BMW Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
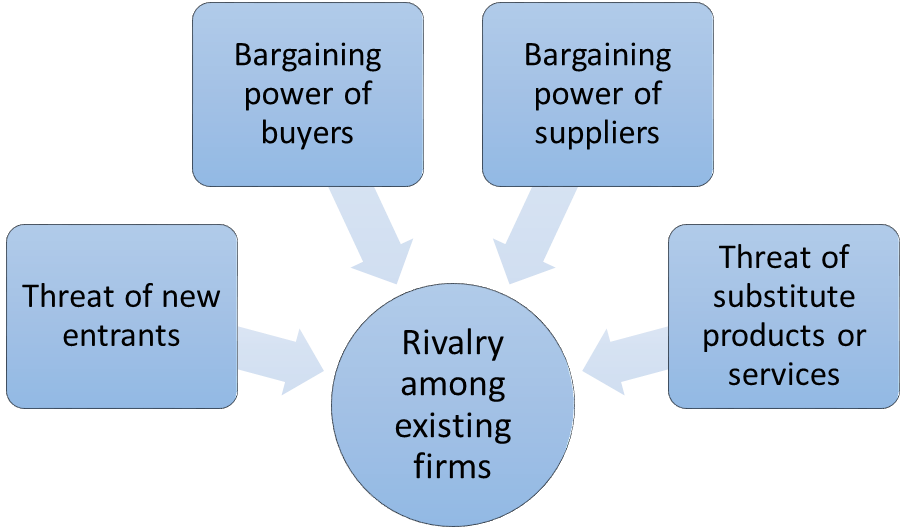
Porter’s Five Forces is a strategic analytical model developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] and it is used to assess the overall competitive climate in an industry. Porter’s five forces are represented in Figure 1 below:
Figure 1 BMW Porter’s Five Forces
Threat of substitute products or services is insignificant. It is important to clarify that there are different substitute products and services for luxury cars than cars in general. Specifically, substitute products and services for cars in general as means of transportation include bicycles, motorcycles, underground (subway), buses and other forms of public transportation. The threat of substitute for cars in general as a means of transportation can be assessed as high.
Luxury car segment, on the other hand, is different in a way that they are purchased to satisfy needs beyond transportation. People purchase BMWs, Rolls-Royces, Porches and Mercedes Benzes as a means of self-expression to satisfy their need for self-perception of achievement, success and status. From this point of view, it can be argued that the threat of substitute products and services for luxury cars is insignificant, because owning a luxury car is a ‘must-have’ for wealthy people and the need for a luxury car often comes before the need for luxury watches, yachts, villas and other attributes of a rich lifestyle
Rivalry among existing firms is intensive. There is a fierce competition in the global market of the premium car segment and the extent of differentiation between vehicles of each individual brand is significant. The level of advertising expenditure and the efficiency of the marketing communication strategy play critical role in the luxury car segment since businesses operating in this segment attempt to charge extra money for the perception of status, achievement, recognition and success associated with owning their vehicles.
As it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, in 2015 BMW maintained a leadership position in the global luxury car markets with more than 1.9 million units vehicles sold in one year. BMW is closely followed by other German luxury car brands Mercedes-Benz and Audi in terms of sales volumes of vehicles.
Figure 2 Global luxury car market in 2015[2]
Bargaining power of BMW Group suppliers is not significant. BMW group has about 13,000 suppliers of various sizes[3] and the importance of having business with BMW for each supplier is paramount. The majority of products and services provided by the majority of suppliers are not unique and this fact further reduces BMW supplier bargaining power. Moreover, due to its pursuit of the product differentiation strategy, for BMW the cost of supplies relative to the selling price of its vehicles is insignificant…
BMW Group Report contains a detailed discussion of BMW Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Value Chain Analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on BMW Group. Moreover, the report contains analysis of BMW Group’s marketing strategy, discusses leadership and organizational structure and addresses the issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Porter, M. (1979) “How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy” Harvard Business Review
[2] Statista (2016) Available at: http://www.statista.com/statistics/262921/global-production-of-luxury-cars-by-make/
[3] Sustainable Value Report (2015)