
The twenty first century has been accepted as a century of information with the amount of information increasing with a geometrical progression, however this tendency is associated with a set of challenges that include protection of intellectual property which can be defined as any patterns of original creation that can be purchased or sold. Main forms of intellectual property protection are patenting, trademarks, trade secrets and copyright. Patenting is a popular way of protecting intellectual property, and patents are obtained for inventions that have potentials to generate revenues for inventor. Patents allow the patent holder to market the invention and patenting rights to the third party or license the invention when retaining intellectual property rights. Patents are considered to be intangible assets and many global businesses possess considerable amount of such type of asset. For example, gross carrying amount of patents of Ford Motor Company has exceeded USD 27 million by 2012 with the net carrying amount of USD 7 millions (Annual Report, 2012). Due to increasing numbers of innovations, and willingness of businesses to take advantage of these innovations there are many patent infringement lawsuits amongst many multinational corporations at any given time. For example, one of the most recent and noteworthy patent infringement disputes is the one between Finland-based global communications corporations – Nokia and HTC its Taiwan-based direct competitor. Patent infringement dispute initiated by Nokia for the use of Broadcom and Qualcom chip for HTC One model has attracted extensive media coverage due to its scale and significance and Nokia has emerged as a victor in the dispute with detrimental impacts on HTC in terms of damage to the brand image and future profits (Arthur, 2013). Moreover, there are instances where businesses decide to end their patent infringement disputes due to cost considerations of lawsuits, damage to…

It has been stated that Total Quality Management (TQM) “is difficult to define precisely because it is a philosophy of total organisational involvement in improving all aspects of quality” (Allen, 2004, p.68), nevertheless, in a broad manner TQM can be defined as a quality improvement philosophy that adopts a holistic approach and requires active participation of all employees. Initially developed by Edward Deming in 1940s, TQM became a buzzword in the US several decades later due to its implementation by a range of large companies such as Ford Motor Company, Motorola, and Xerox. University and colleges, as well as, many other organisations in all industries can apply TQM elements in practice in order to increase the level of customer satisfactions significantly. TQM elements include understanding customer needs, doing things right the first time, continuous improvement, regular assessments of quality related costs, developing effective systems and procedures etc. ‘Getting things right the first time’ is one of the fundamental TQM elements. This approach substitutes quality inspection practices with constant search and utilisation the potentials for quality improvement. The approach of ‘getting things right the first time’ can benefit the college in terms of avoiding waste of resources, and saving substantial amounts of time and money. TQM principle of continuous improvement is associated with Kaizen philosophy and its applicability is extended beyond organisational environment to cover personal life, relationships, social life etc. Main advantages of Kaizen principles for the college The value of continuous improvement or Kaizen for the college is even grater taking into account the fact that implementation of this principle does not require vast financial investments on behalf of the college and improvements can be introduced in a gradual manner. Another vital TQM element can be identified as understanding customer needs in the first place so that relevant products…
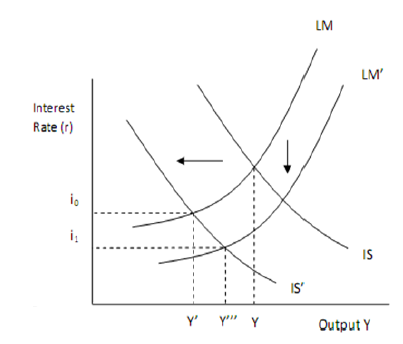
Great Depression is rightly perceived as the main stimulating factor behind the emergence of Keynesian framework and ISLM model and the model proved effective to deal with the crisis to a certain extent. However, a set of significant shortcomings associated with ISLM model such as neglecting expectations, static nature of the model, unrealistic closed-economy assumption, assuming prices to remain fixed etc. have led to the evolution of alternative models. Proposed by Robert Mundell and Marcus Fleming, the Mundell-Fleming model represents an economic model that explains the nature of relationship between the nominal exchange rate and the output of the economy in the short run. Traditionally, this model has been used to justify the argument that maintenance of fixed exchange rate, movement of free capital and independent monetary policy in a simultaneous manner is impossible to achieve. The main difference between Mundell-Fleming model and ISLM model relates to the fact that while ISLM model is effective under a closed-economy, Mundell-Fleming model attempts to analyse an open-economic system. In other words, unlike ISLM, impacts of international finance and international trade are acknowledged in Mundell-Fleming model. Different countries respondent the global economic crisis of 2007 – 2009 differently taking into account unique set of internal and external factors, however, macroeconomic responses to the crisis by many developed counties can be effectively explained with the use of ISLM model. Dramatic decline in the level of consumer spending which also caused the decline of consumer confidence in markets has facilitated the shift of IS curve in ISLM model to the left. Range of responses by governments to this event included reducing the level of interest rates significantly. For example, interest rates were reduced in US, UK and Japan to 0.25 per cent, 0.5 per cent and 0.1 per cent respectively. Reduction of the level of…

