Porter’s Five Forces
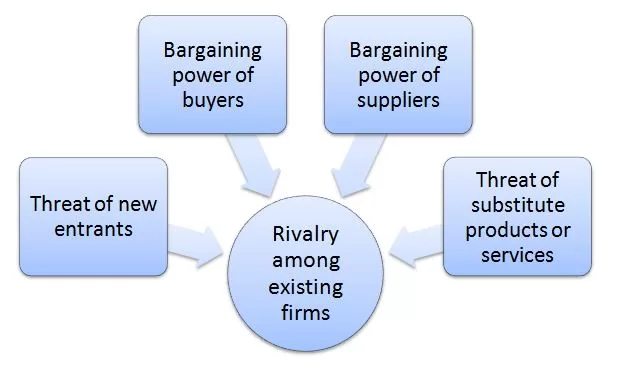
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Square Porters Five Forces are illustrated in figure 1 below: Figure 1 Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Square Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into the fintech sector is considerable. The following points affect the formation of the threat of new entrants into Square’s industry. 1. Time of entry. Banking and finance is already being disrupted globally and Square has been at the forefront of changes. Nowadays it has become evident that the old ways of conducting financial affairs where businesses had to wait for days, if not weeks to get their loan applications reviewed and employees have to wait for several days to get their cheques cashed will become history soon. Accordingly, some entrepreneurs, as well as, many established financial institutions are currently realizing their own projects to claim their piece of pie in the formation of the new global financial landscape. 2. Expected retaliation from current market players. While there are many entities interested in participating in the formation of new financial systems, any new market entrant will face retaliation from Square. It has to be noted that Square even stood up against deep-pocketed behemoth called Amazon. In 2014 Amazon copied Square’s main product, card reader, undercut its price by 30% and offered free two-day shipping and live customer support.[2] In response Square increased its focus on the quality of its products and customer services. By the end of 2015, Amazon had to discontinue its Register card reader. 3. Legal and regulatory barriers. Finance and banking is one of the most heavily regulated industries worldwide. There are consumer protection laws, anti-money laundering laws, broker-dealer regulations, virtual currency regulations,…
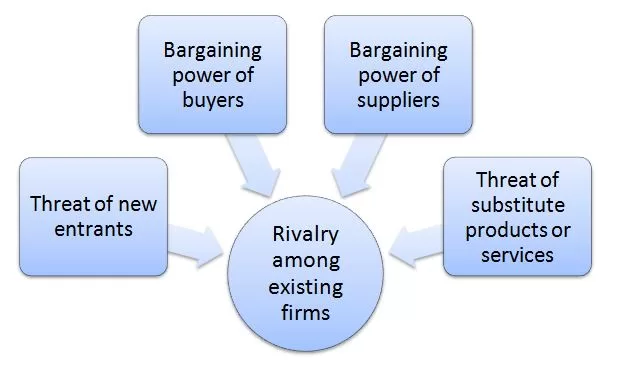
Uber Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework analyses five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in figure below: Uber Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Uber Porter’s Five Forces analysis Threat of new entrants into internet-based ride-hailing sector is significant. The following factors play role in the formation and extent of the threat of new entrants into mobility platform sector: 1. Simplicity of the business model. Nothing about Uber business model or its app is secret. In other words, Uber business model and its app can be replicated by any other company without massive amounts of capital requirements. Thanks to internet-based nature of the business model, new entrants to the market will not have issue to access distribution channels. Furthermore, due to low entry barriers into the ride-hailing industry, the numbers of local and global competitors for Uber have been consistently increasing during the past few years. 2. Scaling issues. While addressing technical aspects of the business such as developing ride-haling app and website may not be difficult, achieving necessary scale in operations is challenging for new entrants. In other words, mobility platform has to attract substantial amount of drivers in order to be successful and this requires time and massive capital investments. 3. Expected retaliation from existing market players. Current market leaders such as Uber, Lyft and Curb defend their territories fiercely and they are expected to retaliate against new entrants to the market. Bargaining power of buyers in Uber Porter’s Five Forces analysis The bargaining power of buyers in taxi industry is great. Buyer bargaining power depends on the following: 1. Abundance of offers. Buyer bargaining power is mainly fuelled by the abundance of competition in the industry. Uber customers are highly price sensitive. If…
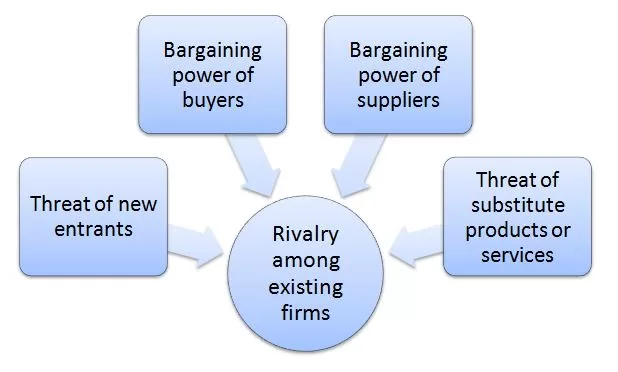
