Posts by Raj Krishnamurthy
The evolution of online research methods has transformed multiple industries, including the dating scene. With digital tools and data-driven approaches becoming increasingly sophisticated, people now have access to precise, targeted ways of finding potential partners. For those interested in dating mature women, understanding how to effectively research and meet local milfs can make all the difference in navigating today’s online dating landscape. The Role of Research Methodology in Modern Online Dating Research methodologies play a crucial role in digital dating, helping users refine their approach and increase their chances of successful connections. The methods used in online dating closely mirror those found in academic and business research, including: Qualitative Research: Understanding the behavioral patterns of potential partners by analyzing their profiles, posts, and interactions. Quantitative Research: Using statistical data from dating sites and social media to determine the most active times, preferred interests, and compatibility scores. Content Analysis: Reviewing dating platform algorithms, user testimonials, and expert insights to refine dating strategies. Applying these research methodologies can help daters approach online interactions with a structured, informed perspective, ultimately improving their success rates. Data-Driven Strategies to Meet Local MILFs Finding and connecting with local MILFs is not just about swiping right—it requires a well-researched approach to increase your chances of meaningful interactions. Below are research-backed methods to optimize your online dating experience: 1. Identifying the Best Platforms Different dating platforms cater to different demographics, and choosing the right one is crucial. Research studies show that niche dating sites often yield higher success rates for specific preferences. For those interested in meeting local MILFs, selecting platforms that cater to mature dating or casual encounters can significantly improve results. 2. Optimizing Profile for Engagement Research indicates that profiles with detailed descriptions, high-quality images, and clear intent statements tend to perform better. Structuring your profile…
By Raj Krishnamurthy
Category: Luxury

The literature review has established viewpoints of other authors about unique characteristics of tourism industry. Literature review has revealed the following unique characteristics of tourism industry as summarised by TSA project in 2008: Firstly, the tourism is not an industry. The rationale behind this viewpoint relates to the idea that tourism comprises a wide range of individual businesses in a wide range of areas such as catering, transportation, entertainment, manufacturing and others. However, this viewpoint is not shared by all authors and many prominent authors in the area of tourism such as Webb (2009), Solomon and Rabolt (2009) and Rajagopal (2010) still refer to tourism as an industry. Secondly, in tourism consumers come to products. It is not possible to import tourism products and services or to provide them to customers through other channels and this point can be specified as an important distinctive feature of tourism industry from other industries. Thirdly, in tourism location is a part of the product. In tourism industry it is difficult to make a clear distinction between the value of a tourism destination and a wide range of products and services offered in this destination. In other words, tourism interconnects many separate businesses into a single entity (Schiffman et. al., 2012). Moreover, according to literature review findings there are range of systems that can be applied in order to characterise tourism destinations. For example, a system proposed by Pearce (2005) identifies six different labels in tourism industry and explains characteristics of each label. Label Emphasis Characteristics and examples of the system Activities Physical Listings, profiles, GIS approach Settings Physical Public management agencies use of zones using a biophysical basis Facilities Physical Micro-environments and service escapes: the immediate physical features of the tourist space Service Social Personnel: the characteristics of personnel in the service…
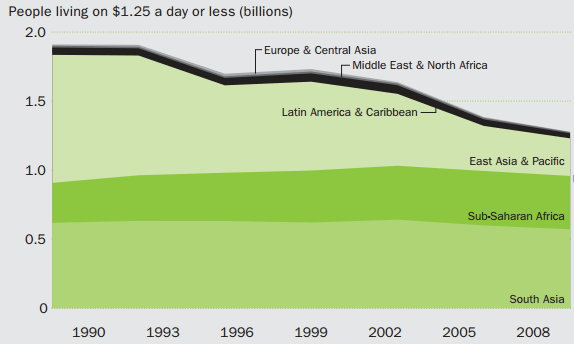
Rapid technological development during the last several decades coupled with a series of breakthroughs in information technology has immensely contributed to the development of national economies for a wide range of countries with positive implications on standards of life of people. At the same time, global poverty still remains one the most pressing issues with almost half of the world – more than 3 billion people living on less than $2.50 a day (Shah, 2016, online). The issue of global poverty is periodically addressed by a set of organisations such as World Bank, One International, WHO, CARE and others, as well as, within the framework of The Group of Twenty (G20) forum. This article represents a critical assessment of the role of World Bank in particular in dealing with global poverty. The article starts with the general discussions about the World Bank and its current contribution in eliminating global poverty. This is followed by analysis of criticism of World Bank performance in dealing with global poverty. Moreover, this article identifies potentials for World Bank to deal with global poverty more effectively. The World Bank Group is an international financial institution that pursues its mission of ‘Help Reduce Poverty’ with the participation of 188 countries. The World Bank Group consists of five organisations that are The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), The International Development Association (IDA), The International Finance Corporation (IFC), The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA), and The International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). Each of these organisations contributes to World Bank mission in a unique way. It is important to clarify that generally the term ‘World Bank’ refers to only IBRD and IDA, and these two organisations along with IFC, MIGA, and ICSID are incorporated within the World Bank Group. Within the scope of this…

