Theory X and Theory Y
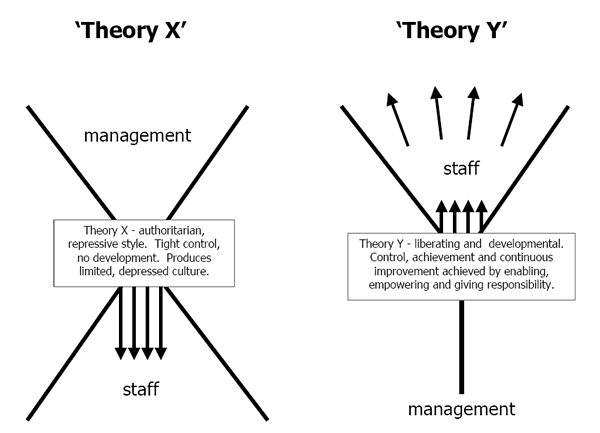
Theory X and Theory Y framework proposed by McGregor in his classic book The Human Side of Enterprise (1960) consists of two alternative set of assumptions. Theory X percieves employees to be lazy, irresponsible and untrustworthy, while according to theory Y employees are approached as one of the most valuable assets of the company.
According to Theory X assumptions employees do not like their work, they lack ambition and responsibility and employees prefer to be led rather than leading others.
Theory X assumes average human being to dislike the work and avoid it whenever possible. The following statements relate to Theory X assumptions:
- Most people must be controlled and threatened so that they can produce an adequate level of output
- Responsibility is avoided by an average human who desires security above all
- An average human being has a little ambition and has to be closely supervised at all times
Theory Y set of assumptions, on the other hand, is based upon the idea that employees are generally enthusiastic about their work, they are creative and self-directive, and also employees readily accept responsibility.
Theory Y is based on the following alternative assumptions:
- The expenditure of physical and mental effort in work is as natural as play or rest
- Methods of making people work are not limited to control and punishment, high level of commitment in organisational aims and objectives can result in self-direction
- Commitment to organisation can be achieved by designing satisfying jobs
- If proper conditions are created, an average human can not only learn how to take responsibility, but he can also learn to seek responsibility
In practical levels, McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y framework aims to demonstrate the potential of employees that organisations should recognise so that the level of organisational efficiency can be increased.
However, as Agnes (2010) informs, the numbers of companies concentrating on theory theory Y management perspective are increasing in the search of obtaining overall efficiency and competitive edge in the marketplace.
It has to be stressed that “an important aspect of McGregor’s ideas is his belief that managers who hold either set of assumptions can create self-fulfilling prophecies – that is, through their behaviour they create situations where others act in ways that conform the original expectations” (Schermerhorn, 2011, p.38). As Palmisano (2008) confirms, this specific theoretical framework mainly serves to communicate potential benefits of Theory Y practices to Theory X type of managers.
References
Agness, L, 2010, Change Your Business with NLP: Powerful Tools to Improve Your Organisation’s Performance and Get Results, Wiley Publications
McGregor, D, 2002, Theory X and Theory Y, Workforce, Vol.81, Issue 1
Palmisano, D.J. (2008) “On Leadership: Essential Principles for Success” Skyhorse Publishing
Schermerhorn, J.R., Osborn, R.N. & Hunt, J.G. (2011) “Organisational Behaviour” John Wiley & Sons