
Tesla marketing strategy has been dubbed as USD0 (zero dollar) marketing strategy[1] largely for its avoidance of paid advertising. Instead, the electric automaker focuses on social media marketing. CEO Elon Musk boasted that “Tesla shells out virtually nothing on advertising and endorsements, and relies heavily on word of mouth.”[2] Tesla 7ps of marketing focuses on product and place elements of the marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other elements. Moreover, product and place elements of the marketing mix have been adapted as main sources of Tesla competitive advantages. Specifically, Tesla produces fully electric cars that are fast and attractively designed. Moreover, the electric automaker does not deal with car dealerships and distributors and sells its vehicles directly to end-users. Tesla target market segment represent individuals and households who are not indifferent towards environmental issues and negative environmental implications of CO2 emissions. Tesla effectively appeals to the emotional needs of the target customer segment to feel themselves as environmentally responsible via purchasing electric cars and using solar panels. Tesla marketing strategy is based on the following principles: 1. Marketing through customer experience. Telsa referral program effectively enhances customer experience by offering USD 1000,00 credit and additional accessories and perks. These include Solar Roof, 21” Arachnid Wheels for Model S or 22” Turbine Wheels for Model X and VIP invitation for Tesla Unveiling events, among others.[3] 2. Effective use of social media. CEO Elon Musk has evolved as the face of Tesla and his direct engagement with customers via social media attracts media attention with generally positive implications for the brand. Musk uses his social media accounts as efficient tools for Tesla marketing strategy. 3. Cross-promotional opportunities. Tesla CEO Elon Musk also owns and runs other businesses, namely, SpaceX and Solar City. These companies benefit from unique cross-promotional opportunities. For example, Space X launched…
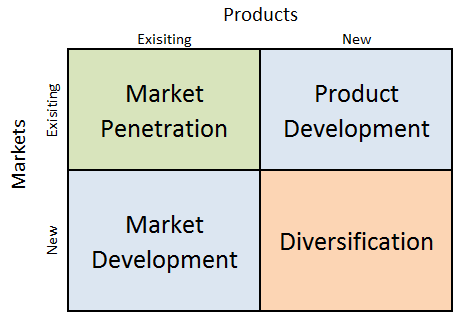
Tesla Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that can be used by the alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer to make strategic decisions. According to Ansoff Matrix, there are four different strategy options available for businesses: market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Tesla Ansoff Growth Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Tesla uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. This strategy involves selling existing products to existing markets. Tesla uses market penetration strategy extensively. The company is focused on selling its Model S, Model X and Model 3 electric vehicles, Powerwall 2 and Powerpack 2 energy storage products, as well as, solar panels, inverters, racking, electrical hardware and monitoring devices in the US and 35 other countries[1]. 2. Product development. This strategy implies the development of new products to sell to existing markets. Tesla engages in new product development infrequently. This is mainly due to overly high cost of new product development in electric vehicles and power storage sectors. In Battery Day event in September 2020, CEO Elon Musk announced that the electric car maker had plans to enter into mining business. The company acquired the rights to a 10,000-acre plot in Nevada. In this site it plans to extract the metal using simple table salt, and would build a lithium refinery to supply a new factory in Texas. While the initial plan for Tesla is to use lithium for its own needs as raw material, the electric automaker can start selling this expensive material to others as well. 3. Market development. Market development strategy involves finding new markets for existing products. Tesla is evaluating a number of new markets to enter, India being in the shortlist. CEO Elon Musk “indicated it was the company’s Indian-born chief financial officer, Deepak Ahuja, who was…
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Tesla PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the long-term growth prospects of the alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer. There is a wide range of political factors that can potentially affect automobile manufacturers. Specifically, political factors for Tesla include freedom of press, corruption and bureaucracy in local markets and trade unions activities. Moreover, home market lobbying practices by governments and trade controls also belong to the list of political factors that can affect Tesla. Political Factors in Tesla PESTEL Analysis Political stability Political stability is one of the most important political factors affecting the company. Tesla uses cobalt extensively as a raw material to build its Model S, Model X, Model 3 vehicles. About 58% of the world’s cobalt production comes from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DCR).