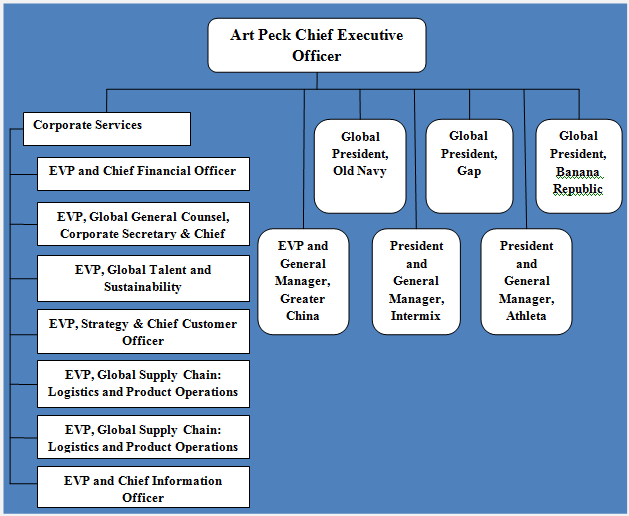
Gap Inc. Organizational Structure: A Hybrid Structure that is Expected to Change
Gap Inc. organizational structure can be characterized as hybrid integrating certain elements of divisional and hierarchical organizational structures. Gap organizational structure has the following pattern:
Gap Inc. organizational structure
As it is illustrated in figure above, Gap organizational structure is divided into five divisions with each division representing a separate brand and headed by a president. At the same time, the organizational structure of each division is highly hierarchical and there are multiple levels of management between the president of the division and a shop floor assistant.
In 2016, as a part of an initiative to address declining sales and profitability, Gap CEO Art Peck announced plans for global restructuring that includes reducing the numbers of Gap stores in the US, withdrawing the Old Navy fascia in Japan and making head office redundancies.[1] Moreover, store closures also involved Banana Republic brand bringing the total expected store closure count to 75 by the end of fiscal 2016.[2]
There are also occasional brand-specific changes in organizational structures led by the presidents of respective brands. For example, a major restructuring introduced in Gap brand in 2015 included combining e-commerce and marketing organization into one unit and elimination of Creative Director role resulting in Rebekka Bay’s departure from the company.[3]
Organizational structure of Gap Inc. may be subjected to further changes to a considerable extent in the foreseeable future to address serious challenges the company is facing. Specifically, net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased 4 percent to USD 15.8 billion compared with USD 16.4 billion for fiscal 2014. Gross profit for fiscal 2015 was USD 5.7 billion compared with USD 6.3 billion for fiscal 2014.[4] Accordingly, we can expect the company to engage in downsizing of management layers along with further store closures in developed countries to concentrate more in strategic developing countries such as China, India and former USSR-blog countries.
Gap Inc. Report comprises a comprehensive analysis of Gap Inc. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Gap Inc. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Gap Inc.’s marketing strategy and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Waller-Davies, B. (2016) “Gap sales and profits decline as global restructure begins” Retail Week, Available at: https://www.retail-week.com/sectors/fashion/gap-sales-and-profits-decline-as-global-restructure-begins/7011345.article
[2] Gap reports earnings in line with Street expectations, announces 75 store closings (2016) CNBC, Available at: http://www.cnbc.com/2016/05/19/gap-inc-reports-earnings-in-line-with-street-expectations-announces-75-store-closings.html
[3] Gap Inc. Press Release (2015) Available at: http://www.gapinc.com/content/gapinc/html/media/pressrelease/2015/med_pr_gapbrand_12915.html
[4] Annual Report (2015) GAP Inc.