
Literature review has shed a light upon essential qualities for individuals holding leadership positions in organisations. Having a clear vision and the ability of articulating it in an efficient manner appears as one of the most important leadership skills in the majority of sources addressed during the preliminary literature review. According to Wart (2008) effective leaders are able to formulate motivating vision and create a situation where the vision is shared by all employees within the organisation. Communication skills are also crucially important to be possessed by organisational leaders (Gallos, 2008, Bertocci and Bertocci, 2009). Gallos (2008) explains the importance of communication skills for organisational leaders by referring to the fact that leaders need to communicate with different organisational stakeholders in a daily basis, and each category of these stakeholders pursue varying aims and objectives. According to Stanfield (2009) and Bertocci and Bertocci (2009) decisiveness marks important trait for organisational leaders. When discussing this specific leadership trait Stanfield (2009) refers to The Great Man leadership theory, and argues that individuals born with leadership skills are tend to be more decisive than individuals who have acquired their leadership skills on the course of their lives. However, Stanfield (2009) does not offer any evidences based on empirical studies to justify this viewpoint. Similarly, self-confidence has been viewed by Goldsmith et al. (2010) and Gold et al. (2010) as another important leadership trait. Goldsmith et al. (2010) conclude that the value of self-confidence as a leadership trait increases in times of crises when leaders need to be able to take decisions while a wide range of factors remain uncertain. In their analysis of an alternative leadership quality, integrity, Gold et al. (2010) convincingly argue that the lack of integrity associated with any organisational leader is difficult to conceal in modern times due to…

According to the report published by the Chinese Ministry of Health (2002), it is said that the provision of health care services in the country is based on three-tiered system. While in rural areas the village health stations, town’s central hospitals and county hospitals form the three tiers, in urban areas the three tiers consist of neighbourhood health clinics, district hospitals and municipal hospitals. Dib et al (2009) note that this three-tiered system is aimed to ensure the efficient and effective provision of health care services while creating trusts and closer relationship between patients and doctors. As a first point of contact for patients, the health institutions at the lower level of the tier are designed to provide prevention and primary health care services. In practice, the private clinics account for majority of these low-level health instructions as they provide primary care services, health check-ups and cure minor diseases. On the other hand, county and municipal hospitals at the upper level of three-tiered system provide impatient, outpatient and emergence care services to the patients referred from lower level health institutions and hospitals (Chen Xiaohong, 2007). However, Yu Guangjun et al (2007) argue that this vertical structured three-tiered system itself is the one of the key reasons behind the failure of the Chinese health care system. The difficulty in getting transferred from low-level health institutions and obtaining access from hospitals at the top level of hierarchy due to long-waiting lists for registration and treatment, unnecessary long bureaucratic processes pinpoint the difficulties faced by patients, particularly in rural areas. Moreover, given the huge size of country’s population, the author argues that lack of trained doctors and health care professionals, shortage of medical equipments and facilities further diminish the ability of hospitals and other health institutors to receive and treat the patients. On…

As the oldest living civilization, history of the Chinese medicine goes back to nearly two thousand years. The methods and theories of the Chinese medicine considered as one of the oldest in the history of medicine and they have been practiced and developed further over the centuries. However, as many scholars note, China did not have organized and centralized health care network system until middle of the 20th century. The health care services were mainly provided by small, private clinics, local, individual healers as well as some religious or charity institutions, while big central health care station, which could qualify as a hospital, mainly cared after royal family and served the needs high-ranking officials and military personnel. This highlights the fact that private clinics and practitioner had played significant role in the history and development of the Chinese health care system. The earliest contemporary hospitals began to appear in China from 18th century in the form of missionary hospitals run by western churches. According to the statistics cited by Meng Qingyue et al (2000), prior to the formation of Chinese Communists state in 1949, there were around 768 hospitals providing health care services in the country. While only 248 of them were government-funded, remaining 520 were private hospitals indicating the private sector dominated the provision of health care services throughout the history of Chinese health care system. However, following the arrival of socialism and foundation of communist state in 1949, the role of private sector in the Chinese health care has diminished significantly within very short period of time. Ministry of health, which was set up by the government as a responsible body for overseeing the provision of health care services and running of country’s health care network, soon began transferring private hospitals into public ones. The Cultural Revolution, which…

