Porter’s Five Forces
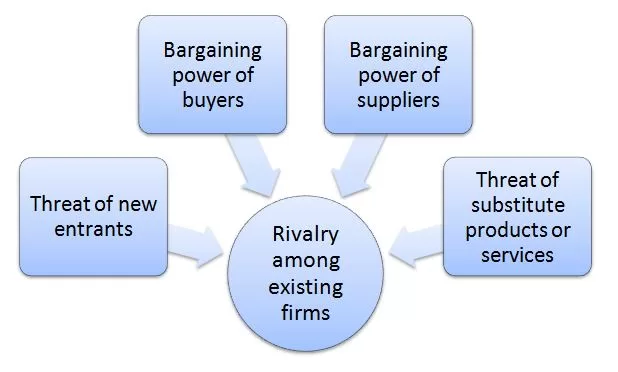
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. BYD Porter’s Five Forces are illustrated in figure below. Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in BYD Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into EV sector is low to moderate. The following are the main factors that determine the intensity of this threat. Massive capital investments Requirement for huge capital investments is a significant entry barrier for potential entrants into the EV market. In order to succeed new players would have to introduce improvements in battery range and life, charging speeds, efficiency or vehicle performance. Any of these achievements would necessitate investments in research and development and it would be hard for new market players to compete with deep-pocketed existing market players in this front. For example, Volkswagen plans to invest €35 billion in EV R&D by 2025[2], while Ford has allocated USD50 billion by 2026 for the same purposes[3]. Possible retaliation from current market players New entrants in the EV EV market can expect varying degrees of retaliation from existing businesses, depending on several factors. For example, established automakers such as Tesla and BYD can reduce prices on their own EVs to undercut new players, increase marketing and advertising efforts to maintain brand awareness or lobby against government policies favouring new entrants. Moreover, oil and gas companies feeling threatened by the shift away from fossil fuel may spread misinformation about the environmental benefits of EVs or pressure lawmakers to delay or limit EV incentives Customer switching costs These are the expenses, efforts, and time involved for customers to switch from their current EV brand to a new one. They can be tangible (financial) or intangible (psychological and time-related). For tangible expenses,…
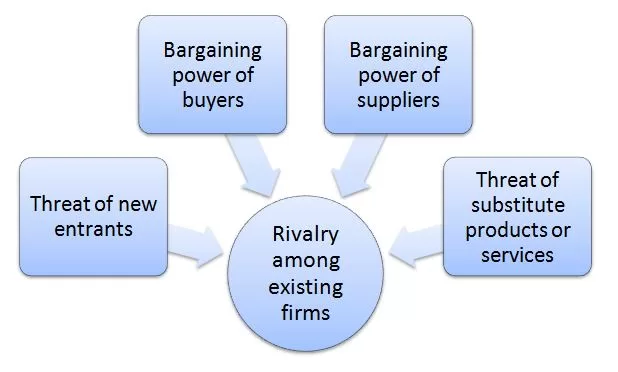
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Marriott Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The threat of new entrants into the global hotel industry is moderate. There are a number of factors that make it difficult for new entrants to enter the hotel industry. These include high capital requirements, the importance of brand recognition, lack of access to distribution channels and the importance of economies of scale. Capital requirements The hotel industry is highly capital-intensive. New entrants need to have a significant amount of capital to invest in building or acquiring hotels. According to data from hospitality consulting firm HVS, ground up construction of a full-service hotel typically costs USD 323,500 per room in the US.[2] The similar pattern is echoed in many other markets as well. Accordingly, capital requirements are a significant entry barrier for new players into the hotel industry. Brand recognition Established hotel brands such as Marriott, Hilton, IHG Hotels & Resorts, Hyatt and Wyndham Hotels & Resorts have a significant advantage over new entrants. These companies have been developing and promoting their brands for decades and accordingly, have a strong reputation and customer loyalty. Moreover, effective branding enables established market players to command premium prices, further solidifying their position. New entrants, on the other hand, will have no visible brand, making it difficult for them to successes in the market. Distribution channels Distribution channels for hotels include direct channels, such as their own websites and reservation call centres, and indirect channels, such as online travel agencies (OTAs), global distribution systems (GDSs), and tour operators. Established hotel brands such as Marriott have well-established distribution channels.…
