Uber Value Chain Analysis
Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis.
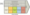
Uber Value Chain Analysis
Uber Primary Activities
Uber Inbound logistics
Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service.
Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services.
Uber Operations
Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide.
Business operations are divided into four reportable segments:
1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages:
a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and tap-request for their driver to arrive in minutes.
b) Ride. Customers are able to see contact information of their driver, as well as, vehicle details on the app. This ensures that customers get into the right car. There is an emergency button in the app that will share the trip information with emergency services, if pressed.
c) Pay and Go. When they reach their destination, customers simply hope out of the car and rate their driver. Customers don’t need to have cash or credit cards with them; Uber automatically charges credit card on file.
2. Delivery. This segment offers customers to search and find local restaurants, order meals and either pick-up from the restaurant or arrange the meal to be delivered to them. In some locations grocery and convenience store items can also be delivered through Uber.
3. Freight. This segment relies on Uber technology, brand awareness and experience to connect carriers with shippers on its platform. Specific advantages offered to users include upfront, transparent pricing and the ability to book a shipment in a matter of seconds.
4. Advanced Technologies Group (ATG). ATG segment was founded in 2015 to advance autonomous driving, which is widely perceived as the future of mobility. However, the segment was sold to Aurora Innovation, Inc. in January 2021 due to financial considerations.
Uber Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics in value chain analysis is associated with warehousing and distribution of products. Outbound logistics does not fully apply to service sector such as ride-hailing due to inseparability of delivery and consumption of services. As discussed above, Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide and internet-based nature of its business model is a major source of value for the global taxi technology company.
Uber Marketing and Sales
Uber sales and marketing costs amounted to USD 3,58 USD 4,63 and USD 3,15 billions in 2020, 2019 and 2018 respectively.[1] The ride-hailing giant mainly relies on social media marketing and word-of-mouth marketing to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment. Moreover, Uber uses print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences and public relations as part of its marketing strategy. Convenient payment method is a major source of value addition for the company. Uber automatically charges the credit card registered with the app. Therefore, customers don’t have to have cash or credit card when they reach destinations.
Uber Service
High level of customer service is one of the core competitive advantages for Uber. Good customer service is effectively integrated into Uber business model. Riders rate their drivers on the scale of 1 to 5 after each journey and accounts of drivers with average low riding scores are promptly deactivated. Drivers therefore have an incentive to maintain a clean car and provide good service.
Each ride receipt includes a map and a GPS track. Customers can complain if their driver took a longer route to reach the destination. Uber is assessed to be prompt in issuing refunds in such situations.
Uber Technologies Inc. Report contains a full version of Uber value chain analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Uber. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Uber leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Uber marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.