Six sigma is “business management strategy used by many different industries in an effort to improve the quality of products or services produced by the business through the removal of defects and errors” (Business Dictionary, 2014, online). The primary commercial objectives of Six Sigma programs is associated with application of strategy based on measurements in order to improve wide range of processes and sub-processes with positive implications on quality of products and services. Application of Six Sigma philosophy is not exclusive to manufacturing processes, and the framework can be applied to a wide range of organisational practices and processes such as IT, administration, quality assurance, design, purchasing etc. Some of the leading companies operating diverse sectors such as General Electric, Motorola, Pepsico and even Amazon.com have been able to reduce the levels of operational costs and achieve greater levels of customer satisfaction through successful implementation of Six Sigma principles. Six Sigma philosophy integrates the principles of strategic planning, benchmarking, supply-chain management, organisational learning into a single approach in a synergistic manner, thus successful application of Six Sigma can benefit from advantages associated with each of these individual management principles. Along with its numerous advantages discussed above Six Sigma has certain disadvantages that include necessity for employees to undergo formal Six Sigma training programs before implementation of its principles. Moreover, positive implications of Six Sigma programs may not be evident in short-term perspective, and period of time of at least several months is required before Six Sigma programs make positive contribution to the levels of revenues after their implementation. Nevertheless, substantial advantages of Six Sigma outweigh its few disadvantages, and therefore application of Six Sigma in an appropriate manner makes a good business sense. DMAIC abbreviation stands for define, measure, analyse, improve and control, and each of these words represent consequent…

Baldwin and Ford’s Transfer of Training Model (1988) is based on the idea that the transfer of learning depends on training inputs that include trainee characteristics, training design and work environment. However, an important point in the model is that the outcome of training is impacted by trainee characteristics and work environment in a direct manner, whereas the impact of training design depends on the levels of training outputs such as learning and retention. Baldwin and Ford’s Transfer of Training Model (1988) Source: Baldwin and Ford (1988) The Transfer of Training Model has made a valuable contribution on the study of training transfer. The main benefit of the model in practical levels can be explained in a way that it allows framework for evaluating the impact of each individual input factor in training and identify and utilise the potentials for improving the impact of elements associated with each individual factor. References Baldwin, T.T & Ford, J.K. (1988) “Transfer of training: A review and directions for future research” Personnel Psychology, 41 (65)

Iran was the first state in the Persian Gulf to find oil in 1908, and since 1920s petroleum has served as the main industry in Iran. There is a general consensus in the literature that the overthrow of the Shah of Iran and the revolution in Iran in 1977 came as a great surprise to many individual and organisational observers. This revolution has been political, as well as, cultural. Increasing levels of rentierism in Iran under the rule of Shah, at the same time when neglecting the needs and concerns of ordinary people can be specified as one of the major factors contributing to the emergence of revolution. Specifically, it has been noted that “after the mid-1960s, this state did not need to wrest taxes from its own people, and the economic basis of its revenues was an industry oriented primarily to exports, and employing only a tiny percentage of the domestic labour force” (Skocpol, 1994, p.244). However, it can be argued that the level of rentierism in Iran has changed only a little after the revolution due to a range of reasons such as high levels of corruption, leadership incompetence, and lack of motivation from the government leadership. Moreover, Gordon et al. (2008) assess the average degree of rentierism in Iran for the period between 1972 and 1999 to be 55 per cent. According to Gordon et al. (2008) rentierism has been causing deep economic structural weaknesses in Iran and this along with political uncertainty and environmental vulnerabilities represent complex challenges for Iran in short-term and long-term perspectives. Negative implications of rentierism are also noted by Duero (2009), who links rentierism in Iran to the issues of unemployment and underemployment, demographic problems and the issues associated with patterns of energy production and consumption. It has been assessed that government’s…

