Value-Chain Analysis
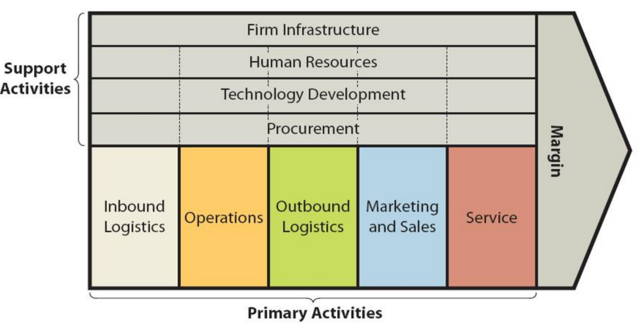
BYD value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of BYD value chain analysis. BYD Primary Activities BYD Inbound logistics BYD inbound logistics is one of the key sources for value creation for the EV behemoth. BYD has more than 11,000 cooperative suppliers, 41% of which are located in Southern China, 34% in Eastern China, 9% in Northern China.[1] The electric automaker aims to produce as many spare parts in-house as possible, thus decreasing dependence on external vendors, at the same time increasing profit margins. For example, for BYD Dolphin only tyres and windows are delivered by suppliers and all other components are produced by the company itself.[2] BYD prioritizes long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, securing stable access to critical materials and components like lithium, cobalt, and semiconductors. This reduces procurement risks and price fluctuations. The company leverages cutting-edge technologies like digital supply chain management systems, artificial intelligence for demand forecasting, and automated warehouse robots. BYD Operations In the operations stage, BYD engages in the manufacturing and assembly of its products. This includes the production of EVs, batteries, solar panels, and energy storage systems. Efficient production processes and quality control measures are crucial in this stage. BYD operations can be divided into the following four segments. Automobile. BYD delivered a total of 1,802,000 vehicles in 2022, with a year-on- year growth of 149.9%, including around 1,788,000 new energy vehicles, with a year-on-year growth of 217,6%.[3] Rail Transit. The company produces medium-capacity “SkyRail” and low-capacity “SkyShuttle” filling the technological and industrial gap in rail transit and providing effective solutions to traffic jams in cities all over the world. Renewable energy. As a provider of integrated renewable energy solutions, BYD produces relevant products like batteries, solar energy…
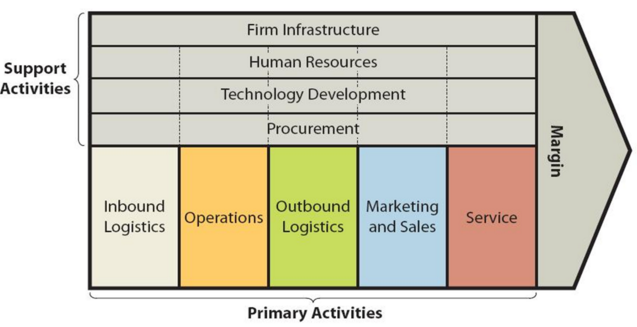
Value chain analysis is an analytical tool that helps to find business activities that can create the most value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of Marriott value chain analysis. Marriott Value Chain Analysis Marriott Primary Activities Marriott Inbound logistics The inbound logistics activities for Marriott International involve the procurement, transportation, and storage of the goods and services that the company needs to operate its hotels and resorts. These activities are essential to the company’s ability to provide its guests with a high-quality experience. Marriott International procures a wide range of goods and services from suppliers such as food and beverage, linen, furniture, toiletries and other supplies. The largest hotel chain in the world has a strong supplier network and is able to negotiate competitive prices. The company also has a team of experienced procurement professionals who are responsible for managing the inbound logistics process. Marriott Operations Marriott’s operations can be divided into four key areas: 1. Hotels. Marriott operates and franchises hotels under its various brands. It also manages hotels on behalf of other owners. 2. Vacation ownership. Marriott operates a vacation ownership program called Marriott Vacation Club International. This program allows members to purchase vacation points that can be used to stay at Marriott-affiliated vacation resorts. 3. Timeshare exchange. Marriott operates Interval International, a timeshare exchange program that allows members to swap their timeshare weeks for stays at other resorts. 4. Food and beverage. Marriott operates restaurants and bars in many of its hotels. It also provides catering services. Marriott Outbound Logistics Generally, outbound logistics within value chain analysis refer to all the activities involved in delivering the finished product or service to the customer. This includes warehousing, order fulfilment, transportation, and delivery. For Marriott International outbound logistics activities include the following:…