Marketing research can be specified as the main tool to impact consumer behaviour in order to increase the levels of consumer loyalty and achieve long-term growth of the businesses. Marketing research can be divided into the following stages: The first stage is associated with problem definition. Range of marketing research problems related to consumer behaviour may include but not limited to assessment of impacts of prices changes or re-branding initiatives on consumer attitudes, establishing the levels of brand value amongst target customer segment etc. The second stage relates to secondary data collection and analysis. Relevant data available in government publications, statistical information, as well as, findings of previously published marketing research papers can be utilised in an extensive manner during this stage. The third stage in marketing research process refers to collection of primary data. The majority of marketing researches are facilitated through primary data collection and analysis. The most popular methods of primary data collection for marketing research include surveys, focus groups, interviews, storytelling, experiments and observations. Moreover, marketing research can also be conducted with application of conjoint analysis, purchase panels, database marketing and netnography. The fourth stage involves primary data analysis. Data analysis can be qualitative, quantitative or integrated according to the nature of problems being researched. Adoption and maintenance of an objective approach plays important role at this particular stage of marketing research process. The fifth stage is devoted to formulation of recommendations. Specifically, alternative set of recommendations or inter-related recommendations can be offered to senior level management on the basis of primary data analysis. The sixth stage in marketing research process involves selection and implementation of a strategy. In most cases internal or external members of team responsible for conducting marketing research do not engage in implementation of recommendations in practical levels. Therefore, it is important…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Consumer Behaviour

The topic of consumer behaviour is one of the massively studied topics by the researchers and marketers in the past and still being studied. Researchers show different reasons as to why consumer behaviour has been the topic of many academics and researchers. One of the common views is that understanding consumer behaviour has become a factor that has a direct impact on the overall performance of the businesses (Kotler and Keller, 2012). Another view suggests that understanding consumer behaviour has become crucial especially due to fierce competition in retail industry in the UK and worldwide (Lancaster et al, 2002). This chapter will introduce some other areas of research background of consumer behaviour addressing the works of researchers and marketers. Moreover, consumer decision making process, in particular, five stages of consumer decision making process will be discussed in detail. Introduction It is worth noting that consumer buying behaviour is studied as a part of the marketing and its main objective it to learn the way how the individuals, groups or organizations choose, buy use and dispose the goods and the factors such as their previous experience, taste, price and branding on which the consumers base their purchasing decisions (Kotler and Keller, 2012). One of such studies of consumer buying behaviour has been conducted by Acebron et al (2000). The aim of the study was to analyze the impact of previous experience on buying behaviour of fresh foods, particularly mussels. In their studies the authors used structural equation model in order to identify the relationship between the habits and previous experience on the consumer buying decision. Their findings show that personal habits and previous experience on of the consumers have a direct impact on the consumers’ purchase decision in the example of purchasing fresh mussels. They also found that the image of the…

Motivation, personality and perception belong to the list of central themes in the area of consumer behaviour. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (1943) is one of the most significant theoretical frameworks in the area of human motivation and this theory relates to the study of consumer behaviour in a direct way. Maslow (1943) divides human needs into five layers arranged in a hierarchical manner: psychological, safety, social, and esteem needs. In simple terms, the core idea behind Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (1943) can be explained in a way that businesses need to appeal to the most immediate and urgent needs of customers in order to generate sales. For example, an individual who is yet to satisfy his or her safety needs is not motivated to purchase products and services associated with high social status, thus individuals belonging to this category should not be targeted for premium range of products and services. From this perspective, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (1943) is related to segmentation, targeting and positioning practices to a certain extent. Personality represents another important physiological variable with certain implications on consumer behaviour and personality elements or traits include self-confidence, sociability, adaptability, deference etc. In-depth knowledge about important aspects of personalities of target customer segment allows businesses to manipulate with elements of marketing mix in general and promotion element in particular in terms of making an effective appeal. For example, marketing research findings of a premium brand watch manufacturing company may indicate that the majority of representatives of target customer segment are highly ambitious individuals aspiring to top management positions in multinational corporations. This information can be used to impact consumer behaviour by engaging in product placement marketing strategy via displaying the use of the premium watch by highly successful senior managers in various media productions. High levels of subjectivity of…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Consumer Behaviour

The most popular approaches to consumer behaviour can be divided into cognitive, behaviourist and psychodynamic categories. Cognitive approach to consumer behaviour focuses on information processing capabilities of consumers (Schmitt, 2003). Specifically, according to cognitive approach environment and social experiences provide individuals with abundant information to be processed, and the outcome of information processing results in individuals behaving in certain ways as consumers. For example, individuals may receive information about forecasted economic downturn in a national level and this information can serve as a stimulus to behave in certain manners. Specifically, according to cognitive approach although the forecasted economic downturn has not happened yet, nevertheless consumers may reduce levels of their spending budgets as a response to the stimulus. Behaviourist approach to consumer behaviour, on the other hand, is associated with the impact of external events. Lantos (2010) link this approach to infamous experiments of Russian scientist Ivan Pavlov and these experiments involved developing certain behavioural patterns via external factors. Practical implementation of this approach in the field of marketing can be observed in relation to Nescafe products. Specifically, integrated marketing strategy of Nescafe attempts to foster a specific pattern of behaviour amongst target customer segment whereby consumption of a cup of Nescafe coffee has to be the first thing to do in the morning. Importantly, Loudon et al. (2010) make a clear distinction between cognitive and behaviourist approaches to consumer behaviour in a way that in cognitive approach information from external sources are processed by consumers in apparent manners, whereas in behaviourist approach consumers may not be fully aware of the impact of external environment. Accordingly, Loudon et al. (2010) consider behaviourist approach to be superior compared to cognitive approach in terms of motivating perspective consumers to commit to the purchase. Lastly, psychodynamic approach “includes all theories in psychology that…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Consumer Behaviour

