Posts Tagged ‘catering’

Marriott Supporting Local Communities In 2022 alone, employees contributed over 1.6 million volunteer hours across the globe, focusing on environmental and social issues to positively impact their communities. The company aims to locally source 50% of produce by year-end 2025 Marriott Educating and Empowering Workers In 2022, 78% of all associates* completed career- or skillsrelated training. The largest hotel chain in the world has been listed as Fortune 100 Best Companies to Work For® Great Place to Work® in 2022 Marriott and Gender Equality and Minorities A majority of Marriott’s Board are minorities or women Listed as one of 50 Best Companies for Latinas to Work for in the U.S., LATINA Style 2022 The company aims to increase representation of people of colour in U.S. executive positions to 25% by year-end 2025. 47% of Marriott’s global executives (vice president level and above) are women 22% of Marriott’s U.S. executives (vice president level and above) are people of colour Energy Consumption by Marriott In 2022, numerous Marriott-managed hotels across the globe implemented energy efficiency projects, saving approximately 45,000 MWhs of energy. 9% Global Reduction in Energy Consumption per Square Meter of Conditioned Space from 2016 Baseline 1% of electricity consumption sourced from renewable energy in 2022 Water Consumption by Marriott The company aims to reduce water consumption per occupied room by 15% from a 2016 baseline by year-end 2025 3% Global Reduction in Water Consumption per Occupied Room from 2016 Baseline Waste Reduction and Recycling by Marriott The hotel chain aims to reduce waste-to-landfill by 45% and food waste by 50% from a 2016 baseline by year-end 2025 In Thailand, 27 Marriott hotels donated over 33,000 kg (72,000 lbs.) of food and surplus food to Scholars of Sustenance (SOS) throughout 2022. Carbon Emissions by…

Key Components of Marriott ecosystem include the following: – Properties. Marriott has a portfolio of over 8,000 hotels in 138 countries and territories. This includes a variety of brands, from luxury to budget-friendly, to meet the needs of all types of travellers. – Loyalty programs. The hotel chain has three loyalty programs – Marriott Bonvoy, Ritz-Carlton Rewards, and Starwood Preferred Guest. These programs offer members exclusive benefits, such as free nights, room upgrades, and early check-in and check-out. – Technology platform. The largest hotel chain in the world has a robust technology platform that powers its website, mobile app, and loyalty programs. The company also uses technology to improve the guest experience, such as with contactless check-in and mobile keys. – Partners. The company has a wide range of partners, including airlines, car rental companies, and credit card companies. These partnerships allow Marriott to offer its guests a one-stop shop for their travel needs. Marriott’s ecosystem is designed to provide guests with a seamless and personalized experience. For example, when a guest books a hotel room on the Marriott website, they can also book a flight and a rental car. They can also use their Marriott Bonvoy points to pay for their hotel stay, flights, and car rental. Marriott’s loyalty programs also play an important role in its ecosystem. By rewarding guests for their loyalty, Marriott encourages them to stay at Marriott hotels and use Marriott partners. This helps Marriott to build long-term relationships with its guests. The Marriott International ecosystem benefits both Marriott and its guests. For Marriott, the ecosystem helps to increase revenue and improve customer loyalty. The hotel chain is able to generate additional revenue from its partners, such as airlines and car rental companies. The company is also able to improve customer loyalty by providing guests with a seamless and personalized experience. For guests, the ecosystem provides a number of benefits such as convenience, savings…
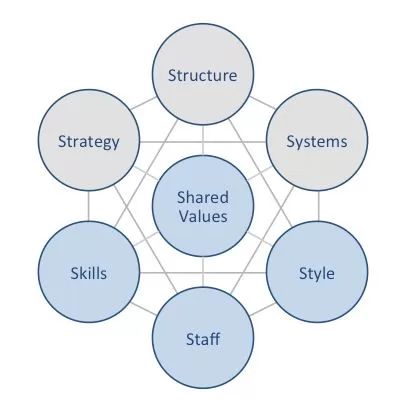
Marriott McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness for the largest hotel chain in the world. According to this framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Marriott McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Marriott McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Marriott International’s business strategy is focused on providing high-quality hospitality services to a wide range of customers. The company has a portfolio of over 30 brands, ranging from budget-friendly to luxury, to appeal to different needs and budgets.[1] The hotel chain pursues asset-light business model and growth through acquisitions business strategy. Moreover, Marriott has been focusing on bleisure travellers as part of its business strategy. Structure Marriott International has a decentralized organizational structure, with each brand operating as its own business unit. This allows the company to tailor its offerings and services to the specific needs of each market. Marriott also has a strong focus on operational excellence, with a number of systems and processes in place to ensure that its hotels are run efficiently and effectively. Systems Marriott International has a number of systems in place to support its business operations, including a reservation system, a loyalty program, and a property management system. The company is also investing heavily in new technologies, such as mobile check-in and self-service kiosks. Marriott International Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Marriott McKinsey 7S Model.…
