Samsung Corporate Social Responsibility
Samsung Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programs and initiatives are facilitated through the Sustainability Management Council, which consists of 14 related departments that handle issues from 10 different areas, including society and the environment.[1]
Samsung Global Code of Conduct is based on the following principles:
- Compliance with laws and ethical standards
- Maintenance of clean organizational structure
- Respecting customers, shareholders and employees
- Caring for the environment, health and safety
- Being socially responsible corporate citizen
CSR aspect of the business is managed by Samsung CSR Committee. The company releases Supplier Responsibility Progress Report annually and it includes the details of CSR programs and initiatives engaged by the company. Samsung Electronics addresses CSR aspects of the business in four directions: social contributions, green management, health and safety and sharing growth.
Samsung Supporting Local Communities
- Samsung Tech Institute encourages independence and self-reliance among young adults via systematic vocational education. The initiative had 39,659 beneficiaries by the end of 2015.
- Samsung SMART School addresses an important gap in the global education by improving educational environment for students residing in disadvantaged areas. In 2015 alone 224,753 students attended Samsung SMART School.
- Samsung Solve for Tomorrow is a program that aims to tackle important social issues. The program engages students and non-profit organizations to identify the most pressing social problems and to find and to implement solutions to these problems
- Samsung Care Drive facilitates a range of healthcare programs in order to deal with the help of technology. As of 2014, the company had 30 active programs primarily in China, Russia, and several countries in Africa.
- Samsung Nanum Village aims to target the roots of poverty via providing an effective infrastructure to socially disadvantaged segments of the population. Within the scope of this program, partnerships are formed with national and local governments to provide an extensive support for education infrastructure, medical facilities, clean water and the construction of community centres.
- An average number of Samsung employee volunteering hours amounted to 11.3 hours during 2014
- In Korea Samsung opened the sixth House for Hope in 2015 to improve the conditions of local community child centres
Samsung Educating and Empowering Workers
- Employee benefits provided in Korea and abroad in 2015 totalled to KRW 3.853 billion
- Training time per employee in 2015 amounted to 78 hours
- Samsung Career Consulting Centre has been used by 5,500 people
- Samsung conducts its STaR (Samsung Talent Review) Sessions in association with its EDP (Expertise Development Process) annually. It is a talent nurturing process that supports employees in designing an individual career path and establishing a clear vision with their supervisor. In Korea alone 2000 employees undergo STAR sessions annually.
Labour and Human Rights at Samsung
- The company conducted 235 supplier inspections for child labour prevention in China in 2015
- In Malaysia Guidelines for Migrant Workers in cooperation with Business for Social Responsibility (BSR) to help eradicate forced labour
Employee Health and Safety at Samsung
- Building health and safety management systems is a matter of priority for Samsung. The company complies with OHSAS 18001 standard for occupational health and safety management systems across its workplaces around the globe.
- Samsung attempts to operate its workplaces in safe conditions at all times. A continuous monitoring and improvement has been instituted and accordingly, the company organizes occasional emergency scenarios for the occasions of harmful chemical substance spills, fires, explosions and natural disasters.
- Samsung supports employee health and safety by constructing ergonomic applications in the working environment and prohibiting business trips to regions with high risks for infectious diseases such as Ebola and MERS
Samsung and Gender Equality and Minorities
- Disabled employment rate by the multinational electronics company amounted to 1.6%, 1.68% and 1.7% in 2013, 2014 and 2015 respectively
- The table below illustrates changes in ratio of female employees by job function during the past several years.
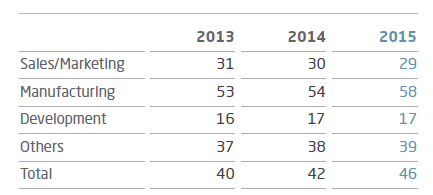
Ratio of female employees by job function[1]
Waste Reduction and Recycling by Samsung
- Samsung collected a total of 2.26 million tons of waste products from 2009 to 2015, and aims to collect 3.8 million tons (cumulative) of waste products by 2020.
- In 2015, the company applied a total of 34,322 tons of recycled plastics (6.3 percent of total plastic use) to monitors, printers, washing machines, refrigerators, vacuum cleaners, and earphone cases
Carbon Emissions by Samsung
- Within the scope of Eco-Management 2020 and Planet First initiatives introduced by Samsung, greenhouse emissions were reduced by 70% and accumulated 250 million tons of greenhouse gas reduction was achieved since 2008.
- Green communications initiative that aims to share the value of Samsung Green Management implemented various open projects around the globe. These include environmental educational courses and events and support of employee interests to participate to such events.
- The company operates green workplaces by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and usage water, as well as, increasing waste recycling in its offices.
- Samsung achieved cumulative 156 million tons green house gas (GHG) reduction at product use stage during the period 2009 – 2015.
Water Consumption by Samsung
The flow of water resources by Samsung is illustrated in figure below.
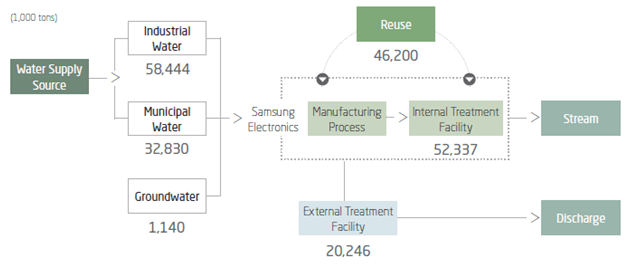
Flow of water resources at Samsung Electronics[3]
Samsung and Sustainable Sourcing
- Samsung maintains Supplier Consulting Team that comprises a roster of 100 of directors and executives in the fields of manufacturing, product, development and quality control.
- The company operates a Shared Growth Fund of KRW 1 trillion to help improve business for suppliers that find it difficult to secure funding.
- Seven Shared Growth Implementation Plan introduced in 2010 is an attempt to develop a win-win partnership with suppliers. Win-Win Partnership Academy instituted by Samsung aims to assist its suppliers to improve their businesses.
Samsung other CSR Initiatives and Charitable Donations
- Developing green technology and products is adapted as one of the core principles by the company in terms of reducing its environmental impact. Samsung has received certifications for an accumulated 3,027 product models as of the end of 2014, from 11 nations including Korea, the US, China and European countries.
Samsung Group Report contains a full analysis of Samsung corporate social responsibility including Samsung CSR issues. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Samsung. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Samsung leadership, business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Samsung marketing strategy and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
[1] Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics
[2] Source: Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics
[3] Source: Samsung Sustainability Report (2016) Samsung Electronics

