Posts Tagged ‘Globalisation’

This essay critically analyses the level of destructive impact of colonialism on China’s growth output between the 1840s and the 1940s. The essay contains the contrast of opposite arguments regarding the topic and supports the argument confirming destructive impact of colonialism on China’s growth output between the 1840s and the 1940s by providing relevant and valid justifications. A study of economic history can provide valuable knowledge to economic theorists and practitioners in terms of dealing with economic challenges of present and the future. An in-depth analysis of factors causing the level of economic growth to slow down in particular is necessary so that these factors can be dealt with to fuel economic prosperity in any given region. Colonialism can be defined as “the control or governing influence of a nation over a dependent country, territory, or people” (Colonialism, online, 2016). While forming new colonies may prove to be a profitable strategy for powerful countries in many levels, economies that become victim to colonialism experience a set of substantial economic and social setbacks such as loss of sovereignty in terms of using economic resources, and negative impact upon cultural identity. The essay starts with assessing the level of China’s economic growth between the 1840s and the 1940s providing evidences why it was slow for this specific period. This is followed by discussions of colonialism and its negative impacts on the level of China’s economic growth between the 1840s and the 1940s. In order to adhere to the specified word limit for this essay political implications of colonialism are not addressed in this essay, and the main focus have been made on effects of colonialism on national economics using the case study of China. Moreover, an alterative viewpoint on the issue is also explored in this essay by assessing the impact of…
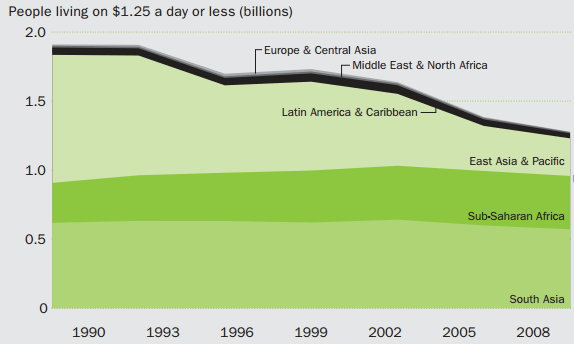
Rapid technological development during the last several decades coupled with a series of breakthroughs in information technology has immensely contributed to the development of national economies for a wide range of countries with positive implications on standards of life of people. At the same time, global poverty still remains one the most pressing issues with almost half of the world – more than 3 billion people living on less than $2.50 a day (Shah, 2016, online). The issue of global poverty is periodically addressed by a set of organisations such as World Bank, One International, WHO, CARE and others, as well as, within the framework of The Group of Twenty (G20) forum. This article represents a critical assessment of the role of World Bank in particular in dealing with global poverty. The article starts with the general discussions about the World Bank and its current contribution in eliminating global poverty. This is followed by analysis of criticism of World Bank performance in dealing with global poverty. Moreover, this article identifies potentials for World Bank to deal with global poverty more effectively. The World Bank Group is an international financial institution that pursues its mission of ‘Help Reduce Poverty’ with the participation of 188 countries. The World Bank Group consists of five organisations that are The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), The International Development Association (IDA), The International Finance Corporation (IFC), The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA), and The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). Each of these organisations contributes to World Bank mission in a unique way. It is important to clarify that generally the term ‘World Bank’ refers to only IBRD and IDA, and these two organisations along with IFC, MIGA, and ICSID are incorporated within the World Bank Group. Within the scope of this…

Introduction Described as the greatest geopolitical catastrophe of the 20th century by the current president of Russia Vladimir Putin (BBC, 2005, online), the collapse of the Soviet Union has caused profound changes in global political and economic affairs, impacting the lives of hundreds of millions of people. Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) has been formed in 1922 and it has enjoyed the culmination of its influence in the global scale following its victory in World War Two within the period from mid 1960s to mid 1980s being able to send the first man to the outer space in 1961 and achieving relative stability in the standard of life of member state citizens. Initially, Soviet Union comprised only six member states in 1922 – Russian, Ukrainian, Byelorussian, Azerbaijan, Georgian and Armenian Soviet Socialist Republics; however its size has been gradually increased during the following two decades until 1941 to reach the numbers of member states to 15 through expanding into Central Asia and Balkan states. Nevertheless, due to the range of reasons discussed below the existence of USSR came to its end officially in 1991. Although more than two decades have passed since the collapse of the USSR this topic is regularly explored in academic levels due to its importance and impact to the formation of present geo-political situation. This essay attempts to analyse the major reasons and implications of the collapse of the Soviet Union. Economic, cultural, social and political factors contributing to the collapse of the Soviet Union are discussed in this essay and implications of this event on regional level for former USSR blog countries, as well as, on the global landscape are assessed. Economic factors contributing to the collapse of the Soviet Union Assessment of economic factors that led to the collapse of the Soviet Union…

1. Introduction Elecdyne is a Tokyo-based manufacturer of consumer electronics products that has been operating in local market in Japan for over three decades. Currently employing 100 members of workforce, Elecdyne strategic level management is keen to explore the potentials of revenue maximisation through internationalisation. This article represents a critical analysis of Elecdyne international market expansion opportunities. The article starts with a brief analysis of Elecdyne current situation and an overview of business environment for the company with the application of STEEP framework. This is followed by analysis of country profiles of UK, Russia and Turkey as a potential new market for Elecdyne using a weighted scaling system. The article is completed by specifying strategic direction for Elecdyne and providing rationale for the choice of direction being offered. 2. Current/Future Business Environment It has been noted that “an organisation does not exist in isolation but is part of a broader business environment, making it an open system” (Amos et al., 2008, p.3). Accordingly, Elecdyne is faced with a set of challenges caused by external factors that need to be addressed in timely and effective ways. Challenges imposed to Elecdyne by external environment can be effectively illustrated through STEEP table where the abbreviation stands for social, technological, economic, ecological and political factors affecting the business. Social Ø Intensifying level of cultural globalisation Ø Ageing of population in developed countries (Blakemore and Warwick-Booth, 2013) Ø Changing patterns of families (single parents, same sex parents etc.) Technological Ø Declining duration of life cycle for consumer electronics products Ø Increasing frequency of technological innovations Ø Technological breakthroughs in the area of electronics products recycling Economic Ø Declining profit margins for consumer electronics products due to intensifying competition Ø Likelihood of economic crises such as global recession of 2007 – 2009 Ø Rising costs of operations…

Introduction Increasing forces of globalisation have altered the terms and nature of conducting business considerably and irreversibly. As a result of globalisation businesses have been presented with a range of opportunities to contribute to the level of their revenues and these opportunities primarily include outsourcing various business processes abroad and exporting products to other countries. General Electric Company (GE) is a globally diversified technology and financial services company and its products and services include aircraft engines, power generation, water processing, and household appliances to medical imaging, business and consumer financing and industrial products (General Electric Co, Bloomberg, 2013). GE has achieved an international growth of 18% during 2011 which has contributed to company consolidated revenues of $147 billions during the same period of time. Moreover, 13,000 jobs were created by GE in US during 2011, and international sales of American-made products by GE had amounted to $18 billion during that year (GE Annual Report, 2011). This report evaluates the impact that globalisation has had on the policies of GE and specifies changes needed to be implemented taking into account the recent economic crisis in the USA and the global financial recession. The report addresses GE policy changes impacted by globalisation in an individual manner by referring to other relevant publications, and changes proposed for GE in the report have been justified in a detailed manner. Impact of Globalisation on GE Policies GE has attempted to take full advantage of possibilities provided by globalisation by formulating relevant policies mainly during the last decade under the leadership of its CEO Jeff Immelt. Financial Time’s Crooks (2012) recites the following words from Immelt: “When I became CEO [in 2001] we were 70 per cent inside the US industrially. Now we are 60 per cent outside the US”. The specific impacts of globalisation…