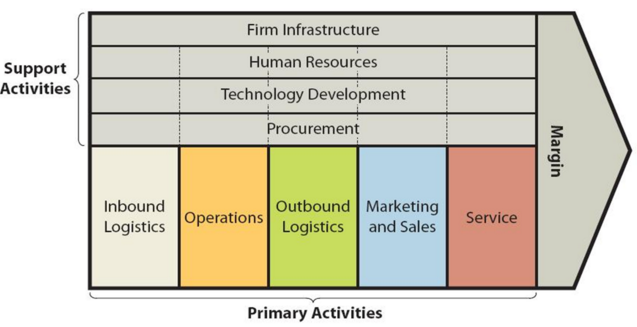
Value chain analysis is an analytical tool that can be used to find business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the on-demand media provider. Figure below illustrates the essence of Netflix value chain analysis. Netflix Value Chain Analysis Netflix Primary Activities Netflix Inbound logistics Inbound logistics involves the processes associated with receiving and storing raw materials to create output. For a streaming service such as Netflix content is the raw material. Establishing strategic relationship with content producers and intellectual property holders such as Warner Brothers, Dream Works and Sony Pictures are the main sources of inbound logistics value creation for a streaming business. Netflix is utilizing these sources extensively. Currently, Netflix is increasing investments to produce its own, original content such as Squid Game, BoJack Horseman and Stranger Things as a differentiator amid intensifying competition. This shift has certain implications on inbound logistics aspect of the business. Specifically, focus on original content requires greater involvement in inbound logistics for the largest streaming service in the world. Netflix Operations Operations are the stage where inbound logistics are transformed into outbound logistics. For Netflix, operational efficiency and cost advantage are the main sources of value creation at this stage. The on-demand media provider has to maintain its video streaming platform effectively in terms of ease of access, quick search, stability, and security of the server. Netflix Outbound Logistics Outbound logistics refer to the distribution of products and services to customers. Usual sources of value creation in outbound logistics include Delivering to consumers directly without intermediaries, Cooperation with other businesses to share distribution costs and extensive integration of information and communication technologies. Considering that Netflix delivers digital media through streaming and downloads, the relevance of outbound logistics aspect of value chain analysis for the largest streaming service in…
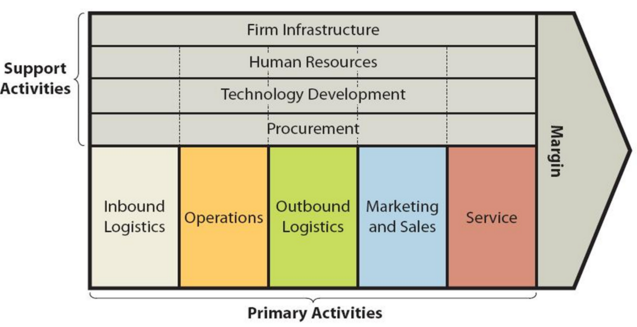
Apple value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Apple value chain analysis. Figure 1 Apple Value Chain Analysis Apple Primary Activities Apple Inbound logistics Inbound logistics primary activity refers to receiving and storing of raw materials for their consecutive use in manufacturing. Apple works with hundreds of suppliers around the globe and maintains a highly sophisticated supply-chain management as illustrated in Figure 2 below. Figure 2 Apple operations roadmap[1] Apple supply chain involves more than 3 million people working for thousands of businesses in 52 countries[2] The multinational technology company’s purchase commitments typically cover its requirements for periods up to 150 days[3]. Tim Cook is an experienced word-class supply chain professional. Steve Jobs had convinced him to join Apple as head of supply chain in 1998 when the tech giant was in trouble, risking the bankruptcy. As part of massive supply chain turnover Tim Cook cut the numbers of suppliers, reduced the number of warehouses by half and established relationships with contract manufacturers. Cook has been able to reduce Apple inventory turn over from 1 month to 2-5 days. Cook further reduced the numbers of suppliers after becoming CEO in 2011. As a result of these and other initiatives, Apple supply chain practices have become a benchmark for efficiency for global businesses. The main sources of value in Apple inbound logistics relate to the economies of scale due to the massive scope and scale of business operations as discussed below and the development of strategic relationships with suppliers. Moreover, Apple Inc. exercises an immense bargaining power in dealing with its suppliers and as a result, the company is able to secure cost advantage in the purchase of…
