Apple Value Chain Analysis
Apple value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Apple value chain analysis.
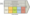
Figure 1 Apple Value Chain Analysis
Apple Primary Activities
Apple Inbound logistics
Inbound logistics primary activity refers to receiving and storing of raw materials for their consecutive use in manufacturing. Apple works with hundreds of suppliers around the globe and maintains a highly sophisticated supply-chain management as illustrated in Figure 2 below.

Figure 2 Apple operations roadmap[1]
Apple supply chain involves more than 3 million people working for thousands of businesses in 52 countries[2] The multinational technology company’s purchase commitments typically cover its requirements for periods up to 150 days[3]. Tim Cook is an experienced word-class supply chain professional. Steve Jobs had convinced him to join Apple as head of supply chain in 1998 when the tech giant was in trouble, risking the bankruptcy. As part of massive supply chain turnover Tim Cook cut the numbers of suppliers, reduced the number of warehouses by half and established relationships with contract manufacturers. Cook has been able to reduce Apple inventory turn over from 1 month to 2-5 days. Cook further reduced the numbers of suppliers after becoming CEO in 2011.
As a result of these and other initiatives, Apple supply chain practices have become a benchmark for efficiency for global businesses. The main sources of value in Apple inbound logistics relate to the economies of scale due to the massive scope and scale of business operations as discussed below and the development of strategic relationships with suppliers. Moreover, Apple Inc. exercises an immense bargaining power in dealing with its suppliers and as a result, the company is able to secure cost advantage in the purchase of resources.
Apple Operations
Apple does not own any manufacturing facilities and prefers to outsource manufacturing of its hardware to other companies in developing countries, notably China. While this strategy provides advantages such as focus on core competence of the business such as research and development and designing new products, it also has disadvantages. Specifically, outsourcing makes the company brand image vulnerable to labour issues at supplier facilities which has been the case with Apple a number of times.
The world’s largest IT company by revenue tries to keep operations lean, but it does not apply six sigma principles like its competitor, Samsung.
Apple operations are divided into the following reportable operating segments:
1. Americas segment includes North and South America. This is the largest segment for the tech giant in terms of sales. In 2022, the sales in Americas segment increased by 11% compared to previous year to exceed USD 169,65
2. Europe segment comprises European countries, India, Middle East and Africa. In 2019 sales in Europe segment had declined by 3% compared to previous year. However, the situation has improved the following year and in 2020 sales reached USD 68, 64 billion, an impressive increase of 14%. In 2020 the company generated total revenues of USD 95,12 billion from this segment.
3. Greater China segment consists of China, Hong Kong and Taiwan. Sales in Greater China segment has been declining for the past few years mainly due to intensifying local competition. Specifically, sales have declined by 8% in 2020 and 16% in 2019 compared to respective previous years. The management was able to turnaround the business in this segment generating revenues of USD 74,2 billion in 2022, an increase of 9% compared to 2021.
4. Japan Sales in Japan segment did not change in 2020 compared to the previous year. However, in 2022 reported revenues declined by 9% compared to the previous year due to the weakness of the locally currency yen relative to the U.S. dollar.
5. Rest of Asian Pacific Sales in this segment have increased by 10% and 2% in 2020 and 2019 respectively. In 2022 revenues reached USD 29,38 billion, an increase of 11% compared to the previous year.[4]
Apple operations are conducted by 164,000 full-time equivalent employees worldwide.[5] Outsourcing of manufacturing to locations with lower costs of resources is the main source of value for Apple operations. Specifically, only some models of Mac computers are manufactured in USA and Ireland and the majority of Apple products are outsourced to manufacturing units based in Asia.
Apple Outbound Logistics
Apple outbound logistics involve warehousing and distribution of ready iPhones, iPads, Mac computers and other products produced by the company. For technology items such as smartphones, tablets and laptops inventory depreciation rates are very high due to short product life cycles. Apple management recognises this critically important aspect of the business. CEO Tim Cook once compared his business to diary business and accordingly, the company tries to keep minimum inventory in their warehouses.
The company ships finished products to Apple Stores that are typically located at high-traffic locations in quality shopping malls and urban shopping districts. Apple outbound logistics also facilitates deliveries to the warehouses of wholesalers and retailers.
E-commerce sales are rightly acknowledged by the company as a massive source of value in terms of inbound logistics, because e-commerce is more cost effective compared to sales via Apple Store. Due to the efforts of the company in this direction, Apple Inc. has become the third largest retailer in the US in terms of size of e-commerce business, only behind Amazon.com and Wal-Mart Stores Inc.
Moreover, a greater level of market penetration into Asia in general and China in particular can be specified as an additional source of value for Apple Inc. from outbound logistics point of view. This is because selling in this particular geographical market would not involve massive outbound logistics expenses and this cost advantage can be passed to customers to increase the overall appeal of offers.
Apple Marketing and Sales
Apple sells its products through the following seven sales channels:
- Apple retail stores
- Apple online store
- Direct sales force
- Third-party cellular network carriers
- Wholesalers
- Retailers
- Value-added resellers
The tech giant is consistently increasing the share of sales through direct sales channels, as opposed to indirect sales channels. In 2022, the Apple’s net sales through its direct and indirect distribution channels accounted for 38% and 62%, respectively, of total net sales..[6] Apple has been increasing its focus on enterprise sales during the past few years and CEO Tim Cook announced an extensive reliance on Channel Partners to further increase the volume of enterprise sales.
Apple Service
Apple is famous for exceptional quality of customer services during all three stages: pre-purchase, during the purchase and post-purchase. The company maintains Apple experience centres in major cities around the globe where anyone can use its products to become convinced about the quality. Apple sales assistants are usually trained and polite young males and females who are technically savvy and happy to demonstrate product features and capabilities.
Post-purchase customer service is also impressive with unique iPhone trade-in programs that allow iPhone users to upgrade their phone to newer models with additional payment. Customers can return to Apple only items that they purchased directly from Apple, either online or at an Apple Retail Store. Products can be returned within 14 calendar days after the purchase.
Apple Stores have emerged as hubs, where customers can go when they are not sure about something or when something goes wrong. There are cases where customers had their cracked iPhone screens repaired at an Apple Store for free.[7]
Apple Inc. Report contains a full version of Apple value chain analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Apple. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Apple leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Apple marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Figure taken from SupplyChainOpz (2015) Available at: http://www.supplychainopz.com/2013/01/is-apple-supply-chain-really-no-1-case.html
[2] ESG Report (2022) Apple Inc.
[3] Annual Report (2022) Apple Inc
[4] Annual Report (2022) Apple Inc
[5] Annual Report (2022) Apple Inc.
[6] Annual Report (2012) Apple Inc.
[7] Villas-Boas, A. (2019) “I don’t want to switch from Android to iPhone because Apple’s ecosystem is too good” Business Insider, Available at: https://www.businessinsider.com/apple-iphone-macbook-ecosystem-so-good-i-dont-want-iphone-2019-12