Introduction Modern businesses are granted with vast opportunities in terms of revenue maximisation through entering new markets. Implementation of international market expansion strategy involves strategic-level decision making in relation to global branding strategies, the choice of market entry strategies such as wholly-owned subsidiaries, exporting, licensing, or forming joint-ventures, as well as, deciding on the level of standardisation or adaptation of products and service in new markets. Market entry strategies, branding strategies and the levels of standardisation or adaptation of each single element of marketing mix can be rightly specified as critical success factors directly impacting the success of business in the new market. This essay represents a critical analysis of standardisation vs. adaptation in international marketing in the twenty first century. The essay starts with discussing advantages and disadvantages of standardisation. This is followed by critical analysis of adaptation strategy as an effective customer-orientation strategy by referring to relevant real-life business case studies. The essay is completed by drawing conclusions on standardisation vs. adaptation debate and its relevance to the modern marketplace. Standardisation as a cost saving strategy Standardisation involves using “the same range of products, the same pricing, promotional and location strategies” (Gupta and Randhawa, 2008, p.77). Rationale behind standardisation practices relate to homogenisation of consumer wants and needs due to intensifying forces of globalisation (Winer, 2009). Standardisation can focus on core competitive advantage of the brand and it “allows for a consistent and strong brand to be developed across all markets” (Donelly, 2009, p.150). A Conceptual Model of International Marketing Strategy in relation to standardisation vs. adaptation has been introduced by Theodosiou and Leonidou (2003). According to the model, the degree of standardisation or adaptation is impacted by antecedent factors which have external and internal characteristics. External characteristics of antecedent factors consist of environmental factors, market characteristics, customer issues,…
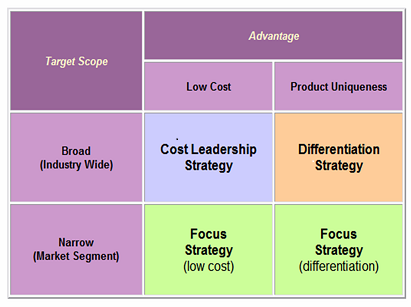
Executive Summary This article represents a business plan sample for Product Placement Opportunities®, a marketing services company that provides a platform for medium sized businesses to engage in product placement in a cost-effective manner through its website www.pp-opportunities.com. The business plan sample is built upon the gap in the in the marketing services industry that relates to allowing media, special event and computer games businesses to utilise their product placement opportunities in a direct manner, without using the services of marketing agencies. The comprehensiveness of the business plan sample is ensured by explaining mission statement, business strategy and objectives in a detailed manner. The main source of revenue for Product Placement Opportunities® relates to charging media, special event and computer games and other businesses for adverting their product placement opportunities on www.pp-opportunities.com. Price skimming pricing strategy has been chosen as the most suitable for the business. Analysis of principal personnel qualifications and experience contained within the plan highlights the ways in which competitive advantages are going to be derived. Moreover, cash flow forecast, profit and loss accounts forecast and balance sheet associated with the business plan have been developed on the basis of situational analysis and analysing market size for Product Placement Opportunities® services. The business plan sample also contains discussion related to relevant legal requirements, such as the company’s legal structure, commercial dealings, insurance and others. Glossary of Terms Business plan – “a document that sets out the basic idea underlying a business and related startup considerations” (Longenecker et al, 2005, p.117) Product placement – “an advertising technique used by companies to subtly promote their products through a non-traditional advertising technique, usually through appearances in film, television, or other media” (Business Dictionary, 2016, online) Organisational mission – “organisation’s fundamental purpose for existing, defining who the organisation is, its values, and the…
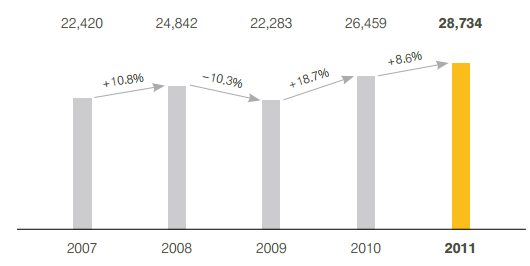
1. Introduction Mergers, acquisitions and formation of alliances are commonplace in global airline industry and they are fuelled by the search of competitive advantages in order to achieve long-term growth. However, the implementation of mergers, acquisitions and formation of strategic alliances in practice can be associated with a set of complex challenges that might include differences in organisational culture, clash of personalities within top level management, lack or absence of strategic fit between the two companies and others. Lufthansa Group is a global airline company that employs more than 120,000 workforces that have contributed to generate 713 million EURO through serving 100.6 million passengers during the year of 2011 alone (Annual Report, 2011). Germanwings is a budget airline company that employs 1355 members of staff and served 7.52 million customers in 2011 offering flights to more than 90 destinations with 33 Airbus A 319 airplanes (Facts and Figures, 2013, online). Germanwings is wholly owned by Lufthansa since 2009. This report investigates a range of business issues related to the acquisition of Germanwings by Lufthansa German Airlines in 2009. The report starts with analysis of motives for choosing acquisition method among other alternatives by Lufthansa. This is followed by discussions of strategic and organisational fit between Lufthansa and Germanwings. Moreover, this report addresses potential gains and risks faced by Lufthansa due to the acquisition of Germanwings. The report is concluded with assessing outcomes relative to expectations in relation to this specific airline acquisition. 2. The Motives for Choosing Acquisition Method by Lufthansa Top level management of Lufthansa have selected the method of acquisition among other alternatives such as initiating a merger or forming a strategic alliance in relation to Germanwings due to the set of reasons that include less time required to complete the acquisition, increasing the market share, overcoming entry…