[1] According to a report by Amnesty International, cobalt rush has increased the cases of conflicts, corruption and child labour in Congo[2]. Accordingly, it can be argued that political instability and warfare in Congo can create supply chain risk for Tesla in relation to cobalt, an important component for electric vehicles. Government incentives for electric vehicles Government incentives to promote vehicles run by alternative fuel due to negative environmental implications of CO2 emissions is a noteworthy political factor for Tesla. The impact of this factor is positive and so far Tesla was able to benefit to a maximum extent. For example, US government offers USD 7500.00 tax credits to every buyer of new electric vehicles as an incentive, but there is a cap of 200,000 deliveries of electric vehicles in the US for each automaker. Tesla was the first manufacturer to hit the threshold back in 2018. Thanks to the new…
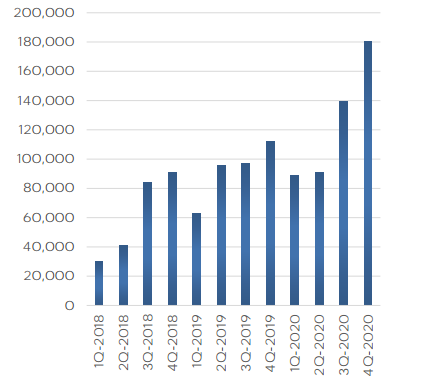
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following Table 1 illustrates Tesla SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. First mover advantage 2. Increasing numbers of vehicles sales 3. Expertise in innovation 4. Brand equity Weaknesses 1. Expensive price tags of Tesla vehicles 2. Huge amount of debt (USD 11.69 billion) 3. History of over-promising and under-delivering the quantity of vehicles 4. Limited global presence Opportunities 1. Development of lower priced models 2. Strengthening of Tesla ecosystem 3. Shifts in consumer environmental attitudes 4. More government incentives Threats 1. Manufacturing delays risks 2. Crashes and fires in Tesla cars 3. Threat of new competition 4. Decrease in the price of oil Table 1 Tesla SWOT analysis Strengths in Tesla SWOT Analysis 1. Tesla benefits from the first mover advantage in alternative fuel vehicles manufacturing to a considerable extent. The company was established in 2003 with the mission “to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy”, right after auto giant General Motors recalled and destroyed its EV1 electric cars.[1] Today, Tesla is an undisputed global market leader in electric vehicles segment. It can be argued that being the first global company exclusively focusing on electric vehicles, Tesla is in a good position to achieve a long-term growth. 2. The numbers of electric vehicles sold by Tesla has been increasing. As illustrated in Figure 1 below, the alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer delivered 180,000 vehicles in the last quarter of 2020. Increasing numbers of vehicles sales is strategically important for the company in a way that it allows benefiting from economies of scale and consequently, the alternative fuel vehicles manufacturer can become more profitable. Figure 1 The numbers of Tesla vehicles delivered worldwide[2] 3. Innovation is placed at the core of Tesla business strategy and…

Tesla organizational culture integrates the following five key elements: 1. Ambitious innovation. Tesla has been founded right after auto giant General Motors recalled and destroyed its EV1 electric cars.[1] Starting a business in a segment where large and experienced players such as GE have failed is a clear indication of abundant ambitions of founders including Elon Must. Founders have adapted product and process innovation as a strategic tool to realize their ambitions in practice. Ambitious innovation has been deeply ingrained in Tesla organizational culture. 2. Adherence to ‘First Principles’ method. Elon Musk insists that employees use First Principles method, also known as reasoning from first principles in dealing with problems. It has been noted that “first principles thinking requires you to dig deeper and deeper until you are left with only the foundational truths of a situation”[2]. Arguably, process and product innovations at Tesla can be credited to the successful application of first principles to a significant extent. 3. Doing things differently. Tesla corporate culture encourages employees at all levels to experiment with different ways of doing business. The electric automaker is well known for challenging the status quo of conducting business. Especially, the company’s marketing and HR practices are fundamentally different from other global auto manufacturers. 4. Lack of bureaucracy. Day-to-day operations and communications in the company are not bounded by strict levels of management and bureaucracy. An email from CEO Elon Musk sent to employees a few years ago stressed that “anyone at Tesla can and should email/talk to anyone else according to what they think is the fastest way to solve a problem for the benefit of the whole company. You can talk to your manager’s manager without his permission, you can talk directly to a VP in another dept, you can talk to me, you can talk…