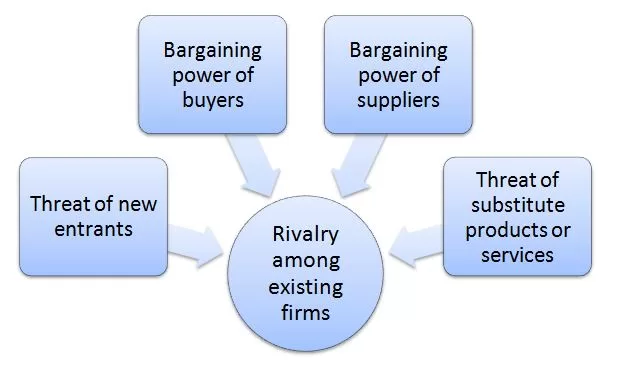
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1. Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Netflix Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants into the on-demand media streaming is low. Setting up a video steaming website is not difficult from a technical point of view. However, adding an adequate amount of content with the permission of copyright holders and gaining market share is highly difficult. The following are the most noteworthy challenges for new market entrants. Market saturation The market of on-demand media streaming is highly saturated with the streaming giants such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, Hulu, Apple TV+, HBO Max and others dominating the global market. The majority of representatives of the target customer segment i.e. people with phones, tablets or TVs with internet connection are already subscribed to one or more of the leading streaming services mentioned above. It will be challenging for new market entrants to attract enough subscribers to make a break-even in this sector High entry costs Major market players such as Netflix focus on original content in general and its quality in particular to differentiate themselves in the market. As illustrated in Figure 4 below, the titles of original content produced by the largest streaming service in the world, as well as the hours watched by its customers have been consistently increasing for the past 10 years with the exception of a decline in 2021. Figure 2 Netflix original content by years of transmission[2] Netflix original content spending exceeded USD 5,8 billion in 2022[3] and its main competitors also spend billions of dollars annually for creating new films and programs. Accordingly, the…
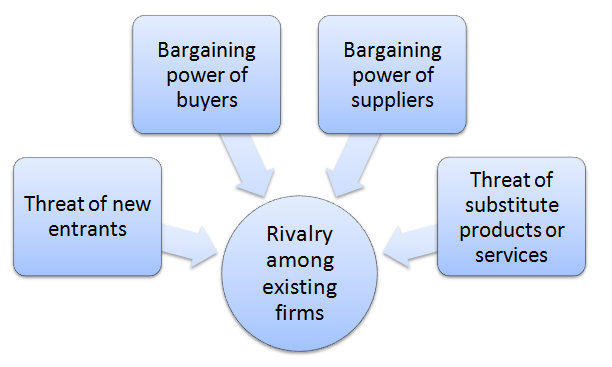
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Apple Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Apple Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into consumer electronics industry is not substantial. The following factors, among others, determine the threat of new entrants into the industry to compete with Apple: 1. Massive capital requirements. Manufacturing technological devices and producing operating systems require massive capital investments. As illustrated in Table 1 below, the top players in the market invest billions of dollars in R&D in order to keep the pipeline of new products and services active. New market entrants will have to produce new products and services that will have to compete with products and services of top players that invest billions of dollars every year in R&D. Rank Company R&D spending (USD) 1 Amazon 70.3 billion 2 Alphabet 38.1 billion 3 Meta Platforms 34.0 billion 4 Apple 25.3 billion 5 Microsoft 23.0 billion 6 Samsung Electronics 18.2 billion 7 Intel 17.5 billion 8 Roche 16.0 billion 9 Volkswagen 14.0 billion 10 Johnson & Johnson 14.0 billion Table 1 Top R&D spenders among technology companies in 2022 Moreover, capital is needed to obtain resources in general and to attract human resources and talented employees in particular. Accordingly, it is safe to argue that access to capital can prove to be a substantial entry barrier for new businesses. 2. Economies of scale. Economies of scale are substantial entry barrier into consumer electronics and tech industry. New players will find it difficult to compete with established global brands such as Apple, Samsung, Google and HTC that are able to gain cost advantage…
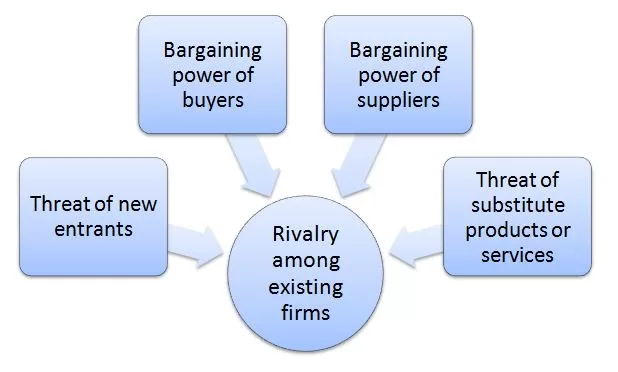