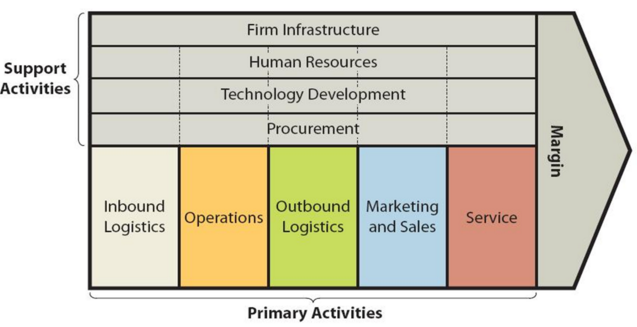
Value chain analysis is an analytical tool that helps to find business activities that can create the most value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of Marriott value chain analysis. Marriott Value Chain Analysis Marriott Primary Activities Marriott Inbound logistics The inbound logistics activities for Marriott International involve the procurement, transportation, and storage of the goods and services that the company needs to operate its hotels and resorts. These activities are essential to the company’s ability to provide its guests with a high-quality experience. Marriott International procures a wide range of goods and services from suppliers such as food and beverage, linen, furniture, toiletries and other supplies. The largest hotel chain in the world has a strong supplier network and is able to negotiate competitive prices. The company also has a team of experienced procurement professionals who are responsible for managing the inbound logistics process. Marriott Operations Marriott’s operations can be divided into four key areas: 1. Hotels. Marriott operates and franchises hotels under its various brands. It also manages hotels on behalf of other owners. 2. Vacation ownership. Marriott operates a vacation ownership program called Marriott Vacation Club International. This program allows members to purchase vacation points that can be used to stay at Marriott-affiliated vacation resorts. 3. Timeshare exchange. Marriott operates Interval International, a timeshare exchange program that allows members to swap their timeshare weeks for stays at other resorts. 4. Food and beverage. Marriott operates restaurants and bars in many of its hotels. It also provides catering services. Marriott Outbound Logistics Generally, outbound logistics within value chain analysis refer to all the activities involved in delivering the finished product or service to the customer. This includes warehousing, order fulfilment, transportation, and delivery. For Marriott International outbound logistics activities include the following:…
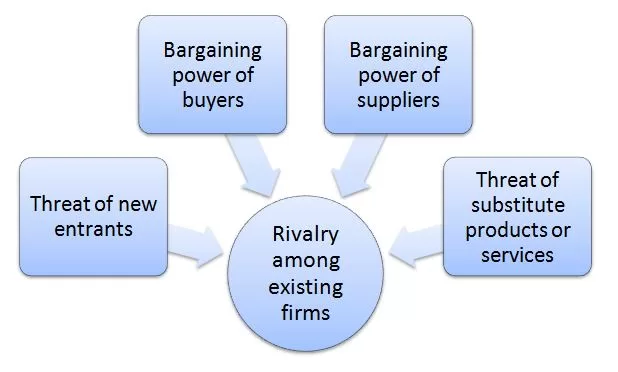
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Marriott Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The threat of new entrants into the global hotel industry is moderate. There are a number of factors that make it difficult for new entrants to enter the hotel industry. These include high capital requirements, the importance of brand recognition, lack of access to distribution channels and the importance of economies of scale. Capital requirements The hotel industry is highly capital-intensive. New entrants need to have a significant amount of capital to invest in building or acquiring hotels. According to data from hospitality consulting firm HVS, ground up construction of a full-service hotel typically costs USD 323,500 per room in the US.[2] The similar pattern is echoed in many other markets as well. Accordingly, capital requirements are a significant entry barrier for new players into the hotel industry. Brand recognition Established hotel brands such as Marriott, Hilton, IHG Hotels & Resorts, Hyatt and Wyndham Hotels & Resorts have a significant advantage over new entrants. These companies have been developing and promoting their brands for decades and accordingly, have a strong reputation and customer loyalty. Moreover, effective branding enables established market players to command premium prices, further solidifying their position. New entrants, on the other hand, will have no visible brand, making it difficult for them to successes in the market. Distribution channels Distribution channels for hotels include direct channels, such as their own websites and reservation call centres, and indirect channels, such as online travel agencies (OTAs), global distribution systems (GDSs), and tour operators. Established hotel brands such as Marriott have well-established distribution channels.…