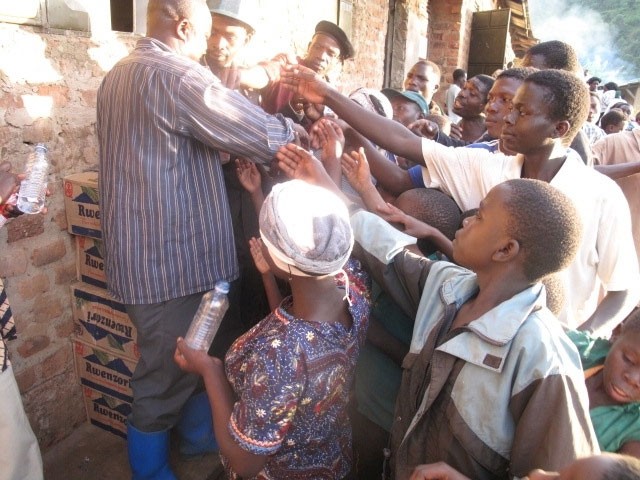
Introduction Foreign aid can be defined as “any action by a government or citizen of one country, which helps to promote economic development in another country” (Kazimbazi and Alexander, 2011, p.28). Many countries situated in Africa do receive substantial amount of foreign aids from other countries, international organisations and private philanthropists. Foreign aid is mainly provided in the forms of financial aid, technical support and food aid. According to Wall Street Journal (2009), over the past 60 years the amount of foreign aid provided to Africa has exceeded USD 1 trillion and foreign aid has been provided to deal with a wide range of serious problems such as extreme poverty, fighting with HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases, internal conflicts and abuse of human rights, child labour and human trafficking etc. This essay critically analyses the topic of foreign aid and growth in Africa in general and in Uganda in particular. The essay starts with discussions of means and methods of delivery of foreign aid to Uganda. This is followed by analysing the benefits of foreign aids and level of dependency of Uganda on foreign aid. быстрые микрозаймы онлайн Moreover, the opposite viewpoint addressing the disadvantages of foreign aid to Uganda and an overview of popular arguments of sceptics of foreign aid have been included in this essay. The essay is concluded by discussing a range of alternatives to foreign aid in order to achieve economic development in Uganda. Republic of Uganda has more than 34,5 million population with the life expectancy of 54 years for men and 55 years for women (BBC Uganda Profile, 2013). Comprising 241,038 square kilometres, Uganda is bordered with Kenya in the east, Tanzania and Rwanda in the south, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the west (Barlas and Yong, 2010). Today Uganda is faced…
1. Introduction Mergers, acquisitions and formation of alliances are commonplace in global airline industry and they are fuelled by the search of competitive advantages in order to achieve long-term growth. However, the implementation of mergers, acquisitions and formation of strategic alliances in practice can be associated with a set of complex challenges that might include differences in organisational culture, clash of personalities within top level management, lack or absence of strategic fit between the two companies and others. Lufthansa Group is a global airline company that employs more than 120,000 workforces that have contributed to generate 713 million EURO through serving 100.6 million passengers during the year of 2011 alone (Annual Report, 2011). Germanwings is a budget airline company that employs 1355 members of staff and served 7.52 million customers in 2011 offering flights to more than 90 destinations with 33 Airbus A 319 airplanes (Facts and Figures, 2013, online). Germanwings is wholly owned by Lufthansa since 2009. This report investigates a range of business issues related to the acquisition of Germanwings by Lufthansa German Airlines in 2009. The report starts with analysis of motives for choosing acquisition method among other alternatives by Lufthansa. This is followed by discussions of strategic and organisational fit between Lufthansa and Germanwings. Moreover, this report addresses potential gains and risks faced by Lufthansa due to the acquisition of Germanwings. The report is concluded with assessing outcomes relative to expectations in relation to this specific airline acquisition. 2. The Motives for Choosing Acquisition Method by Lufthansa Top level management of Lufthansa have selected the method of acquisition among other alternatives such as initiating a merger or forming a strategic alliance in relation to Germanwings due to the set of reasons that include less time required to complete the acquisition, increasing the market share, overcoming entry…
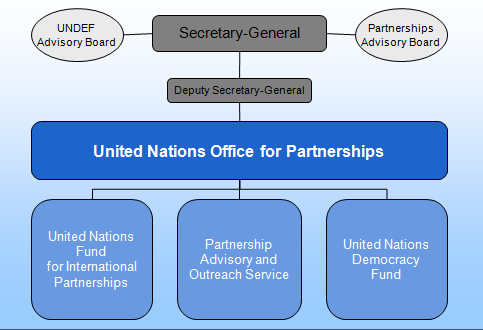
1. Introduction This article attempts to answer the question What is the United Nations? Moreover, the article represents a detailed analysis of the level of effectives of the UN in global governance. The article starts with discussing the role of functions of the UN, explaining the roles and functions of each UN’s six organs in an individual manner. This has been followed by identification of gaps in global governance and discussions about the role of the UN in terms of the extent of filling each gap. Furthermore, the article critically analyses the overall level of effectiveness of the UN in global governance and discusses the potentials for increasing the level of effectiveness in the UN in global governance by proposing a set of recommendations. Increasing level of integration and cooperation between counties in various levels creates a need for reputable international bodies that could assist in