Hilton Value Chain Analysis
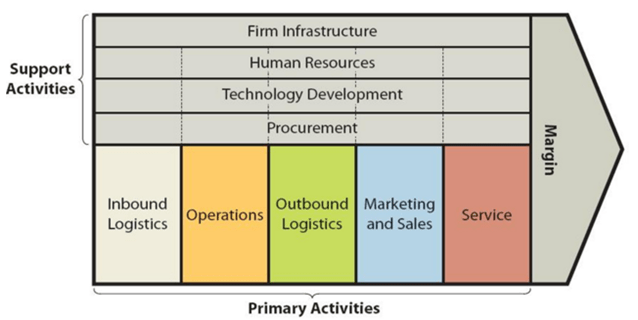
Hilton value chain analysis identifies business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The framework of value chain analysis divides business activities into two categories: primary and support activities. The figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis:
Hilton Value Chain Analysis
Primary Activities
Inbound logistics
Hilton inbound logistics represents a highly sophisticated system that ensures smooth operations in 572 hotels and resorts in 85 countries around the world.[1] Hilton’s “procurement group aggregates buying into national contracts for its various brands, and enables local providers where it makes sense to do so”[2] Hilton’s supply chain management and inbound logistics is unique in a way that the company makes deals directly with suppliers, then negotiates markups with the distributors that handle warehousing and delivery. This practice is an important source of value for the business since it enables the control of the whole supply chain.
Operations
Hilton Worldwide operates its business via the following three segments:
- Ownership segment. This segment consists of 146 hotels with 59,463 rooms which are owned or leased by Hilton Worldwide.
- Management and franchise segment consists of 4,419 hotels with 691,887 rooms. These are owned by third parties and managed by Hilton Worldwide. The company also licences its brand to franchises. As of December 2015, Hilton Worldwide franchised 3,875 hotels with 533,039 rooms.
- Timeshare segment consists of 45 properties comprising 7,152 units. This segment is engaged in marketing and selling timeshare intervals, operating timeshare resorts and timeshare membership clubs and providing consumer financing.
Hilton operations are divided into four geographical segments:
- Americas
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
- Asia Pacific
The main sources of value in Hilton’s business operations include the highest level of standard of service, a high level of service personalization and integration of information and communication technologies into the various aspects of service provision.
Outbound logistics
Generally, outbound logistics refer to activities required to deliver the finished products to the customer. Hilton outbound logistics is associated with a set of competitive advantages such as service provision of a highest standards, the provision of transportation services to customers moving out of the hotel and others.
Marketing and sales
Hilton marketing and sales practices rely on the application of various components of the marketing communication mix in an integrated manner. Hilton Worldwide employs more than 700 sales professional around the globe[3] Hilton Worldwide sales team is assigned with the tasks of soliciting bookings from business and leisure travelers, travel agencies, and conventions. In 2015, the company earned the total revenues of about USD 11.2 billion an increase of about 7 per cent compared to the previous year. [4]
Hilton HHonors program adds value to the company’s marketing and sales primary operations to a great extent. The program encourages the customers “to return to the brand time and time again since they get points which lead to free room nights as well as perks during their stay including free wifi and room upgrade.”[5] Currently, there are more than 50 million Hilton HHonors members worldwide.[6]
Service
A high quality of service is one of the main sources of Hilton competitive advantages. Hilton customer service team members are fluent in more than 10 languages. The customer services can be reached by Twitter and the social media team address customer travel issues 24/7.[7]
Hilton Reservations & Customer Care (HRCC) was awarded the 2009 Stevie’s Award for Best Customer Service Team and Best Customer Service Complaints Team. In 2010, they won the People’s Choice Stevie’s Award for Favourite Customer Service.[8]
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains a detailed discussion of Hilton Value Chain Analysis. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces and McKinsey 7S Model on Hilton. Moreover, the report contains analysis of Hilton marketing strategy, leadership and organizational structure and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Annual Report (2015) Hilton Worldwide
[2] Terry, L. (2007) “Hospitality Logistics: Supply Chains Made to Order” Inbound Logistics, Available at: http://www.inboundlogistics.com/cms/article/hospitality-logistics-supply-chains-made-to-order/
[3]Hilton Worldwide (2016) Available at: http://hiltonworldwide.com/development/performance-advantage/hilton-worldwide-sales/
[4] Annual Report (2015) Hilton Worldwide
[5] Maddux, S. (2015) “Hilton Worldwide: Creating Value for Hotel Owners, Customers and Investors” Harvard Business School, Available at: https://rctom.hbs.org/submission/hilton-worldwide-creating-value-for-hotel-owners-customers-and-investors/
[6]Annual Report (2015) Hilton Worldwide
[7]Annual Report (2015) Hilton Worldwide
[8] Hilton Worldwide (2016) Available at: http://hiltonworldwide.com/development/performance-advantage/reservations-customer-care/