Marriott marketing communication mix consists of communication channels to communicate the marketing message to the target customer segment. These channels are print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing. Marriott Print and Media Advertising Print advertising Marriott International’s print advertising campaigns typically appear in high-end magazines and newspapers, such as Condé Nast Traveler, Travel + Leisure, The New York Times, and The Wall Street Journal. These ads often feature stunning photography of hotels and resorts from Marriott portfolio brands, as well as aspirational messages about the travel experience. For example, a recent Marriott print ad for the St. Regis Bora Bora Resort featured a photo of a couple swimming in a crystal-clear lagoon, with the headline “Where dreams come true.” The ad also highlighted the resort’s luxurious accommodations, world-class dining, and exclusive amenities. Media advertising Marriott International also invests in media advertising, such as television and radio commercials. These ads are typically more general in nature than print ads, and they focus on Marriott’s core brand values, such as comfort, convenience, and quality. For example, a recent Marriott television commercial featured a group of friends travelling to different cities around the world. The ad showed the friends staying at different Marriott hotels, and it emphasized the fact that Marriott offers a variety of accommodations to suit every budget and travel style. Omnichannel approach Marriott International takes an omnichannel approach to its print and media advertising. Specifically, the company uses a variety of different channels to reach its target audience, and it integrates its advertising campaigns across all channels. For example, a Marriott print ad might include a QR code that allows consumers to learn more about the hotel or resort featured in the ad. The QR code might also allow…

Marriott segmentation, targeting and positioning involves a series of marketing decision making for the largest hotel chain in the world. Segmentation involves dividing a market into smaller groups of customers with similar needs, wants, and behaviours. Generally, companies can engage in segmentation using a wide range of variables, such as demography, geography, psychographics, and behaviour. Marriott International uses the following segmentation bases: Segmentation Variable Description Demographics Age, income, education level, occupation, family size, and household income. Geography Region, country, city, and type of location (e.g., urban, suburban, rural). Psychographics Interests, values, lifestyle, and travel habits. Behavior Travel frequency, type of accommodations booked, and loyalty program membership. Segmentation bases for Marriott International Targeting is the process of selecting one or more of the identified segments to focus marketing efforts on. Businesses generally target segments that are most likely to be interested in their products or services, and that are most profitable to serve. Marriott targets business, leisure and luxury customer segments. Positioning is associated with creating a unique identity for a product or service in the minds of target customers. Effective positioning involves defining the product or service’s key features and benefits, and communicating them to customers in a way that differentiates the product or service from competitors. Customer Segment Marriott Amenities and Services Economy travellers Basic amenities and services Business travellers High-speed internet, business centres, meeting rooms, concierge services, executive lounges, complimentary breakfast Leisure travellers Swimming pools, kids’ clubs, family-friendly activities, restaurants, bars, fitness centers, spas Luxury travellers High-end accommodations, personalized service, gourmet dining, luxury amenities, exclusive experiences Customer segments and Positioning of Marriott Amenities and Services Marriott International Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Marriott segmentation, targeting and positioning and Marriott marketing strategy in general. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic…

Marriott marketing mix (Marriott 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in Marriott Marketing Mix (Marriott 7Ps of Marketing) Marriott offers a wide range of services to its guests. These include, but not limited to accommodation, meetings and events, food and beverage, as well as, fitness and recreation. The level of services varies according to the brand tier. The table below illustrates Marriott brand tiers and respective brands. Brand Tier Brand Names Classic Luxury The Ritz-Carlton, St. Regis, JW Marriott, Ritz-Carlton Reserve, The Luxury Collection, W Hotels, EDITION, Marriott Hotels Premium Sheraton, Delta Hotels, Le Méridien, Westin, Renaissance Hotels, Gaylord Hotels Select Courtyard Hotels, Four Points, Spring Hill Suites, Protea Hotels, Fairfield Inn & Suites, City Express, AC Hotels, Aloft Hotels, Moxy Hotels Long Stays Marriott