Competition is becoming intensive for virtually all types of products and services and due to this tendency responsibilities of marketing department of companies have increased. Marketing mix can be specified as an effective framework that can be used to increase the overall value of products and services to customers. This article contains analysis of each element of marketing mix by using a variety of secondary data sources. The notion of marketing mix refers to a balance of marketing methods needed to sell products and services. Marketing mix consists of four core elements – product, price, place and promotion that are jointly known as ‘four Ps’. Extended marketing mix contains additional ‘three Ps’ consisting of people, process and physical evidence. Product element of marketing mix Anything that has a potential to satisfy specific customer needs can be specified as product. In modern marketplace learning about customer needs and wants through marketing research precedes development of products and services. Product variables include but not limited to its design, durability, technical features and capabilities, ease of maintenance and others. Businesses use branding in order to differentiate their products and services from other products and services offered in the market. For example, while there is a wide range of soft drinks offered in the market, Coca-Cola drink in particular has a large market share, partially due to successful branding strategy of the company. Importantly, benefits of successful branding go beyond any particular single product to assist the sales of other products offered by the company as well. Positive image of Apple brand assists sales of MacBook desktop computers, as well as, other products offered by the company such as IPhone and IPad. Benefits of products and services have tremendous on the levels of revenues and these benefits can be divided into three categories:…

This article represents a critical analysis of marketing communications materials used by Coca-Cola Company, a global beverage manufacturer and retailer based in Georgia, United States. The Coca Cola Company is a global manufacturer, marketers and seller of non-alcoholic beverages and syrups based in Atlanta, US. Range of brands owned by the company includes Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Coca Cola Zero, Sprite, Fanta, Powerade, Minute Maid, Aquarius, Dasani, Schweppers and others. This article focuses on marketing communication materials associated with one of its core products, the Coca-Cola drink. Established in 1886, the company currently sells in more than 200 countries and beverage trademarks owned and licensed by the company account for 1.9 billion of approximately 57 billion beverage servings around the globe on a daily basis (Annual Report, 2013). The article starts with description and analysis of various types of media employed in order to promote the Coca-Cola, followed by the identification of objectives of Coca-Cola campaign. Then, extensive analysis of images and words used in Coca-Cola campaign is undertaking in order to ensure a greater scope for the current research. Moreover, attempts are made to analyse the appeal of Coca-Cola marketing messages, as well as, assessments are provided at what extent Coca-Cola marketing campaigns were achieving their objectives. Types of Media used to Promote Coca-Cola Media can be defined as a “facilitating institution who suggest appropriate message within the operative constraints of space” (Tyagi and Kumar, 2004, p.341) and is considered to be one of the most effective advertisement methods among marketing practitioners. Spurgeon (2008) divides media into two categories: published media and visual/aural media. Published media includes newspapers, magazines, trade and professional press, as well as internet. Visual and aural media, on the other hand, include television, radio, cinema, posters, billboards, and direct mailing. Various types of media are used…

The 21st century has been dubbed as an information age (Bell and Blanchfower, 2011) and internet in general, and social media in particular are playing an instrumental role in facilitating the spread of information throughout the globe at a rapid speed. Moreover, increasing levels of interactivity of social media platforms is further contributing to the level of their popularity, and nowadays social media has been effectively adopted by many businesses along a wide range of industries as a highly effective marketing and communication platform. At the same time, the level of use of social media varies between various industries, as well as, individual organisations within a particular industry, and while some organisations are beginning to realise substantial opportunities offered by social media, others are already utilising these opportunities to a full extent. This essay contains a critical evaluation of the role of social media on the popularity of a tourism destination. The essay starts with discussions about increasing influence of social media on consumer behaviour. This is followed by critical analyses of potential benefits of social media to hospitality organisations. Moreover, issues related to negative impacts of social media on the performance of hospitality organisations are also addressed in this essay. Essay is concluded by providing a set of recommendations to strategic and marketing managers of hospitality organisations in terms of benefiting from opportunities offered by social media to a maximum extent. Introduction 1 Increasing influence of social media on consumer behaviour in service sector 2 Potential benefits of social media to hospitality organisations 5 Negative impacts of social media on the performance of hospitality organisations 8 Recommendations for managers of hospitality organisations in relation to social media 10 Conclusions 14 References 16 Cathay Pacific DoubleTree Club Hotel Facebook Hampton Hotels Twitter How do I receive the report? Once payment…
