
Founded in 2010 in Manhattan USA by Adam Neumann and Miguel McKelvey, WeWork Inc. is a global flexible workspace provider that comprises a network of 756 locations in 38 countries. The co-working giant has approximately 590 thousand physical memberships as of December 2021 (Annual Report, 2021). In the US in 2021 WeWork represented approximately 0.5% of all commercial office space and 63% of Fortune 100 companies are WeWork members WeWork’s mission is to empower tomorrow’s world at work. The workspace provider has a business strategy of digitalizing the real estate business and offering space as a service. The company had severe leadership and ethical challenges under controversial co-founder and the first CEO Adam Neumann, but the current CEO Sandeep Mathrani is bringing discipline and maturity to the leadership. The hierarchical organizational structure of the company has allowed Mathrani to turn around the business to a certain extend via reducing operational costs and focusing on the core business. The co-working and office space operator has considerable strengths such as solid international presence, brand recognition and experience in its niche. At the same time, WeWork has certain serious weaknesses that include the absence of profitability and high level of indebtedness. Moreover, WeWork brand image has been severely damaged due to management and ethical issues under the leadership of Adam Neumann as discussed throughout this report. WeWork Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on WeWork. Moreover, the report contains analyses of WeWork’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and ecosystem. The report also analysis marketing strategy, ecosystem and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Executive Summary 2. Business Strategy 3. Leadership 4. Organisational Structure 5. Organizational Culture…
Founded in 2010 in Manhattan USA by Adam Neumann and Miguel McKelvey, WeWork Inc. is a global flexible workspace provider that comprises a network of 756 locations in 38 countries. The co-working giant has approximately 590 thousand physical memberships as of December 2021 (Annual Report, 2021). In the US in 2021 WeWork represented approximately 0.5% of all commercial office space and 63% of Fortune 100 companies are WeWork members[1]
WeWork’s mission is to empower tomorrow’s world at work. The workspace provider has a business strategy of digitalizing the real estate business and offering space as a service. The company had severe leadership and ethical challenges under controversial co-founder and the first CEO Adam Neumann, but the current CEO Sandeep Mathrani is bringing discipline and maturity to the leadership. The hierarchical organizational structure of the company has allowed Mathrani to turn around the business to a certain extend via reducing operational costs and focusing on the core business.
The co-working and office space operator has considerable strengths such as solid international presence, brand recognition and experience in its niche. At the same time, WeWork has certain serious weaknesses that include the absence of profitability and high level of indebtedness. Moreover, WeWork brand image has been severely damaged due to management and ethical issues under the leadership of Adam Neumann as discussed throughout this report.
WeWork Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on WeWork. Moreover, the report contains analyses of WeWork’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and ecosystem. The report also analysis marketing strategy, ecosystem and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility.

The term ecosystem was coined by British botanist Arthur Tansley in 1930s to describe community of organisms that interact with each-other and their environments. Later in early 1990s, James F. Moore applied the term ecosystem into business environment and used the term business ecosystem for the first time. Nowadays, the term business ecosystem is extensively used in high tech industry. Business ecosystem can be defined as “a network of different entities that are dynamic and interact with each other to create and exchange sustainable value”[1]. Specifically, it is a network of different entities that provide greater effectiveness and capacity than the sum of its individual elements. Alternatively, business ecosystem is “a purposeful business arrangement between two or more entities (the members) to create and share in collective value for a common set of customers.”[2] Moore (1997)[3] divides business ecosystems into the following four stages: 1. The pioneering stage, where the ecosystem is formed. 