
Dell Inc., one of the world’s largest computer manufacturers in the world, has developed its business in a unique way, by selling equipment directly to customers around the globe. The company was founded in 1984, and has grown from its original base inTexas,USA, into a key international player in the computer industry. Dell Computer Corporation has been extremely successful generating a 13 billion empire only within 13 years of operation in computers market. “Direct Business Model” has enabled the company to be that successful within short period of time. This strategy, as implemented by the founder of Dell Company Michael Dell, let the company to configure computers and sell them directly to customers or final users at incredibly low prices. This was due to eliminating the mark-ups by intermediaries and the risks of carrying slow-moving, large inventories in the warehouses. Direct model turned out to be a success factor for the company as it not only helped to produce and offer computers and services in lower prices, but also enabled the company to interact with customers and satisfy their needs and wants through producing customer-build computers for them. Most importantly Dell proposed the idea of “Virtual Integration” that gave a competitive edge and comparative advantage for the company over its competitors. Financial analysis International markets are now extremely competitive due to the liberalization of the world trade and investment environment in new technology and IT systems. Strategy is often regarded with identifying and taking action that lowers the costs and differentiate Dell’s product offering through superior design, quality, service, and functionality. Dell has been achieving consistent solid annual growth both on sales and net profit due to its market dominance, demand and product innovation. Sales of external storage systems increased 73 percent and continue on an annual run rate of…
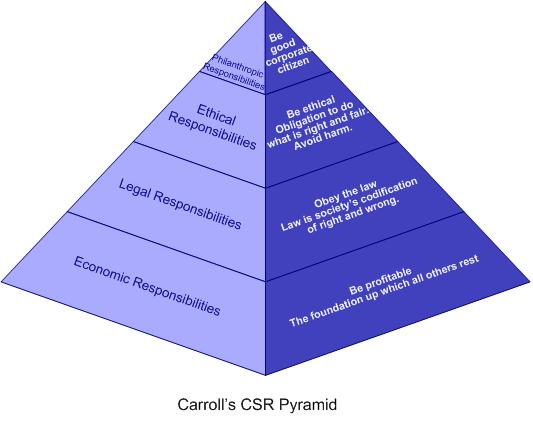
Carroll’s CSR Pyramid. According to Carroll (1983:608), “corporate social responsibility involves the conduct of a business so that it is economically profitable, law abiding, ethical and socially supportive. To be socially responsible then means that profitability and obedience to the law are foremost conditions when discussing the firm’s ethics and the extent to which it supports the society in which it exists with contributions of money, time and talent”. And the different layers in the pyramid help managers see the different types of obligations that society expects of businesses. Adopted from: www.csrquest.net/imagefiles/CSR%20Pyramid.jpg Economic responsibility in Carroll’s CSR Pyramid : It concerns the responsibility of business of producing goods and services needed by society and selling them making a profit. Novak (1996) has contributed to this are by defining seven responsibilities of companies. Companies have shareholders who demand a reasonable return on their investments, they have employees who want safe and fairly paid jobs, and they have customers who demand good quality products at a fair price. So, here comes the first responsibility of the business as it is to be a properly functioning economic unit and stay in business. And this is the base of the pyramid, where all the other layers rest on. Legal responsibility in Carroll’s CSR Pyramid : the legal responsibility of corporations demands that businesses abide by the law and play by the rules of the game. Should companies choose to “bend” or even ignore their legal responsibilities the price can be very high for the business. And US software giant Microsoft has faced a long running anti-trust case in Europe for abusing its monopolistic position to disadvantage its competitors which resulted in tough settlements against the company. Ethical Responsibility in Carroll’s CSR Pyramid : the main concept of ethical responsibility as defined and expressed by Carroll (1991) is that the ethical responsibility consists…
Nowadays Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become an essential part of big, multinational corporations without which any corporation of a substantial size would face difficulties from various fronts – non-government organizations, governments, public (including existing and potential customers), and even workforce itself. People justifiably reason that since global multicultural corporations are earning revenues which are calculated at millions, or even billions of pounds, they are expected to give something back to the community they are operating in or to the wider community to compensate for a wide range of inconveniences and difficulties the operation of the business is causing to local community, nature or the wider area. However, if it is expected from big companies in UK and everywhere to exercise social responsibility in addition their primary function, which is profit maximisation, what should be, the stance of small and medium business in UK regarding giving back something to the community. Opinions differ regarding whether it is expected from small and medium businesses in UK to engage in CSR. Some argue that since small and medium business in UK do not possess large amount of funds that could be spent for the purpose, and even if the business is making any negative impact on local community, be it damaging the nature, exploiting natural resources, or anything else, such an impact would not be substantial enough for the business to reimburse it. Others, on the other hand, insist that corporate social responsibility has to be practiced by all business in UK– small, medium or big, and since a business is making money it should give back. “A business that accepts Corporate Responsibility will be prepared to be responsible for and willing to justify its actions. It will also consider the impact of its actions on a variety of individuals and groups,…