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Tesla Porter’s Five Forces Analysis below contains the application of these factors to analyse the competitive environment for the alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer. Figure 1 Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Tesla Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The threat of new entrants into alternative fuel vehicles manufacturing industry is moderate. The following factors play an instrumental role in the formation of threat of new entrants into electric vehicles industry: 1. Compromise between performance and cost of electric vehicles. One of the major challenges for electric vehicles is the bargain or compromise between their performance and cost. On one hand, almost all major automakers such as General Motors, Ford, Toyota, BMW and others have built electric cars that are not very expensive, but performance of these cars are compromised. Specifically, electric cars were known for being slower compared to traditional cars and their batteries did not last for long. On the other hand, Tesla has been able to develop its Model S, Model X and Model 3 cars that are fully electric and boasts with advanced technical characteristics such as high speed and long milage in a single charge. However, such fully electric advanced vehicles are technically challenging and expensive to produce. Any potential new market entrant is going to face the same set of challenges as General Motors, Ford, Toyota, as well as, Tesla. Taking into account the fact that established market players are yet to find solutions to these challenges, it can be argued that unless they find innovative solutions, the new market entrants are going to be overwhelmed by the same set of issues as well. 2. Economies of scale. Established market players…
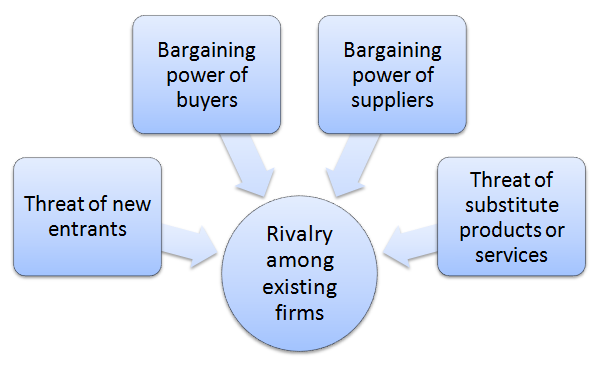
Porter’s Five Forces is a strategic analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1]. The framework consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in an industry. W.W. Grainger Porter’s Five Forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in W.W. Grainger Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants into traditional B2B distribution is not significant. Inter-relationships of the following factors determine the extent of threat of new entrants into industrial distribution: 1. Economies of scale. Economies of scale is a critical success factor in B2B distribution. Grainger purchases more than 1,7 million types of products from approximately 5000 suppliers worldwide.[2] Accordingly, Grainger benefits from the economies of scale to a great extent with positive implications on the cost structure of the business. However, new market entrants are not able to benefit from the economies of scale to a similar extent and therefore, economies of scale emerges as an important entry barrier to the B2B distribution industry. 2. Capital requirements. Industrial distribution is a highly capital-intensive business. In order to be successful and challenge established market players, new entrants need to have wide range of products stored in warehouses and distribution centres. Substantial capital investments are needed to achieve all of these and unless new market entrants do not come up with innovative business models to disrupt the industry, capital requirements are likely to persist as an important entry barrier to the industry. 3. Expected retaliation from existing businesses. Current market players in B2B distribution are likely to retaliate against any new entrants that possess a considerable threat to their market share. This is a noteworthy entry barrier for potential new entrants to the industry. For example, once Amazon Business started to become a formidable player in the global market of…