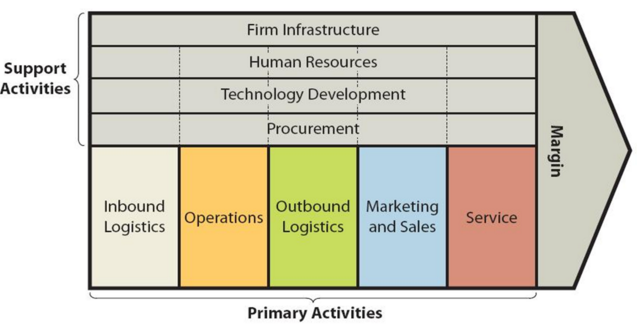
Nvidia value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Specifically, business leaders can create competitive advantage through dividing the business into various activities and analysing each activity individually from value creation perspective. Figure below illustrates the essence of Nvidia value chain analysis. Value chain analysis Primary Activities in Nvidia Value Chain Analysis Nvidia Inbound logistics Nvidia inbound logistics involves managing the supply chain of components and raw materials into the premises of its contract manufacturers. The multinational technology company performs quality checks of semiconductors and other spare parts using test equipment purchased from industry-leading suppliers such as Advantest America Inc. Nvidia benefits from the economies of scale in inbound logistics activities due to the large amount of spare parts and components it purchases. Furthermore, the company has strategic relationships with its key suppliers in place and these relationships play an instrumental role in new product development. Nvidia Operations Nvidia employs fabless manufacturing strategy. It employs third party companies outside of United States for all phases of the manufacturing process, including wafer fabrication, assembly, testing, and packaging.[1] Nvidia does not engage in any of these activities directly and chooses to focus the design, marketing and distribution of its products. The company works with world-class manufacturers to produce its products. Semiconductor wafers are produced by leading companies such as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited and Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd, adapter card products and switch systems are produced by the likes of Flex Ltd., Jabil Inc., and Universal Scientific Industrial Co., Ltd. and Fabrinet manufactures Nvidia cables. Assembly, testing and packaging of products and platforms are done by Amkor Technology, King Yuan Electronics Co., Ltd., Omni Logistics, LLC, Siliconware Precision Industries Company Ltd., Wistron Corporation…
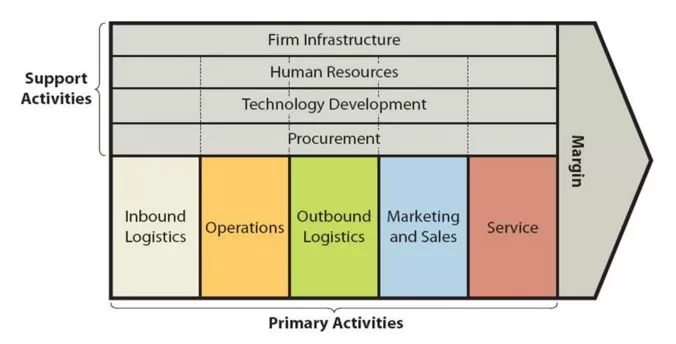
WeWork value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the co-working giant. Figure below illustrates the essence of WeWork value chain analysis. WeWork Value Chain Analysis WeWork Primary Activities WeWork Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involve receiving and storing raw materials and using them for manufacturing. WeWork offers space as a service and as such its value chain analysis, including inbound logistics are affected by the following main characteristics of service: a) Inseperability. In services production and consumption are simultaneous and they cannot be separated. b) Intangibility. Unlike products, services are intangible and they cannot be touched in physical terms. However, intangibility aspect of services relates to WeWork to a lesser degree compared to other types of services. This is because office spaces and furniture and appliances within offices are tangible items. c) Perishability. Services cannot be stored for the later use or sale. Certain number of desks of a co-working operator staying vacant during a certain period of time means waste and loss for the business. d) Heterogeneity. It is difficult to establish a standard for the quality of services. The quality of services is highly dependent on the perception of each individual user. Inbound logistics for WeWork involve finding suitable places for co-working offices and furnishing these offices as creative and attractive workspaces. WeWork Operations Operations within value chain analysis refer to the process of transforming raw materials into products ready to sell. For service companies such as WeWork operations include the processes that make the services possible and deliver the experiences to consumers. WeWork operates a network of 756 locations in 38 countries as of December 2021[1]. The co-working giant attempts to design its offices and workspaces in a creative manner that…