2. The expansion stage, as the ecosystem extends to achieve maximum market coverage and critical mass. 3. The authority stage, where the ecosystem matures. 4. The renewal or death stage, where species must work together to radically improve or reinvent the ecosystem to sustain its ongoing growth. Ecosystem creates entry barriers for new market players, because potential entrants will have to compete not only with specific products and services, but with the entire system of complementary businesses, products and services. Business ecosystem can be divided into three large categories: – Solution ecosystem is a type of ecosystem that produces products and services. – Transaction ecosystem is based on a digital platform that integrates suppliers to the platform and platform users. For example, ride-hailing platforms such as Uber and Lyft connect drivers with riders. – Hybrid ecosystem combines features of both solution ecosystem and hybrid ecosystem. Dimensions…

Organizational structure can be defined as a system for outlining management roles and responsibilities to achieve organizational goals. Organizational structure also determines the pattern of information flow within the organization. For instance, in highly hierarchical structures decisions are communicated from top to down, whereas in flat structures the power for decision making is distributed among various levels. Organizational structure aims to provide efficiency and focus to operations. Appropriate structure should illustrate how the roles and responsibilities of each employee fit within the overall system. Organizational structure has the following four main elements: Chain of command. Illustrating who reports to whom via an organizational chart. Defining departments. Clustering tasks, roles and responsibilities into groups and defining connections between various groups. Extend of control. Categorizing each and every task into departments to avoid a situation where two or more people do the same task. Centralization. Identifying the levels where decisions are made. There are four main types of organizational structures – functional, divisional, flat and matrix. Functional Structure Functional structure is based on specialization of employees and it is the most common organizational structure. It is also referred to as bureaucratic structure and divides company into various departments such as procurement, operations, marketing , finance etc. Divisional Structure Divisional structure is also popular and it divides to company into various divisions on the basis of products, projects or subsidiaries. Flat Structure Flat structure, also referred to as horizontal structure aims to minimize the chain of command providing employees with autonomy in decision making. This pattern is popular among startups. Matrix Organizational Structure Matrix structure is the most complex and accordingly, the least popular. Matrix structure assigns employees across various divisions and supervisors. Employees in such a structure may belong to more than one divisions and report to several superiors. In this portal…
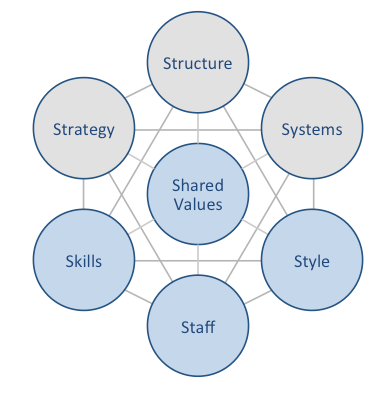
McKinsey 7S model is a tool for analyzing organizational design. The model aims to illustrate how organizational effectiveness can be achieved through alignment of seven key elements. The model divides elements into two categories – hard elements and soft elements. Strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. Shared values are placed at the core of McKinsey 7S model because they are cornerstone to the development of all other elements Hard Elements Strategy. Strategy is a plan to generate profit sustainably on the basis of competitive advantage(s). Answers to the following questions uncover company’s strategy: How company plans to maximize its profits? How company deals with competitive pressures? How the business deals with changes in customer demands, tastes and preferences? Structure. Structure refers to the organization of the business, organizational chart depicting the chain of command. Companies can look for answers to the following questions to identify the pattern of their structure: How divisions/teams are divided? What is the hierarchy of the company? How activities of various divisions are organized? What is the level of autonomy in decision making in various departments? Are the lines of communication explicit or implicit? Systems. Activities and procedures employees use daily to complete their job. The following questions can be used in regard to systems within companies: What are the main systems that maintain performance? How systems are controlled and evaluated? What are benchmarks are used to keep systems on track? Soft Elements Skills. Skills relate to company’s core competencies and capabilities that enable employees to perform efficiently. The following are the main questions related to skills: What are the main important required skills for the company to succeed? Are there any gaps in required skills? What are the skills monitoring and control practices? Staff.…