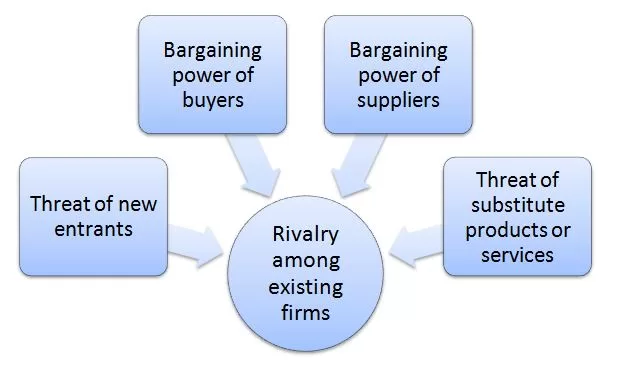
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Airbnb Porter’s Five Forces Analysis are illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Airbnb Porter’s Five Forces 1. Threat of new entrants in Airbnb Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The threat of new entrants into pear-to-pear lodging industry is low. Theoretically, setting up a website should suffice to enter the industry. However, in practice there is a number of barriers to potential new entrants into peer-to-peer lodging industry. These include the following: 1. The time of entry. In e-commerce the role of the first mover advantage is usually paramount and it is usually very difficult if at all possible for the followers to even get close to the market disruptor. Once their business model proved to be viable, internet-based market disruptors such as Amazon, Facebook and Uber were able to gain large market share in the global marketplace in a short amount of time. Funding from investors, word-of-mouth, effective management and hype usually play an instrumental role in assisting e-commerce disruptors to secure their niche and strengthen their position in international markets. This was the case with Airbnb as well. Founded in 2008, the company became a leading global hospitality service brokerage company within a matter of a few years. As of summer 2019, Airbnb boasts More than 6 million listings in more than 191 countries and regions worldwide.[2] The word Airbnb became a synonym for peer-to-peer lodging, leaving little room and market for potential new entrants. Nevertheless, it would be naive to claim that the threat of new entrants does not exist. There is no limit on the numbers of times that a market can be disrupted and as such, any new company with another innovative idea…
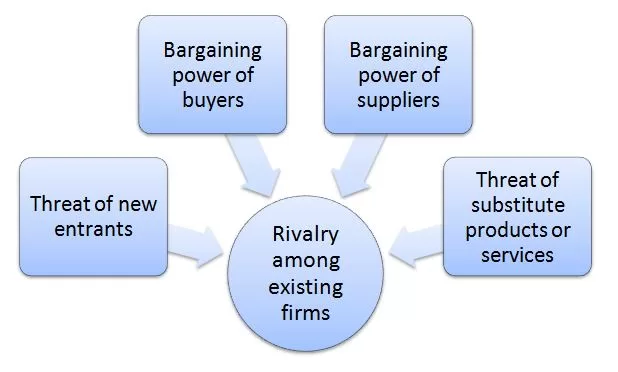
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. Microsoft Porter’s Five Forces are illustrated in figure below: Microsoft Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of substitute products or services in Microsoft Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of substitute products or services for Microsoft is low. The following factors determine the level of threat of substitute products or services for the multinational technology company: 1. Lack of direct substitutes. Range of products offered by Microsoft include operating systems for computing devices, servers, phones, and other intelligent devices; server applications for distributed computing environments; productivity applications; business solution applications; desktop and server management tools; software development tools; video games; and online advertising. The company also designs and sells hardware including PCs, tablets, gaming and entertainment consoles, phones, other intelligent devices, and related accessories. Additionally, Microsoft offers a wide range of software applications and cloud-based computing services such as Bing, Microsoft Azure, Microsoft Dynamics CRM Online, Microsoft Office 365, OneDrive, Skype, Xbox Live, and Yammer. There is no direct substitution for these products and services, however, indirect substitution exists. Indirect substitution for Microsoft products and services belonging to productivity and business processes segment include a wide range of stationary products, planners and organizers. Indirect substitution for Microsoft gaming and recreation products, on the other hand, include but not limited to music, movies, sports, spending time with friends and family members etc. 2. Low buyer propensity to substitute. The level of buyer propensity to choose substitute products or services to Microsoft’s products and services can be assessed as low. This is because according to its mission ‘to empower every person and every organization on the planet to achieve more’, Microsoft products and services are highly convenient to use.…