facilitating international relations, and more importantly, deal with disagreements and conflicts that may occur in international relations. The reality of the present nature of global governance is the outcome of conflict between the need to introduce global rules and regulations, and the willingness of retaining control over national boundaries. The is a set of reputable international organisations currently operating in the global scale such as The United Nations, The World Trade Organisation, The World Bank, North Atlantic Treaty Organisation and others, and each of these organisations engages in global governance with varying levels of effectiveness depending on their aims and objective, resources, sources of funds and other factors. The United Nations (UN) is an international organisation “committed to maintaining international piece and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights” (UN at a Glance, 2016, online). Founded on October 24, 1945, the UN comprises 193 member…

Introduction There always have been disparities between countries in terms of the levels of economic developments and this tendency is most likely to continue in the future. However, there have been attempts by highly developed countries to assist the level of economic development of developing countries through various programs involving financial aids and recommendations. A set of policy recommendations proposed by the US to developing countries has been known as Washington Consensus, and there are mixed opinions about the implementation and outcome of these recommendations (Bandelj and Sowers, 2010). This article critically analyses the ideology of Washington Consensus. The article starts with discussions about factors and circumstances that have caused the emergence of Washington Consensus. This is followed by discussing positive implications of Washington Consensus for certain countries by referring to relevant facts. Moreover, the article highlights major points of criticism of Washington Consensus and the attempts to assess the level of their validity of these points and discusses reasons and circumstances for introduction of Post-Washington Consensus also known as Washington Consensus II. The article is completed by attempting to the future of Washington Consensus prescriptions in modern dynamic global geo-political environment. Emergence of Washington Consensus The term of Washington Consensus has been coined by in 1989 by John Williamson to label “list of ten policies that more or less everyone in Washington would agree were needed more or less everywhere in Latin America” (Williamson, 2008, p.14). Williamson had specified these ten reforms proposed to Latin American countries as a greater level of fiscal discipline, re-ordering of public expenditure priorities, taxation reforms, liberalisations of interest rates, increasing the levels of competitiveness of interest rates, liberalisation of trade, liberalisation of inward foreign direct investment, privatisation, deregulation, and property rights. Latin American countries were facing severe economic challenges throughout the 1980s, and this…

This article contains application of Vernon’s Product Life Cycle on the case study of Shanghai Vision Technology Co., Ltd, a medium sized manufacturer of 3D printers and other innovative products based in Shanghai, China. Products of Shanghai Vision Technology to be sold in new markets follow a specific life cycle pattern. This pattern can be effectively explained using Vernon’s product life cycle which comprises four stages: introduction, growth, maturity and decline. Introduction stage for Shanghai Vision Technology 3D printers and other products commences when the product is offered in new market for the first time. During this stage Shanghai Vision Technology products are purchased mainly by ‘innovator’ and ‘early adopter’ consumer categories and the role of effective integrated marketing strategy is paramount. Growth stage for Shanghai Vision Technology products is associated with rapid increase of the sales volume due to the impact of marketing initiatives and word-of mouth marketing. It is important for Shanghai Vision Technology to ensure the supply of its products in the market during this stage. Maturity stage is reached when the majority of Shanghai Vision Technology target customer segment already posses 3D printers and other products offered by the company and its competitors. Maturity stage is associated with market saturation. Decline stage is inevitable for Shanghai Vision Technology products, as well as for products of any other company regardless of the industry and size of the market. Determining the timeframe of this stage in an appropriate manner and introducing new products to the market during the later stages of decline plays an important role for Shanghai Vision Technology in terms of retaining its share in new markets. …