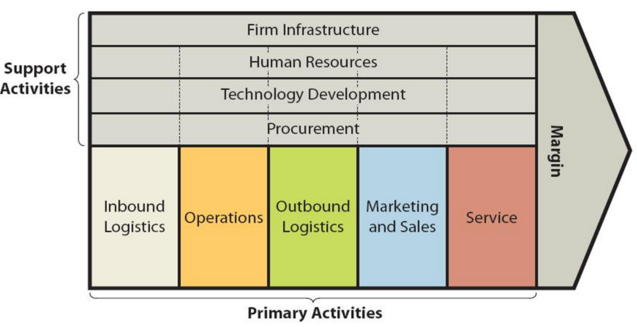
Starbucks value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage for the global coffeehouse chain. Figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis. Starbucks Value chain analysis Starbucks Primary Activities Starbucks Inbound logistics Starbucks inbound logistics and supply chain was subjected to a dramatic restructuring in 2010 after Howard Schultz had returned to the role of CEO for the second time. The restructuring initiative of Starbucks inbound logistics involved simplification of supply-chain management and the creation of a single, global logistics system. Unroasted Arabica coffee beans are brought from Asia, Africa and Latin America to the US and Europe in containers via sea. Also, the coffee chain purchases green coffee beans from multiple coffee-producing regions around the world. These are delivered to one of the following regional roasting plants and distribution centres: Kent Flexible Roasting Plant – Kent, Washington. Augusta Roasting Plant – Augusta, Georgia. Sandy Run Roasting Plant – Gaston, South Carolina. York Roasting Plant and Distribution Center – York, Pennsylvania. Evolution Fresh Juicery – Rancho Cucamonga, California. Coffees are roasted and packaged and taken to dozens of central distribution centres around the globe. Along with coffees from regional distribution centres, central distribution centres also receive deliveries from vendors for a wide range of products starting from coffee machines to napkins. Central distribution centres make more than 70,000 deliveries per week to Starbucks 25,085 stores located in 75 countries.[1] The world’s largest coffeehouse chain also grows its own coffee. Since 2013 Starbucks has its first own 240-hectar coffee farm in PoasVolacno, Costa Rica.[2] Such a shift in the sourcing of products can increase the effectiveness of new product development initiatives for the business as the company will have a chance of experimenting with developing new sorts of…
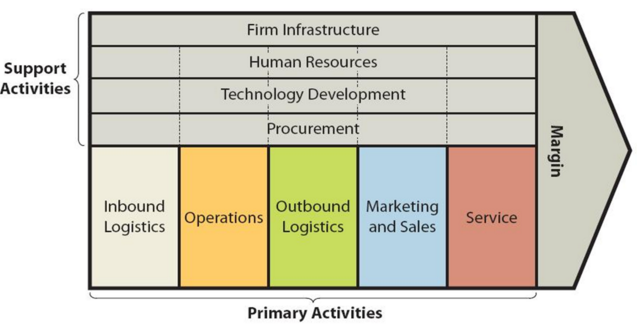
IKEA value-chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the global furniture retailer. “Each step in the manufacture of a product or the delivery of a service can be thought of as a link in a chain that adds value to the product or service. This concept of how business fulfils its mission and objectives is known as the value chain”[1]. Figure below illustrates the essence of IKEA value chain analysis. IKEA Value Chain Analysis IKEA Primary Activities IKEA Inbound logistics Inbound logistics for IKEA is associated with purchasing raw materials and ready items from about 1220 suppliers located in more than 55 countries worldwide.[2] The majority of IKEA products (89%) are sourced from external suppliers across the globe.[3] The world’s largest furniture retailer conducts purchasing via its 31 trading service offices in 26 countries. The top five purchasing countries for The Swedish furniture chain include China 20%, Poland 18%, Italy 8%, Germany 6% and Sweden 5%.[4] IKEA inbound logistics is a major source of value creation for the business. Specifically, the proximity of company’s 31 trading service offices to supplier locations helps to ensure that company can monitor production, test new ideas, negotiate prices and check quality of products and raw materials they are buying. Economies of scale are another factor that decreases the prices of inbound logistics for the furniture retailer. Moreover, flat pack Do-It-Yourself assembly principle for many IKEA products lowers the cost of packaging and makes inbound logistics easier to facilitate. The world’s largest furniture retailer maintains strategic relationships with its suppliers. The average length of supplier relationship is 11 years[5], with some suppliers working with IKEA for several decades. IKEA Operations IKEA operations are divided into three divisions – Franchise, Property and…