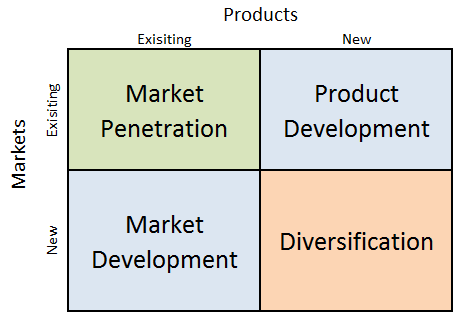
Ansoff Matrix, also known as product/market expansion grid is a marketing planning model that can help firms to formulate product and marketing strategy. H. Igor Ansoff developed this framework and first published in the Harvard Business Review in 1957, in an article titled “Strategies for Diversification.”[1] Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, there are four growth strategies: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. This is the safest businesses growth strategy. Therefore, businesses of all sizes engage in market penetration at all times. Focusing on firm’s core value offering is very important to achieve successful market penetration. Furthermore, firms can achieve greater market penetration by improving marketing strategy, offering sales promotions, engaging in mergers and acquisitions in the same markets and through other means. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Firms can develop new products through effective investments in research and development, acquiring rights to produce products developed by others or acquiring companies producing different products. Ideas for new products can come from employees or customers. All major international companies engage in product development with varying levels of intensity. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Market development strategy includes offering same products to different customer segments and starting selling in new geographical areas, countries and regions. 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets and this is considered to be the riskiest strategy. Firms may decide to diversify into related or unrelated sectors. Successfully engaged, diversification allows businesses to reduce its dependence on a single market and industry. In this portal you can find application of Ansoff Matrix framework on major international companies. [1] Ansoff, H. (1957.) ‘Strategies for Diversification,’ Harvard Business Review, Volume…
Leadership can be defined as “the ability to inspire confidence in and support among the people who are needed to achieve organisational goals” (DuBrin, 2012, p.28).[1] Alternatively, leadership is “the discipline of deliberately exerting special influence within a group to move it toward goals of beneficial permanence that fulfil the group’s real needs” (Haggai, 2009, p.20)[2]. There is a difference between leadership practices in private and public sector. The following is the list of popular leadership theories: Contingency theories of leadership Emotional Intelligence Fiedler’s Theory Leadership Continuum Theory Path-Goal Theory The Great Man Theory There are many types of leadership styles and the following are the most popular leadership styles: Autocratic Leadership Style Consultative Leadership Style Democratic (Participative) Leadership Style Laissez-Faire Leadership Style Transactional Leadership Style Transformational Leadership Style You can find analysis of leadership practices at major international companies in this portal here. [1] DuBrin, A.J. (2012) “Leadership: Research Findings, Practice, and Skills” 7th edition, Cengage Learning [2] Haggai, J.E. (2009) “The Influential Leader: 12 Steps to Igniting Visionary Decision Making” Harvest House Publishers
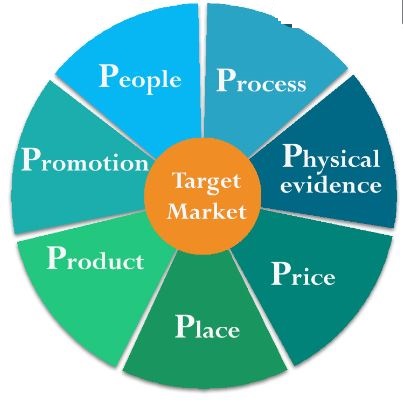
Marketing mix, also known as 7Ps of marketing includes individual marketing elements that form overall offer to customers. The concept was developed by marketing professor E. Jerome McCarthy and originally published in his book Basic Marketing. A Managerial Approach in 1960.[1] Initially the concept consisted of 4 Ps – product, place, price and promotion. As the field of marketing became more sophisticated additional 3 Ps – people, process and physical evidence were added by Bitner and Booms[2]. The additional 3Ps are also called ‘service mix Ps’, because they integrate important aspects of services into the marketing mix concept. Furthermore, in 2007 Larry Londre introduced another 2Ps – Partners/Strategic Alliances and Presentation. However, this latest addition has not been widely accepted among marketing researchers and practitioners, thus here we will stick to 7Ps of marketing. Marketing mix is a useful tool to tailor your products and services to the needs and wants of the target customer segment, but it is not a one-stop-shop for developing a comprehensive