Johnson, Scholes and Whittington (2006) state that Corporate Social Responsibility is concerned with the ways in which an organisation exceeds the minimum obligations to stakeholders specified through regulation and corporate governance. As we have to analyse the CSR in multinational company, we have to closely analyse the CSR approaches in Global level and sometimes in the country specific level. Furthermore, they also indicate that social responsibility which will have universal elements whilst also being applicable to many different localities. As the actions of companies in one country may have an impact on other countries (pollution control or trading practices), there is an increasing need to look at the global impact of an organization’s strategies (Johnson, Scholes and Whittington 2006). Moreover, Gray et al (2007:789) indicate that a business that accepts Corporate Social Responsibility will be prepared to be responsible for and willing to justify its actions. It will also consider the impact of its actions on a variety of individuals and groups, both inside and outside the organization. It is claimed that the organizations have social and environmental reporting where they report their accountability to all stakeholders and other interested parties. This is referred as silent reports. However, the reports which are produced by external sources such as newspapers, magazines and other research institutions are referred as shadow accounts or reporting where if the silent accounts are in line with the silent reports. There are some methods to encourage the Corporate Social Responsibility as mentioned by Gray (2007). Government Intervention: Governments can intervene directly to ensure that a business accepts the consequences of its behaviour. One of the most common methods of achieving this is through the creation of legislation which businesses must adhere to. This could be for the businesses to reduce their carbon footprint by certain percentage…

There have been several researches into the adoption and harmonization of IFRS in EU countries due to the nature and importance of the topic. Street and Shaughnessy (1998) mentioned about several differences between the international reporting standards and reporting standards of major Anglo-American countries. The difference between harmonization and standardization has been analysed by McLeay, Neal and Tollington (1999) and they presented a method to measure harmonization that allows for choice between alternative accounting treatments. Further studies were carried out by Murphy (2000), Van der Tas, (1998) to identify the compliance with IFRS by selected companies by analysing the annual reports of companies from different countries. The early adopter, who adopted IFRS before 2005 optionally were evaluated by group of researchers (Street and Gray, 2001; Taylor and Jones, 1999) and they found out that different companies financial statements showed different levels of usefulness by applying IFRS. Street and Gray (2001) selected a sample of 279 firms that used IFRS in preparing their financial statements. And the research found out that in most cases, disclosed accounting policies were not consistent with IFRS. Another important finding by Schultz and Lopez (2001) suggest that uniform international accounting standards may not result in uniformity among countries especially when the standards allow for significant discretion. Jermakowicz and Tomaszewski (2006) carried out research into the quality of IFRS compared to GAAP and found out two reasons as why reporting under IFRS does not provide higher accounting quality. One of the reasons for their argument is because of domestic standards that limit managerial discretion relating to accounting alternatives. They argue that limiting managerial discretion relating to accounting could eliminate the firm’s ability to report accounting measurements that are more reflective of its economic position and performance. Another reason is the inherent flexibility in principles-based standards that could…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Finance

Financial Reporting is a way of presenting data about a company’s financial position, the company’s operating performance, and the flow of funds over an accounting period. According to ACCA, the objectives of financial reporting standards are defined as follows” The overall objective of the FRS is to require all entities falling within its scope to highlight a range of important components of financial performance to aid users in understanding the performance achieved by an entity in a period and to assist them in forming a basis for their assessment of future results and cash flows.” And moreover, the American Financial Accounting Standards Board defines Financial Reporting as follows” activities which are intended to serve the informational needs of external users who lack the authority to prescribe the financial information they want from an enterprise and therefore must use the information that management communicates to them”. Based on above mentioned definitions, it is understood that a company’s financial information should be communicated to its relevant stakeholders such as shareholders, investors, government, lenders and others who are making business, financial and credit decisions. However, as globalisation is intensifying and creating multinational companies and organizations, accounting practices and regulations became different across different countries and the consistency became a very important and critical issue. It became difficult to measure income and expenditure in the income statement, as well as measuring and recognising assets and liabilities in the balance sheet. Therefore, it is often really hard for anyone making business and financial decisions, to decide when comparing two companies’ financial statements especially if they are located in two different locations. Nobes and Parker (2008) also state that if a number of accountants from different countries, or even one country, are given a set of transactions from which to prepare financial statements, they will not…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Finance
To reach different markets or promote products or services to different locations or different people companies use a method called market segmentation. As Cumming (1994) explains, “Market segmentation describes the division of a market into homogenous groups which will respond differently to promotions, communications, advertising and other marketing mix variable.” Therefore, market segmentation is very important for most of all companies around the world. If a company cannot reach the market or area they will success; or the product or service they provide too expensive so the market they are in cannot afford, surely that company cannot expect to prospers but even fails as a company. Market segmentation Market segmentation is to divide the market into smaller segments. The main reason behind the market segmentation is to make easier to address the needs of smaller groups of customers, particularly if they have many characteristics in common (Breen, 2003). However, there are thing marketer needs to consider to see if a market must be segmented. The market in question must be large enough to segmented. Differences must exist between members of the market and these differences must be measurable through traditional collection methods (McElligiot, 2003). Lancaster et al (2002) argues that there is no “golden rule” when it comes to segmenting consumer markets. The marketing firm might have to investigate using different segmentation variables in order to identify the overall structure of market. Often it may be necessary to use a combination of segmentation variables to define the precise market segment. There are four variables commonly used for segmenting consumer markets: Geographic segmentation Demographic segmentation Psychographic segmentation Behavioural segmentation The first two are geographic and demographic segmentations are physical attribute classification, which refers to the dividing of a market into groups based characteristics, such as location, population, country of origin,…

