IKEA Value Chain Analysis
IKEA value-chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the global furniture retailer. “Each step in the manufacture of a product or the delivery of a service can be thought of as a link in a chain that adds value to the product or service. This concept of how business fulfils its mission and objectives is known as the value chain”[1]. Figure below illustrates the essence of IKEA value chain analysis.
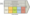
IKEA Value Chain Analysis
IKEA Primary Activities
IKEA Inbound logistics
Inbound logistics for IKEA is associated with purchasing raw materials and ready items from about 1220 suppliers located in more than 55 countries worldwide.[2] The majority of IKEA products (89%) are sourced from external suppliers across the globe.[3] The world’s largest furniture retailer conducts purchasing via its 31 trading service offices in 26 countries. The top five purchasing countries for The Swedish furniture chain include China 20%, Poland 18%, Italy 8%, Germany 6% and Sweden 5%.[4]
IKEA inbound logistics is a major source of value creation for the business. Specifically, the proximity of company’s 31 trading service offices to supplier locations helps to ensure that company can monitor production, test new ideas, negotiate prices and check quality of products and raw materials they are buying. Economies of scale are another factor that decreases the prices of inbound logistics for the furniture retailer. Moreover, flat pack Do-It-Yourself assembly principle for many IKEA products lowers the cost of packaging and makes inbound logistics easier to facilitate. The world’s largest furniture retailer maintains strategic relationships with its suppliers. The average length of supplier relationship is 11 years[5], with some suppliers working with IKEA for several decades.
IKEA Operations
IKEA operations are divided into three divisions – Franchise, Property and Finance divisions, with Franchise Division being the core of the business. IKEA follows de-centralization business strategy in running its global operations. According to this strategy, regional managers are granted decision-making autonomy taking into account unique aspects of their markets, local culture, patterns of local consumer behaviour and other region-specific factors.
The Group owns 40 IKEA furniture production units, mostly located in Europe, as well as two factories that produce furniture components (screws, plugs, etc.).[6] IKEA operates its stores under franchise agreements in 30 countries worldwide. There are 11 franchisees operating IKEA stores in more than 50 markets. Ingka Group, formerly IKEA Group, is the largest IKEA franchisee and it operates 367 IKEA stores in 30 markets employing 158,500 people. [7]
The majority of IKEA products are developed by IKEA Industry, the largest producer of wooden furniture in the world. IKEA Industry consists of 40 production units in 10 countries: China, France, Hungary, Lithuania, Poland, Portugal, Russia, Slovakia, Sweden, and the USA. [8]
The major source of value in IKEA operations relates to cost benefits. Specifically, by locating the massive chunk of its manufacturing units in Eastern Europe and China, the company saves on the cost of human resources to a significant extent. Moreover, the home improvement and furnishing chain uses the latest and sophisticated technologies in manufacturing processes with the positive implications on operational efficiency.
IKEA Outbound Logistics
IKEA inbound logistics involve warehousing and distribution of ready products from 422 stores in 50 markets to end-users. The world’s largest furniture retailer operates 28 distribution centres and 11 customer distribution centres in 16 countries worldwide. Customers are responsible for costs associated with the transportation of goods purchased from IKEA stores. The company offers two types of delivery services. Parcel delivery is a service to deliver small items weighting up to 25 kg and the company charges around USD 12 depending on the location of the specific store.
Truck delivery, on the other hand, is made for purchases exceeding 25 kg and IKEA charges starting from approximately USD 50 for truck delivery. The delivery for goods purchased online is done free of charge. Delivery of goods to customers directly without any intermediaries can be specified as one of the main sources of value in IKEA outbound logistics. Moreover, sources of value creation in outbound logistics for the furniture retailer include using flat packs to save on space, transporting goods by rail and sea instead of vehicles whenever possible and applying fuel-saving techniques in transportation.
IKEA Marketing and Sales
The home improvement and furnishing chain uses print and media advertising, sales promotion, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing techniques in an integrated manner. IKEA is a multichannel retailer and integrates selling through stores, catalogues, website and app. In the past, the furniture giant used to rely in its catalogues extensively for marketing and sales and more than 200 million catalogues are were printed each year globally. Starting from 2018, the company has changed its focus from rooms to product innovation from marketing point of view. However, in 2020 the company announced that it will stop producing catalogues starting from 2022 due to the decline of demand.
IKEA Service
Customer service as one of the primary activities in the value chain is addressed by IKEA via a standard set of techniques and practices such as the provision of online and telephone customer services, offering refunds and exchanges of goods whenever relevant and encouraging customers to provide feedback. If customers find out that some parts of assembly furniture are missing, they don’t have to go back to IKEA store. Customers can find out the missing part number (listed in the assembly instructions), call their local store to ask for replacements and the replacement will be mailed to them.
At the same time, IKEA is not famous for the provision of a superior customer services. Such a situation may have resulted from the aggressive pursuit of cost-cutting initiatives according to cost leadership business strategy. An open letter addressed to then IKEA CEO Peter Agnefjäll titled ‘Dear IKEA: Your Customer Service Is Terrible’ has been written by best-selling author and keynote speaker Bernard Marr on March 2014.
The letter sheds a light into a range of customer services issues the author had to deal with when purchasing white BIRKELAND bed for his eight-year old daughter. These issues include late delivery, the delivery of wrong parts, failure to collect parts that do not belong to the purchase and communication issues. The open letter generated debates and discussions in the social media, thus causing a substantial damage to the brand image.
IKEA Group Report contains a full version of IKEA value chain analysis. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on IKEA. Moreover, the report contains analyses of IKEA leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of IKEA marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1]Needles, B.E., Powers, M. & Crosson, S.V. (2007) Principles of Accounting, Cengage Learning, p.836
[2] Facts & Figures (2019) IKEA, Available at: https://www.ikea.com/ms/en_AU/about_ikea/facts_and_figures/
[3] Inter IKEA Holding B.V. Annual report FY21
[4] Facts & Figures (2019) IKEA, Available at: https://www.ikea.com/ms/en_AU/about_ikea/facts_and_figures/
[5] Let’s grow together: become an IKEA supplier (2022) IKEA, Available at: https://about.ikea.com/en/work-with-us/for-suppliers
[6] Inter IKEA Holding B.V. Annual report FY21
[7] Sustainability Report FY 2018 (2019) IKEA
[8] Sustainability Report FY 2018 (2019) IKEA