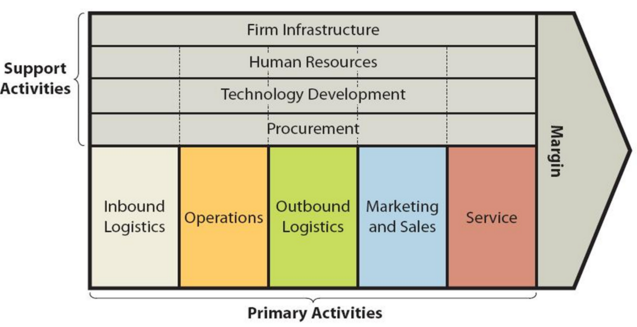
Value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The figure below illustrates the essence of McDonald’s value chain analysis. McDonald’s value chain analysis McDonald’s Primary Activities McDonald’s Inbound logistics McDonald’s inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials and using them to produce its burgers and other items in the menu. Raw materials for the fast food chain include meat, raw vegetables, ketchup, mayonnaise, napkins etc. Economies of scale are the main source of value creation in McDonald’s inbound logistics. The fast food giant has been pursuing backwards vertical integration strategy. This strategy involves companies to expand their roles and capabilities to complete tasks formally fulfilled by other companies in their supply chain. Specifically, McDonald’s “grow their own beef through contracted producers, process their own meat, create their own spices and mixes in factories that they contract, grow their own potatoes and other vegetable through contracted producers, transport their goods on their own.”[1] Backward vertical integration strategy allows the fast food chain to control the quality of their ingredients and reduce the costs of supply. McDonald’s Operations McDonald’s operates more than 40,000 company-owned and franchised restaurants. As of December 2021 in total 37,295 stores, or 93%, were franchised[2]. McDonald’s franchise restaurants have one of the following formats: conventional franchise, developmental license or affiliate.[3] Conventional franchising involves franchisees paying rent and royalties on the percentage of sales along with the payment of initial fees when opening a new restaurant. In this type of franchising, McDonald’s Corporation owns the land and building or secures a long-term lease for the restaurant location and the franchisee pays for equipment, signs, seating and décor.[4] Developmental license involves licensees providing capital for the entire business, including the real estate interest.[5] In developmental license…
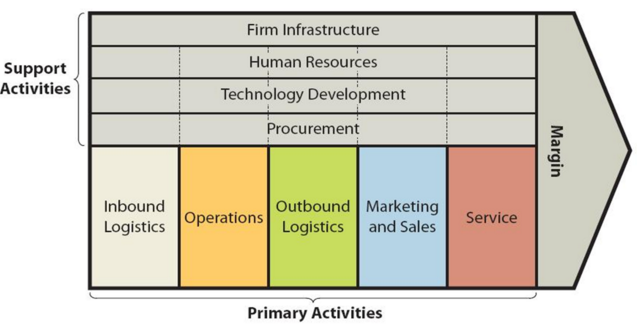
Value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of Amazon value chain analysis. Amazon Value chain analysis Amazon Primary Activities Amazon Inbound logistics Inbound logistics within Amazon value chain analysis involve receiving and storing raw materials to produce goods and services. Due to massive global scope of its operations the e-commerce giant maintains complex, but sophisticated inbound logistics operations. Generally, Amazon does not have long-term contracts or arrangements with its vendors to guarantee the availability of merchandise, particular payment terms, or the extension of credit limits. Fulfilment by Amazon (FBA) is the cornerstone of Amazon inbound logistics for company-owned retail business. Moreover, the economies of scale is an important source of value creation for Amazon inbound logistics. Sellers can also use FBA by stowing their inventory in Amazon fulfilment centres. In this case, Amazon assumes full responsibility for logistics, customer service, and product returns. If a customer orders an FBA item and an Amazon owned-inventory item, the company ships both items to the customer in one box, as a significant gain of efficiency. The use of FBA is an optional choice for sellers and this choice makes the products of third-party sellers eligible for Amazon Prime free two-day shipping, free shipping and other benefits. Amazon uses logistics beyond the point to serve Amazon Marketplace and starting from recently, the company has been offering logistics services to third parties. For example, Beijing Century Joyo Courier Services, an Amazon subsidiary registered with the U.S. government as an ocean shipping provider.[1] From this point of view, efficient logistics infrastructure also belongs to the list of Amazon competitive advantages. Amazon Operations Operations generally comprise the process of transforming raw materials into goods…