marketing strategy. A successful marketing strategy needs to address a range of other frameworks such as segmentation targeting and positioning, marketing communication mix and others. Product Element in 7Ps of Marketing Product or a service is the starting point in the marketing mix. Companies need to take into account the following variables, among others when developing new products: In what type of packaging is the product offered? Are products offered in various colours sizes etc.? What design and technical features differentiate the product in the competition? Are products durable and robust enough to appeal to the needs and wants of the target customer segment? What are the levels of quality and functional performance? Can he product be customized to individual users? Is the product easy to use and maintain? Is the product upgraded regularly? Place…
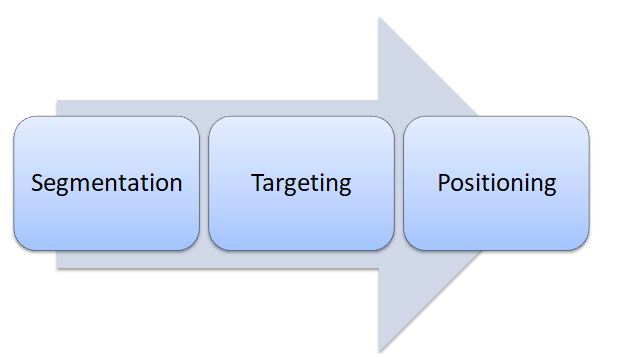
Segmentation, targeting and positioning (STP) is a marketing model that assists classifying population segments according to their needs and common characteristics, selecting specific segments and developing products and services for this particular segment. The basic premise behind STP is that you cannot sell everything to everyone. Therefore, you need to limit your product and service offerings and target limited population segment that have higher chance to purchase them. Today, Amazon is trying to be everything for everyone, but even Amazon started only as an online bookseller to gradually increase its offering to increasing numbers of customer segments. STP is effective because it allows personalisation of products and services to the needs and wants of selected consumers. STP approach shifts the focus from product to consumers and helps in satisfying customer needs and wants profitably. Application of Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning Segmentation targeting and positioning initiatives include the following stages: 1. Segmenting the market. Segmentation is dividing population on the basis of their common traits and characteristics. Segmentation helps identifying niches with specific previously untapped needs. There are many types and bases of segmentation. The table below the most popular types of segmentation. Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Example Geographic Region North America, Asia, Europe Density Urban/rural Climate Hot, cold, wet, dry Demographic Age Teenagers, middle aged, elderly. Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labour force Solitary Survivor II retired Occupation Students, employees, professionals, senior manager, executives Behavioral Degree of loyalty…
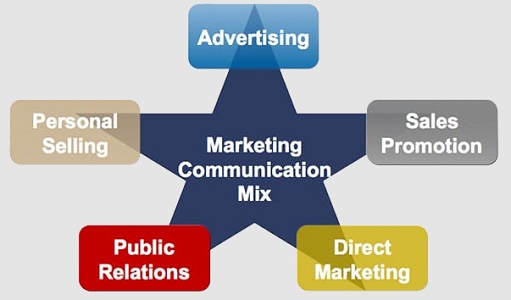
Defined as a “dialogue between business unit and its present and potential customers that takes place during pre-selling, selling and post-selling stages”[1], marketing communication mix, or promotion mix is considered to be a fundamental aspect of business marketing initiatives. Kotler and Keller (2009)[2] divided marketing communication mix into the following six categories: advertising, sales promotion, events and experiences, public relations and publicity, direct selling and personal selling. 1. Advertising is “a paid non-personal communication about an organisation and its products transmitted to a target audience”[3]. The following are important platforms of print and media advertising: TV Radio Magazines Newspapers Billboards & posters Viral marketing Celebrity endorsement Product placement 2. Sales Promotions is a marketing strategy which involves using temporary campaign or offer to increase interest and demand on products and services. The following are popular sales promotion techniques: Seasonal sales promotions. Businesses may reduce the prices of certain items during holidays and festive seasons such as Christmas holidays. Money off coupons. Customers receive coupons by mail, in store or they cut coupons our of magazines or product packaging to purchase the product next time for lower price. Purchase of a product allows the customer to participate in a game to win a price. Discount vouchers. A voucher that can be used to purchase a product at a reduced price. Free gifts. Customers get an item for free if they purchase a product. Point of sale materials. Use of posters, display stands and other promotional tools to present the product to customers within the shop. Loyalty cards. Possibility for customers to earn points for buying specific products or buying from specific sellers. Accumulated points can be exchanged for goods or other offers. For example, Tesco Clubcard, Sainsbury’s Nectar etc. 3. Events and experiences, as a marketing mix component relate to a…
