BMW PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. BMW PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects
Political Factors
There is a wide range of political factors that affect BMW Group in various ways. For example, enforcement of new laws related to CO2 emission and change in EU legislation related to end-of-life vehicle (ELV) recycling are major political factors that affect BMW manufacturing processes. Level of political stability in emerging markets such as Russia, China, and Brazil can be highlighted as additional political factors impacting BMW in a way that political instability in these countries can have negative implications on local consumer spending patterns. Additionally, in case of political instability BMW investments in respective countries may be subjected to risks.
There are also instances where BMW has attempted to influence external political factors to create a favourable political climate for its business operations. The opposition of the company to European commission proposals for a tougher limit on carbon emissions in 2012 can be mentioned to justify this claim. Specifically, it was noted that BMW was lobbying to water down European plans to improve the fuel efficiency of cars at the same time as trumpeting its green credentials as the official car sponsor of the Olympic Games, according to internal documents seen by the Guardian[1].
Economic Factors
Impacts of a wide range of economic factors on BMW performance are evident and significant. Namely, vast GDP fluctuations in EU countries during the last few years with direct implications on consumer spending in EU countries is a substantial economic factor that affects BMW Group performance to a considerable extent.
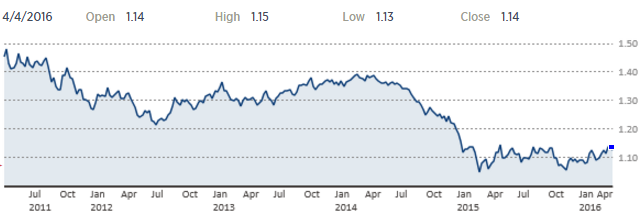
Currency exchange rate can be named as another important economic factor that has direct effects on BMW Group reported revenues. As it is illustrated in Figure below, BMW Group’s home market currency, EURO has been depreciated considerably during the last five years, benefiting BMW Group, since it exports a large share of its products to international markets, including the US.
Changes EUR:USD currency exchange rate[2]21
Moreover, inflation rate is another important external economic factor BMW has to deal with. The company has to increase the prices of its vehicles in a regular manner in order to address increasing inflation. The latest price increase introduced in the US in 2015 ranges from USD250 on the 428i Coupe to USD1000 on the X5 Drive50i crossover. Since the USD 1000 increase is on one of BMW’s more pricey vehicles, it still only amounts to about a 1.4% increase.[3]
BMW Group Report contains the full discussion of BMW PESTEL analysis. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on BMW Group. Moreover, the report contains analysis of BMW Group’s marketing strategy, its leadership and organizational structure and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Vaughan, A. (2012). “BMW accused of hypocrisy over opposition to European car targets” The Guardian, Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2012/jul/09/bmw-hypocrisy-european-car-targets
[2] CNBC (2016) Available at: http://data.cnbc.com/quotes/EUR%3D
[3] Woodyard, C. (2015) “BMW raises prices for 2015” USA Today, Available at: http://www.usatoday.com/story/money/cars/2015/01/03/bmw-price-increases/21215541/