Executive Apartments, Residence Inn by Marriott, TownePlace Suites by Marriott, element by Westin, Homes & Villas by Marriott International Distinctive Autograph Collection Hotels, Design Hotels, Tribute Portfolio Marriott International brands Place Element in Marriott Marketing Mix (Marriott 7Ps of Marketing) At the end of 2022, Marriott International had nearly 8,300 properties and approximately 1.5 million rooms in 138 countries and territories. [1] The largest hotel chain in the world directly operates 2,053 properties with 576,243 rooms and the remaining properties are franchised. The company has a strong presence in major cities, tourist destinations, and business districts. Marriott also has a growing presence in emerging markets. Price Element in Marriott Marketing Mix (Marriott 7Ps of Marketing) Marriott International uses the following pricing strategies: Dynamic pricing strategy. Marriott International uses dynamic pricing to adjust the prices of its hotel rooms based on demand. According to this strategy the price of a room can vary depending on…

Marriott marketing strategy is designed to reach its target audience of travellers and to encourage them to book a stay at a hotel or resort belonging to it portfolio. Marketing costs for the largest hotel chain in the world amounted to USD 635 million in 2022, USD 470 million in 2021, and USD 276 million in 2020[1]. Marriott marketing strategy focuses on the following key elements: – Brand differentiation. Marriott International differentiates its brand from other hotel companies by emphasizing its commitment to quality, service, and innovation. The company also offers a wide range of hotel brands to suit the needs of different travellers, from budget-minded travellers to luxury travellers. – Unique selling proposition. Along with its world-class amenities, commitment to customer services is unique selling proposition for Marriott hotels. Employees are trained to go the extra mile to make guests feel welcome and valued. – Customer segmentation. Marriott International segments its customers into different groups based on their travel needs and preferences. This allows the company to develop targeted marketing campaigns that are relevant to each segment. – Omni-channel marketing. Marriott International uses a variety of marketing channels to reach its target audience, including online, offline, and social media. The company also integrates its marketing campaigns across all channels to provide a seamless customer experience. – Product placement strategy. Product placement is one of the key elements of Marriott marketing strategy. One of Marriott’s most famous product placement deals was with the popular TV show “The Real Housewives of Beverly Hills.” The show featured the cast staying at the Ritz-Carlton, Los Angeles on several occasions. This exposure helped to position the Ritz-Carlton as a luxury hotel brand that was popular with celebrities and other high-profile individuals. Marriott has also placed its hotels in a number of successful movies, including “The Devil Wears…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Marriott PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects of the international hotel chain. Political Factors in Marriott PESTEL Analysis There are some political factors that may affect Marriott International. Such factors include political stability, security and the risk of terrorism in a given territory, US-China trade wars, the rise of nationalism and terrorism and others. Moreover, the level of bureaucracy and corruption, freedom of press and trade union activities are also political factors with the potential impact on Marriott and other international hotel chains. Political stability Political stability is essential for international hotel business. It allows hotel chains to operate in a predictable and safe environment, which is necessary for investment and growth. When there is political instability, it can lead to a number of negative consequences. For example, political instability can deter tourists from visiting a country, which can lead to a decline in demand. It can also increase the costs of operations, such as the cost of security measures and insurance premiums. In some cases, political instability can even lead to Marriott having to close its hotels in a country. For example, in 2022, Marriott was forced to close some of its hotels in Ukraine following the Russian invasion. Trade union activities Trade union activities can have a significant impact on hotel business, both positive and negative. Trade unions can help to improve the working conditions for employees. They can negotiate for higher wages, better benefits, and safer working conditions. This can lead to a more motivated and productive workforce, which can benefit Marriott’s bottom line. Trade unions can also help to improve the…