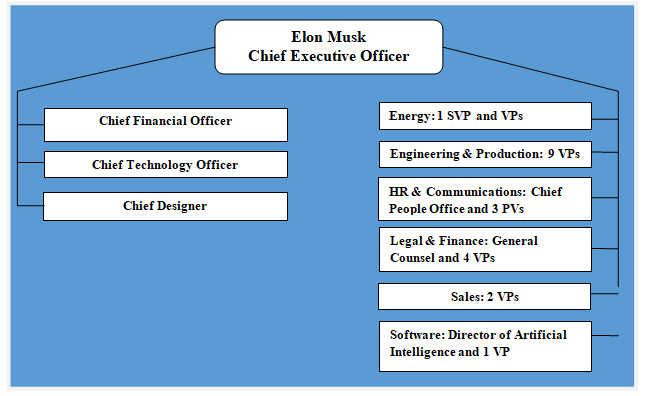
Tesla is a unique company in many ways and this uniqueness also extends to its organizational culture. Tesla organizational structure integrates the following: 1. Unique organizational structure. “Tesla, unlike most companies its size, doesn’t have any known management structure. There’s no organizational chart or public list of senior leaders.”[1] Nevertheless, Tesla organizational structure can be characterized as divisional. 2. Tesla CEO Elon Musk has issues with delegation. Workaholic and micromanagement nature of Elon Musk, as well as his sleep deprivation work habits have become well-known. Famous author and businesswoman Arianna Huffington even wrote an open letter to Musk urging him to get more sleep and learn to delegate. Musk’s issues with delegation has implications on Tesla corporate structure in a way that he has more people directly reporting to him than any other CEO in auto industry. 3. Divisional and flexible structure. Although it is difficult to list Tesla organizational structure under a specific rigid category due to its unique nature, the structure can be characterised as divisional and flexible. As it is illustrated in figure below, Tesla organizational structure comprises a number of divisions such as energy, engineering and production, HR and communications, legal and finance, sales and software. Each division is led by several vice presidents, except software division, which is led by one vice president and Director of Artificial Intelligence. Tesla Organizational Structure Tesla benefits from divisional organizational structure through less bureaucracy compared to many other companies of similar sizes. Divisional organizational structure also helps the electric automaker to increase the speed of communication among different layers of management with positive implications on decision making and flexibility of the business. Tesla Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Tesla organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as…

Tesla leadership is frequently a topic of heated debates. Tesla CEO and co-founder Elon Musk is a controversial figure. At the same time he is admired worldwide for his entrepreneurial and leadership skills. Elon Musk is a successful serial entrepreneur with a reputation as a creative genius who founded PayPal, Space X and the Boring Company. Each of these companies has become highly successful in its respective field in the global scale. Musk also has been a driving force behind the rapid development of Tesla, assuming the roles of CEO and Product Architect with the company. He was considered as an effective visionary leader credited with the successful launch of Tesla Roadster in 2018, the first electric car to use lithium-ion battery cells. Later, Musk oversaw the launch Model S, Model X and Model 3 electric vehicles and acquisition of Solar City Corp. for USD 2,6 billion in stock. The company’s board of directors comprises 10 people, including experienced and accomplished business leaders such as Oracle founder Larry Ellison and former 21st Century Fox CEO James Murdoch. It can be argued that one of the major issues with Tesla leadership is micro-management by CEO Musk and a wide range of roles within the company Musk attempts to perform at the same time. In an interview in August 2018, Elon Musk complained about exhaustion taking a toll on his physical health, working up to 120 hours a week and about times he has to spend three or four days at the factory without going outside.[1] Tesla Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Tesla leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Tesla. Moreover, the report contains analyses of…

Tesla business strategy can be broadly classified as product differentiation. Accordingly, the electric automaker differentiates its vehicles on the basis of sustainability, performance and design. Tesla business plan announced by Elon Musk in company’s website blog in 2006 was the following: Build sports car Use that money to build an affordable car Use that money to build an even more affordable car While doing above, also provide zero emission electric power generation options Tesla mission statement is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Tesla business strategy aims to accomplish this mission via the following three key principles: 1. Focus on electric cars. Tesla was founded on the belief that “people didn’t need to compromise to drive electric – that electric vehicles can be better, quicker and more fun to drive than gasoline cars.”