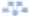Gap Inc. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis: A Highly Competitive Industry with Immense Buyer Bargaining Power
Gap Inc. Porter’s Five Forces analysis includes a critical analysis of five separate forces that shape the overall extent of competition in fashion, apparel and accessories industry. Developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1], five forces analysis remains as one of the most important strategic analytical tools for competitive analysis for more than three decades. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Porter’s Five Forces.
Figure 1 Gap Inc. Porter’s Five Forces
Rivalry among existing firms clothing and accessories industry is fierce. Gap Inc.’s major competitors include Abercrombie & Fitch Co., American Eagle Outfitters, Inc., Belk, Inc., Guess, Inc., J. C. Penney Company, Inc., J.Crew Group, Inc., Michael Kors Holdings Ltd, Urban Outfitters, Inc., Williams-Sonoma, Inc. and others.
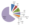
It is important to note that “despite being one of the bigger apparel players in the U.S., Gap Inc. holds less than 5% market share, which clearly indicates the diverse nature of the U.S. apparel industry. Higher shares are held by multi-brand retail chain Macy’s (9%) and general merchandise retailer Wal-Mart (over 7%). J.C. Penney (3.3%) and Target (5.4%) also hold a similar portion of the market, and American Eagle Outfitters, Aeropostale and Abercrombie & Fitch together account for just over 2% of total U.S. apparel sales.”[2] The figure 2 below illustrates a rough pattern of retail landscape in the US.
Figure 2 Apparel market share in the US
Bargaining power of Gap Inc. suppliers is low. The company purchases from about 1000 suppliers with factories in about 40 countries. Gap’s two largest vendors each accounted for only about 5 percent of the dollar amount of its total fiscal 2015 purchases[3]. Accordingly, Gap Inc.’s business is not dependent on any particular supplier and this fact increases its bargaining power in dealing with supplies.
Furthermore, for the majority of suppliers it is critically important to have business with Gap Inc. due to the high volume of its orders. Additional factors that contribute to the bargaining power of the apparel and accessories retailer in dealing with its suppliers include its ability to substitute suppliers and minimum supplier substitution costs in most cases.
Threat of new entrants into fashion, apparel and accessories industry is moderate. Access to distribution channels represents one of the most significant barriers for new market entrants, since it is difficult to find vacant places in attractive locations to open new stores. Moreover, major market players such as Gap, Macy’s and Zara derive tremendous benefits from the economies of scale and this opportunity is not available for new market entries, at least during the first few years of operations. The need for large capital requirements to set up the business and expected retaliation from the current market players are additional challenges to be faced by potential new market entrants…
Gap Inc. Report contains a full version of Gap Inc. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Value Chain Analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Gap Inc. Moreover, the report contains analysis of Gap Inc.’s marketing strategy, discusses leadership and organizational structure and addresses the issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Porter, M. (1979) “How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy” Harvard Business Review
[2] Forbes (2015) Available at: http://www.forbes.com/sites/greatspeculations/2015/07/15/gap-inc-is-gradually-losing-its-share-in-the-u-s-apparel-market-to-fast-fashion-counterparts/#7469a03e7817
[3] Annual Report (2015) GAP Inc.