical outcome. A service concept is explained by Johnston and Calrk (2008, p.42), as a shared understanding of the service nature provided and received, which should encapsulate information about: – The organizing idea, which is the essence – The experience. – The outcome. Lancaster et al (2002, p. 75) inform that consumer buyer behaviour is influenced by a range of environmental and individual factors. Environmental influencers include cultural, social class, groups/family, situational factors and marketing efforts, and individual influencers include psychological aspects, lifestyle, demographics and economic situation. References Johnson, R & Clark, G, 2008, “Service Operations Management”, third edition, Prentice Hall Lancaster, G, Massingham, L & Ashford, R, 2002, “Essentials of Marketing”, fourth edition, McGraw-Hill
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Customer Services
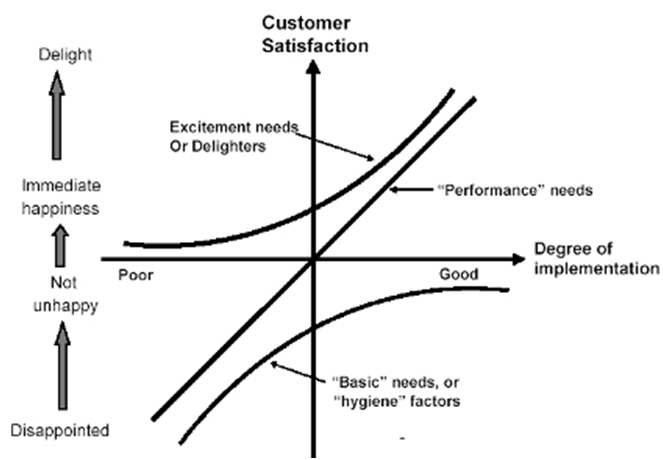
Kano model of Customer Satisfaction was proposed by Kano et al (1996) and it focuses on product attributes on the basis of how they are perceived by customers and their effect on customer satisfaction. The model distinguishes three types of product attributes that contribute to customer satisfaction in varying degrees: basic attributes, performance or spoken attributes, or surprise or delight attributes. Kano model of customer satisfaction is not only valid for manufacturing businesses; rather it also equally can be applied to the service sector, including London Underground and National Rail Services. The basic or expected attributes for London Underground and National Rail services would be to ensure the commute of their customers from one destination to the other. Customers would be highly disappointed when the basic attributes of their services are not ensured, let alone the extremely low level of their satisfaction level if such a situation were to occur. Performance or spoken attributes of services of London Underground and National Rail Services would be the speed at which customers are taken, to their destination, the level of crowdedness inside the carriages, on platforms and stations in general, the level of customer services customers are offered by staff, and others. The level of performance or spoken attributes of services offered by London Underground and National Rail Services make a huge difference on the customer satisfaction, in a way that the better the performance, the higher customer satisfaction level will be. Surprise and delight attributes, are the ones that are not generally expected by customers, but if they are present they will make a significant contribution on the level of customer satisfaction. However, the absence of surprise and delight attributes would not dissatisfy customers due to the fact that customers would not be expecting them in the first place. For instance,…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Customer Services

Johnson and Clark (2008) define service concept as a shared understanding of the service nature provided and received. They also state that service concept has to provide information about the essence of the service, service experience, and service outcome. “The terms customer satisfaction and perception of quality are labels we use to summarize a set of observable actions related to the product or service” (Hayes, 2008, p.33) The most comprehensive definition of satisfaction has been offered by Kotler and Keller who define satisfaction as “person’s feeling of pleasure or disappointment which resulted from comparing a product’s perceived performance or outcome against his/ her expectations” (Kotler and Keller, 2006, p.144). “Perception is defined as consumer’s belief, concerning the service received or experienced” (Rai, 2008). Categorisations of Customer Satisfaction and Service Perception Parasuraman et al (1991) divide customer service expectations into two levels: desired and adequate. Desired level of service expectations is a state of service the customer desires to receive, whereas adequate level of customer expectation is the level of service the customer can only “accept” without being too satisfied with it. If desired and adequate levels of service expectations are to be explained in case of London Underground and National Rail Services customers, desired level of customer expectation would be to go from one destination to the other with no crowded train as quick as possible, whereas, adequate level of customer expectation would be just to go to destination even if the train carriage is crowded, and the train is not moving too fast. Walker (1995) offers conceptualised service encounter model that is divided into three disconfirmation stages: First stage is evaluation stage in which peripheral service is offered before the consumption of the core service. Second stage involves intensive anticipation of core service by consumer. Third stage is the final in…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Customer Services

Customer perceptions are needed to be met and exceeded. It requires from companies to study the buyer behaviour of their existing and potential customers and to devise programs and initiatives to offer superior customer service. According to Parasuraman et al (1991, p.42), customer services expectations consist of two levels: desired and adequate. Desired level of expectations is the level of service a customer wanted to be performed, while the adequate level of expectation is the “acceptable” level of service by the customer. A service quality model, highlighting the main requirements for delivering high quality service which identifies five gaps as causes for unsuccessful service delivery has been formulated by Parasuraman et al (1985, pp.41-50): Gap between expectation of client and perception of management. In order to be able to exceed customer expectations, and in this way to insure customer satisfaction service company management has to have a clear and accurate perception about customer expectations. A lack of such knowledge creates a gap that can be one of the main reasons for service customers not being satisfied. Gap between perception of management and service quality specification. Even if management accurately perceive customer expectations there are still chances of customer dissatisfaction that can be caused by the gap in planning quality of the service according to customer expectations Gap between specification of quality and the delivery of service. Another potential area for customer dissatisfaction relates to the failure of efficiently specified quality service due to various reasons, including incompetent workforce, and inefficient working conditions. The gap between the delivery of service and external communications. In cases where service company employees have relevant skills and willingness to offer efficiently specified quality service, still customers may be left unsatisfied due to external factors Gap between perceived and expected service. Lastly, one of the common causes for customer dissatisfaction in service sector…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Customer Services