As globalisation of world rapidly changes, today’s global managers, whose company operates in many parts of world, face many challenges in securing their business interests in other countries. When a business decides to enter the foreign market there are a several factors that a company should take into consideration before deciding to expand their product or service into foreign market. Among these factors are the cultural differences the company faces. Cultural differences exist between different countries and these differences must be known and evaluated by the marketing firm. According to Lancaster et al (2002) a number of factors contribute a country’s overall culture including religion, education and aesthetic appreciation. In last twenty years, learning cultural differences among nations and need for greater cross cultural awareness have been seen to be a very important factor in improving and facilitating marketing activities of a company outside their country of origin as different cultures has different ways of doing business, different cultural assumptions, values and attitudes. Therefore, culture is important and has to be appreciated by the managers running the company. It simply can make or break relationship and even may cost the business millions of dollars. Moreover, adaptation to the environmental differences from one market to another is seen as the key to successful international marketing. It is vital for international marketer being able to anticipate the uncontrollable factors of both the foreign and domestic market that have great influence on a marketing mix, so he or she can adjust the marketing mix to minimize the effects. After all, due to globalisation of markets and products, today increasing numbers of international marketing staff have to deal with ethical issues in cross cultural global economy. As a result, it is claimed by many international marketing researchers that the concept of “self reference criteria”…

Procter and Gamble was founded in 1837 by William Procter a British citizen who emigrated to theUnited States, and James Gamble a U.S based Irish soap maker and industrialist. The company first sold candles. P& G as it is also called is a fortune 500 multinational corporation headquartered in Down town Cincinnati,Ohio, that manufactured a wide range of consumer goods. As at mid 2010, P& G is the 6th most profitable corporation in the world and the 5th largest corporation in the United States by market capitalisation. It spends more on US advertising than any other company. Total Revenue USD 79.03 Billion (2009) Operating Income USD 16.13 Billions (2009) Total Assets USD134.83 Billions (2009) Total Equity USD 63.099 Billions (2009) Employees 140,000(2009) President & CEO Bob McDonald As at July 1 2007, the company operation are categorised into three “Global Business Unit” with each Global Business Unit divided into “Business Segments” according the company‘s March 2009 earning release. Manufacturing operation are based in the following regions: United States Europe Canada China(31 wholly owned factories) and other parts of Asia Mexico Africa Latin America Australia 22 of P & G’s brands have more than a billion dollars in net annual sales and another 18 have between $500million and $1 billion. Motto “Touching lives, improving Life” 1. Beauty Care Beauty segment Grooming segment 2. Household Care Baby care and family care segment Fabric care and home care segment 3. Health and wellbeing Health care segment Snacks, Coffee and Pet care segment [ Wikipedia free encyclopedai 2010) APPLICATION OF STRATEGY OF INNOVATION AT PROCTER AND GAMBLE Procter and Gamble have continually used the strategy of innovation to lead the consumer goods industry. The constantly changing market place has forced the strategist at Procter and Gamble to focus on innovation as a way of maintaining their position in the…

Initially it had been presumed that consumers simply wanted their products and services with no questions asked but as the case may be people began to peer behind the brand facades and discovered all sorts of things they didn’t like from environmental irresponsibility to exploitation of child labour consequently social and moral concerns began to firmly exist in traditional marketing terms (Mitchell 2007). As a result of this progression major developments in the form of corporate social responsibility (CSR) began to occur. CSR is defined as ‘recognising that companies have a responsibility to a range of stakeholder groups such customers, employees and suppliers (Adkins 2005). Consumer reactions to CSR are not as straightforward as preferred with numerous factors affecting whether a firm’s activities translate into consumer purchases. Although people say that CSR matters in their purchase decisions, the reality is that customer responses to initiatives are not always consistent (Sen and Bhattacharya 2001). However over the past decade, CSR has gradually been integrated into the business activities of companies all over the world where businesses integrate social and environmental concerns into their corporate operations (Demetriou et al 2010). CSR allows businesses the opportunity to strengthen their corporate reputation and profitability by signalling to the various stakeholders with whom the organization interacts that it is committed to meeting its moral obligations. As a result, ‘many businesses have become more closely interrelated with society by focusing on charitable donations, corporate philanthropy, community participation, and Cause-related marketing’ (CAUSE-RELATED MARKETING ) (Demetriou et al 2010). CAUSE-RELATED MARKETING as it is purposefully referred to involves partnering charitable causes with products for marketing programs (Chang 2009) and applying strategies to support these causes whilst building the business (Adkins 2005). Cause related marketing recognises the importance of an alliance between businesses and charitable organisations for the same…