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Nvidia Porters Five Forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Nvidia Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into graphics processing unit (GPU) industry is low. The below are the main factors that determine the level of threat of new entrants: 1. Time of entry. GPUs are highly saturated market with dominant market players already in the business for decades. Moreover, customer loyalty towards dominant players such as Advanced Micro Devices (AMD, Intel Corporation, Qualcomm Inc., Broadcom Inc. and Arm Holdings (a subsidiary of Softbank Group) is high this fact crates entry barrier for potential market entrants. 2. Massive investments. GPU producing requires massive capital requirements of millions of dollars. It will be very challenging for potential market entrance to secure funding for producing GPUs unless they offer unique competitive advantages with the potential to disrupt the market. 3. Specialist knowledge. GPUs are highly advanced technological products. The production requires highly specialist knowledge and technological know-how. New market entrants will face substantial difficulties in terms of finding employees with specialist knowledge who will agree to join a new company in a highly saturated market. Bargaining power of buyers in Nvidia Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The bargaining power of buyers for Nvidia products is generally insubstantial. The following considerations need to be taken into account in this regard: 1. Switching costs. Nvidia’s products are often integrated into larger systems and it is often difficult to replace these products with similar products produced by competitors due to massive costs and expertise knowledge involved. Such a situation limits buyer bargaining power with positive implications for Nvidia. 2.…
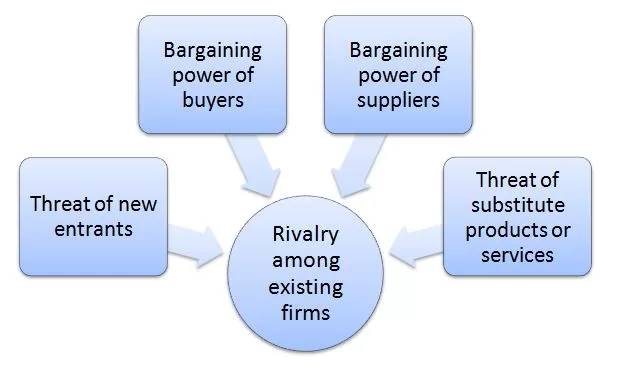
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. WeWork Porter’s Five Forces is illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in WeWork Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into the flexible workspace industry is significant. The following are the major factors that affect the threat of new entrants into the flexible workspace industry. 1. Time of entry. Increasing numbers of start-ups and solopreneurs are increasing demand for flexible workspace. Furthermore, COVID-19 pandemic has proved the inefficiency of committing to long-term traditional real estate lease agreements for many businesses. Instead, companies of all sizes increasingly prefer to flexible workspace to accommodate their changing needs for desks throughout the year. This tendency may motivate new players to enter the industry. 2. Massive capital requirements. Leasing real estate and furnishing them into creative open space is expensive. Investors may not be keen to finance such business proposals due to low profit margins and long payback periods of their investment. Massive capital requirement is a serious barrier for new entrants. WeWork’s co-founder and former CEO Adam Neumann was able to raise billions of dollars for the business by positioning the company as an internet technology company, rather than real estate company it is. 3. Lack of technological barrier. Unlike technological and manufacturing businesses there are no know-how barriers to enter the flexible workspace industry. There is no secret formula or advanced software a company needs to develop to enter the industry. Massive capital requirement is the only barrier and the absence of other barriers may attract new players into the industry. Bargaining power of buyers in WeWork Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The bargaining power of buyers in flexible workspace sector…

Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Starbucks Porter’s Five Forces are represented in figure below: Porters Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Starbucks Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants in international coffee chain industry is low. The following factors reduce the threat of new entrants for Starbuck’s industry within Porter’s Five Forces. 1. Market saturation. Coffee chain market is highly saturated and more so in developed countries. Market saturation implies an increase of a market share for a specific coffee house at the expense of a competitor. New entrants into the coffee house chain business find such a reality discouraging to enter the business and achieve long-term growth. 2. Access to distribution channels. New market entrants are going to face significant issues to access distribution channels because potentially attractive locations for coffee stores are already occupied by coffee chains, restaurants and retail outlets. It took Starbucks 36 years to reach its current status that comprises total more than 33800 company operated and licensed stores.[2] Similarly, other major players such as Costa, Caribou Coffee,McDonald’s, Dunkin Donuts, Pret-a-Manger have secured thousands of advantageous locations during the decades of operations. 3. Economies of scale. Establishing coffee house chains requires massive capital investments. It can prove to be highly challenging to secure investment to establish new business in this industry unless the business plan is based on previously untapped value proposition. Bargaining power of buyers in Starbucks Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of Starbucks buyers is significant. The following considerations need to be taken into account in this regard: 1. Abundance of choice. Customers can choose from a wide range of established coffee chains as well as local specialty coffee…
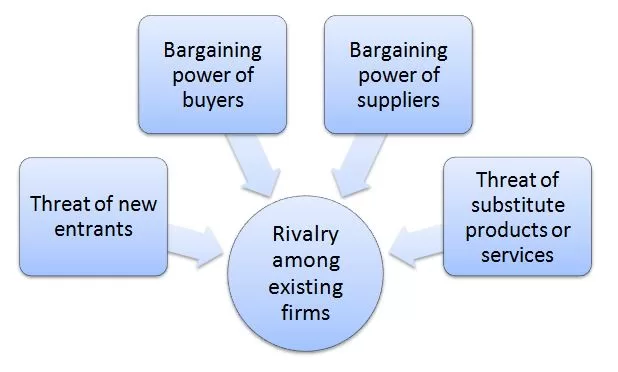
Porter’s Five Forces model is “a generic framework that deconstructs industry structure into five underlying competitive forces or variables”[1]. IKEA Porter’s Five Forces are represented in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants to furniture and home appliances manufacturing industry in general is significant. The following set of factors, among others affects the intensity of threat of new entrants into the industry. 1. Lack of regulatory or technological entry barriers. There are no legal or regulatory barriers to enter the furniture industry. Moreover, knowledge barriers are not substantial as well because furniture producing processes do not involve advanced know-how that is difficult to replicate. 2. Economies of scale. IKEA benefits from the economies of scale to a great extent internationally and this advantage allows the Swedish furniture chain to maintain highly competitive prices. No new market entrant would be able to utilize economies of scale to IKEA’s extent and thus, competing with IKEA on price level remains as a highly challenging, if not impossible task. Such a situation discourages potential new players to enter the industry. 3. Distribution channel barriers. Although there are no regulatory or technological entry barriers as discussed above, distribution channel entry barrier exists. It took more than seven decades for the Swedish furniture chain to establish its global distribution network that comprises more than 500 locations in 63 countries. Without such an extensive distribution network it will be hard for new market entrants to present any real threat for IKEA. Bargaining power of buyers in Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of buyers in furniture and home appliances manufacturing industry is huge. The following factors increase buyer bargaining power: 1. Absence of switching costs for customers. Currently IKEA lacks an ecosystem of products…