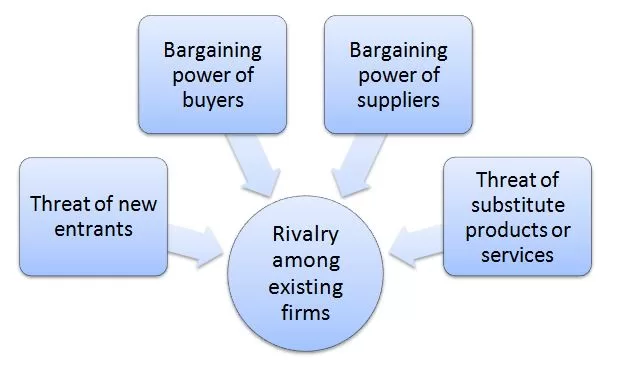
Porter’s Five Forces is an analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1]. Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Threat of New Entrants in Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into the internet technology is low. There are entry barriers for potentially new market players. Economies of scale is one of the major factors and entry barrier for new companies. Xiaomi is able to offer its products for competitive prices because it purchases raw materials in bulk and benefits from the economies of scale to a large extent. Moreover, entry into the electronics and software industry requires formidable capital investments. Xiaomi was initially funded with USD41 million in 2010 and the company went through series of funding and debt financing of several billion USD to reach its current state.[2] It may not be easy for new market entrants to secure funding at such a scale to enter the industry. Additional range of factors that decrease the threat of new entrants to the industry include access to distribution channels and likely retaliation from existing market players such as Apple, Samsung, Xiaomi and Huawei. Bargaining Power of Buyers in Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of buyers in technology and the mobile internet industry is significant. This is caused by primarily high level of competition in the global marketplace. Nevertheless, companies try to reduce buyer bargaining power through developing their ecosystem. For example, “all products belonging to Apple ecosystem are highly compatible with each-other and the purchase of one product belonging to the brand’s portfolio often leads to the purchase of other products. Gradually, it will come to the point that consumers…
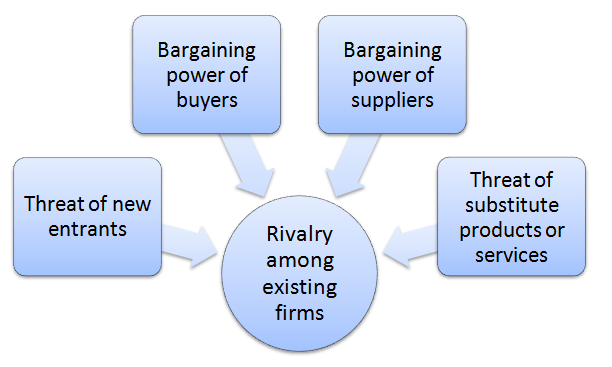
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Samsung Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Samsung Porter’s Five Forces Threat of substitute products or services for each product category offered by Samsung is substantial. Samsung smartphones can be substituted with ordinary mobile phones at any time with no additional costs for customers. Moreover, there is an increasing range of mobile and desktop applications that represent relevant substitute for Samsung’s mobile communications business. Samsung visual display business is threatened by indirect substitution such as increasing popularity of leading active lifestyle and spending time outdoor. In other words, representatives of Samsung target customer segment may prefer to spend time outdoors, rather than in front of TV with negative implications on the volume of sales of Samsung TV’s. Furthermore, increasing popularity of cloud storage is emerging as viable alternative for printing and this tendency may decrease the sales of Samsung printing solutions products in the foreseeable future. Rivalry among existing firms is intense. Approaching market saturation for many product categories in consumer electronics industry intensifies the rivalry among existing firms and there is a little differentiation among the range of products offered. Moreover, the great number and diversity of competitors operating in the market fuels the extent of competition in the industry. In smartphone market segment, one of its critical product categories, Samsung competes with a wide range of suppliers such as Apple, LG, Lenovo, ZTE, Huawei, OPPO and others. Nevertheless, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Samsung has been able to maintain leadership position in the global scale for the last six years. Figure 2 Global market share by leading smartphone manufacturers[2] Bargaining power of suppliers…