[1] Accordingly, the company produced its Roadster, Model S, Model X and Model 3 fully electric cars that quickly became successful among the target customer segment attracting billions of dollars of advance payments. Tesla “aims to disrupt the automotive industry by creating many innovative pieces that fit together.”[2] 2. Ownership of distribution. Tesla does not work with dealers and distributors. Instead, the electric automaker is engaged in direct sales through its website. Moreover, Tesla has company-operated stores and galleries in shopping centres and other places popular among the target customer segment in the US and 35 other countries and regions worldwide. 3. Low cost of ownership. Tesla cars run on electricity, which is considerably cheaper than oil and gas. Moreover, owners of electric vehicles are offered various tax breaks and incentives from local governments in some areas. Tesla has a calculator on its website to tell customers exactly how much they save. Low cost of ownership is one of the main sources of Tesla competitive advantage. 4. Unconventional…
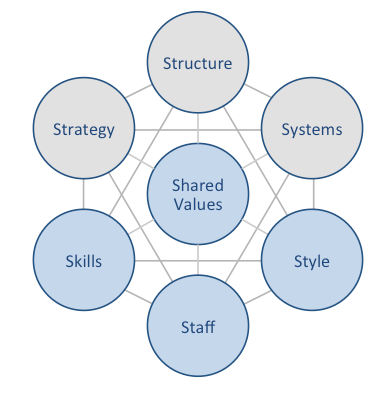
Apple McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to this model, strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Apple McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Apple McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Apple McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Apple pursues differentiation business strategy with a particular focus on the design and advanced features and capabilities of products. The company aims to benefit from the first mover advantage to a maximum extent as it was the case with introduction of iPod, the first device of its kind that stored thousands of songs with simple shuffle capabilities through songs and the development of Macintosh, the first computer to use a graphical user interface. Accordingly, Apple products and services are generally more expensive compared to the competition. Moreover, Apple business strategy involves the creation of a sort of closed ecosystem, where it’s various devices and software sync easily and work well with each other. Advantages the company gains from this strategy include high switching costs for customers and this provides the opportunities to leverage relationships with existing customers to offer other products and services. Furthermore, the multinational technology company has developed a strategy to reduce dependence of the business on the sale of iPhones. This strategy involves putting greater emphasis on services divisions of the business and more investments on research and development of new products and services. The iPhone maker has also specified…

Grainger CSR (corporate social responsibility) programs and initiatives aim to address the issues of social awareness, environmental factors and ethical labour practices while promoting a greener, more culturally conscious attitude to both peers and customers. Grainger CSR Advisory Council has the mission of providing strategic awareness and encouraging transparency. Moreover, the global industrial supply company has CSR Working Group that leads programs to promote CSR goals. The company began using the Global Reporting Initiative’s Sustainability Reporting Standards in 2016 and, since 2017, has been a member of the Dow Jones Sustainability Index.[1] The B2B distributor offers more than 100,000 environmentally friendly products that help customers reduce energy consumption, conserve water, reduce waste and improve indoor air quality. [2] In 2018 the company was included in the top 10 placement in Barron’s “List of 100 Most Sustainable U.S. Companies” for the second time. Grainger Supporting Local Communities Hundreds of Grainger employees volunteered 8500 hours in local communities throughout the US in 2018 Members of Grainger workforce also help communities devastated by natural disasters worldwide In 2018, the global industrial supply company donated more than USD120,000 worth of products to Team Rubicon, a veteran-led group that helps communities worldwide get back on their feet after disasters. Grainger Educating and Empowering Workers All employees have completed Business Conduct Guidelines Training In 2017 the company provided 154 Grainger Tools for Tomorrow scholarships to employees in 85 participating colleges Grainger invested more than USD 4,5 million in employee education and development since 2006 Employee Health and Safety at Grainger Lost time incident rate per 100 employees decreased from 0,4 in 2017 to 0,3 in 2018 Total recordable incident rate per 100 employees totalled to 1,4 in 2017 and 2018 Grainger and Gender Equality and Minorities In total 38% of all workforce in…