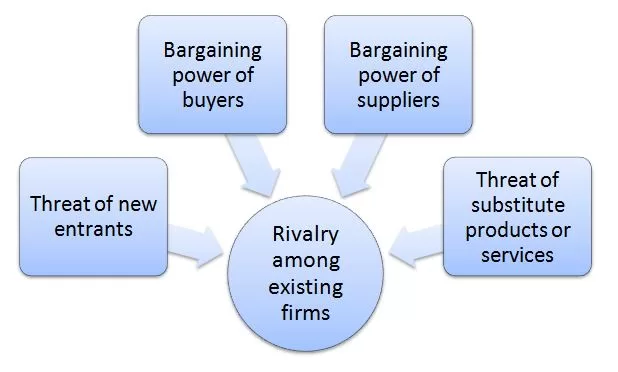
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. McDonald’s Porter’s Five Forces are represented in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in McDonald’s Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into fast food chain industry is moderate. Potential entrants into fast food chain industry have to deal with the following factors. 1. Massive capital investment requirements. Establishing a fast food chain requires huge financial investments to create an infrastructure, secure leases for locations, purchasing equipments and recruiting staff, among others. Securing funding for a new fast food venture can prove to be challenging taking into account high level of market saturation internationally. 2. Economies of scale. Major market players such as McDonald’s, Starbucks Coffee, Burger King, KFC and Subway substantially benefit from the economies of scale with positive implications on their cost structure. New market entrants, on the other hand, cannot benefit from the economies of scale to similar extend and this may prove to be a significant industry entry barrier. 3. Creativity and innovation. Despite fast food industry entry barriers such as huge capital requirements and economies of scale mentioned above, there is still a chance for new companies to successfully enter the industry. They can do so by innovating in terms of foods to offer, as well, as achieving greater technological integration into various business processes. Bargaining power of buyers in McDonald’s Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of McDonald’s buyers is immense. The following set of factors, among others determines customer bargaining power in fast food industry: 1. No switching costs to competition. Customers can switch from McDonald’s to any other fast food chain such as KFC, Pizza Hut, Starbucks and Burger King with no…
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. The essence of Amazon Porter’s Five Forces is represented in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Amazon Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into online retail business is significant. The following sets of factors determine the threat of new entrants for Amazon’s industry. 1. Economies of scale. Amazon is the largest internet retailer and internet company by revenue in the world. The e-commerce giant operates more than 175 fulfilment centres worldwide in more than 150 million square feet of space.[2] Although potential new market entrants can copy Amazon business model, they cannot benefit from the economies of scale at the same extent as Amazon. Therefore, economies of scale can be specified as substantial barrier for new entrants. 2. Time of entry. The global market size for online shopping nearly reached USD 4 billion in 2020.[3] It has been estimated that e-commerce sales will surpass USD 740 billion by 2023 in the US alone.[4] Such an increasing popularity of internet shopping naturally attracts new entrants that will attempt to find new niches and competitive advantages. In other words, time of entry is an important factor that increases the threat of new entrants in global e-commerce. 3. Product differentiation. Amazon was able to reach its current position partly because it found an opportunity in online sales in 1994, when other companies didn’t notice or utilise such an opportunities. Likewise, other companies can find new previously unnoticed opportunities in e-retail to threaten the position of established market players such as Amazon, eBay, Alibaba and others. In other words, global e-commerce can be disrupted by start-ups that may find new sustainable sources of competitive advantage.…