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Google Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Google Porter’s Five Forces Threat of substitute products or services for Google is low. Search remains as Google’s and Alphabet’s core business and it is used by more than a billion people around the globe every day. The threat of substitute for Google’s search can be assessed as low because it remains to be the most convenient and time-efficient way of finding needed information. The threat of substitute products and services for Google’s other services is moderate. For example, people can use mobile text messages or mobile messengers such as What’s Up instead of using Gmail and traditional paper maps can be used instead of Google maps. At the same time, it is important to note that although, there are some direct and indirect substitutes for all Google services, these substitutes do not offer the same level of user convenience, functionality and speed. Accordingly, the threat of substitute products and services for products and services offered by Google can be generally assessed as low. Rivalry among existing firms is fierce. General purpose search engines and information services, such as Microsoft’s Bing, Yahoo, Yandex, Baidu, Naver, and Seznam represent competition for Google search. There are also vertical search engines and e-commerce websites, such as Amazon and eBay (e-commerce), Kayak (travel queries), LinkedIn (job queries), and WebMD (health queries). Some users will navigate directly to such content, websites, and apps rather than go through Google. Social networks, such as Facebook and Twitter also belong to the list of Google competitors. Some users are increasingly relying on social networks for product or service referrals, rather than seeking…
Facebook Inc. Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework assesses an overall extent of competition in the social media industry. Developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] consists of five individual forces as illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1. Facebook Inc. Porter’s Five Forces Rivalry among existing firms in social media industry is fierce. Alphabet Inc. (Google) is the most prominent competitor for Facebook and Google Adsense and Facebook Ads are two most popular competing platforms for online advertising. Generally, the major players in the industry include Facebook, You Tube, Reddit, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, Tumblr, LinkedIn, Yahoo! Answers, Yelp and others. As it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Facebook is the most popular social networking website in the US with an approximate market share of 42.4 per cent. Most popular social networking websites in the USA (as of August 2016)[2] The rate of the industry growth is immense, diversity within the competition is vast with no switching costs for customers and this fact further intensifies the rivalry among existing market players. Moreover, “there are several regional social networks, such as Renren in China, Mixi in Japan, vKontakte in Russia, etc., and these compete with FB for users in their respective geographies. Increased regulation in certain markets such as China is more beneficial to regional players”.[3] Threat of new entrants into social media industry is significant. Although there are certain industry entry barriers such as capital requirements for marketing and expected retaliation from existing businesses, it is generally easy to built websites and mobile apps. New social media platforms based on innovative ideas and/or integrating innovative features can secure funding from investors to pose a threat to the market share of Facebook, Google+ and other established market players. Taking into account decreasing popularity of Facebook among teens,[4] it can be argued that a new social…