Rentier state theory is “a political economy theory that seeks to explain state-society relations in states that generate a large proportion of their income from rents, or externally-derived, unproductively-earned payments” (Gray, 2011, p.1). In simple terms, rentier states derive substantial proportions of their revenues from renting their sources of natural resources to external parties. Rentier states are less motivated to offer concessions to individuals because it is less dependant of taxation to execute its duties, receiving substantial amounts of funds from abroad. Development of rentierism and rentier state theory into academic and practical levels can be divided into the following three phases: classical rentier state theory, the second phase of rientierism and late rientierism. Classical Rentier Theory The first phase of rentierism encompasses the period from the beginning of 1980’s and to the early 1990’s. This period is marked with immediate aftermath of Iranian revolution and Iran-Iraq war of 1980-1988. According to Elbadawi and Maksidi (2010), these both events have played significant role on fluctuations of world oil prices, with implications on global scale. Jenkins et al. (2011) argue that this period of time is associated with a harsh, dictatorial rule of heads of rentier states. Moreover, Jenkins et al. (2011) note about misallocation of wealth, high levels of corruption and overall inefficiencies in rentier Gulf states during the phase. The Second Phase of Rentierism The validity of governments of rentier states being challenged, both, internally and externally is one of the main tendencies marking the second phase of rentierism. Specific factor contributing to these tendencies has been named as phenomenal economic developments in Dubai that served as a point for comparison by people from other oil rich countries in the region. Moreover, during the second phase of rentierism economic scholars acknowledged that the relationship between the levels…
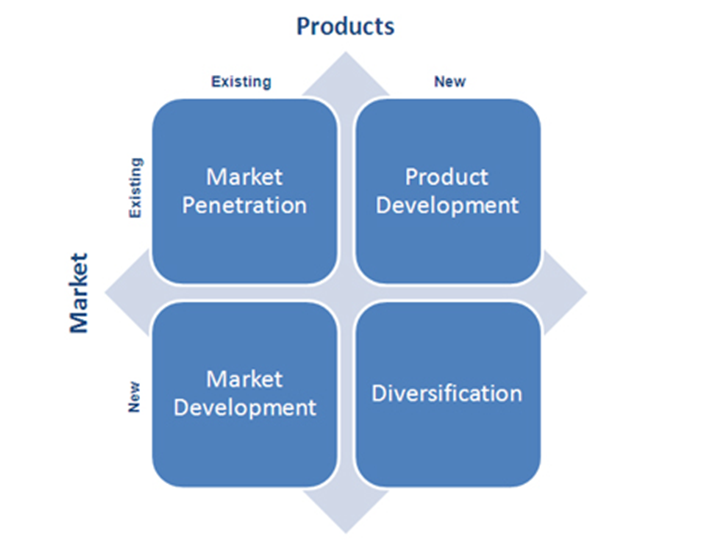
Ansoff Growth matrix assists businesses to increase their revenues by offering four different growth options depending on products and markets. According to the matrix market penetration is a type of growth where the company attempts to increase the level of sales of existing products into current markets. Product development growth strategy, on the other hand, involves introducing new products into current markets. A situation where a business enters new market with its existing products is marked as market development growth strategy. Diversification growth strategy can be achieved through offering new products into new markets. For example, this principle is followed by Warner Bros., although the extent of utilisation of each individual growth strategy varies. Warner Bros. uses market penetration and product development strategies in the US in particular through periodically introducing popular entertainment shows. Due to the following to this strategy for the season of 2012 – 2013, Warner Bros. Television has accounted for more than 30 per cent of top shows on broadcast TV in the US (Annual Report, 2013). Acquisition of 55 per cent of Shed Media plc, one of the leading entertainment firms in the UK for USD 100 million in 2010 (Annual Report, 2013) can be referred in order to illustrate market development strategy of Warner Bros. Diversification strategy, as discussed above is engaged by Warner Bros. in relation to quality of content and the manners of delivery and consumption of films and entertainment products and services. References Annual Report (2013) Time Warner
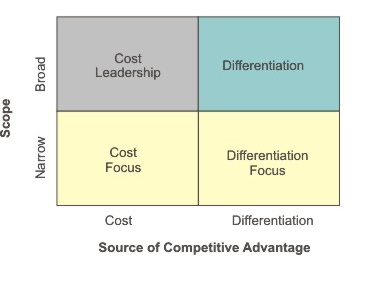
Porter’s generic strategies are one of the most popular tools used when undertaking a competitive analysis in any industry. According to Porter (1985) companies can generally choose from two broad strategies, product differentiation or cost efficiency in broad market scope, or they may pursue product differentiation or cost efficiency strategies within a particular customer segment. To put it simply, companies usually choose to maximise their profit through offering products or services in lower prices, or offering superior quality products or services for higher price. And this can be done for the whole business or for a particular customer segment. A focus strategy “is defined by its emphasis on a single industry segment within which the orientation may be toward either low cost or differentiation” (Czinkota and Ronkainen, 2007, p.196). When pursuing a cost leadership strategy the company prices its products or services at a lower level than competition. Cost leadership strategy is associated with engagement in economies of scale and maintaining strict control of costs. Differentiation strategy, on the other hand, focuses marketing efforts on quality and uniqueness in relation to specific aspects of products or services. There are many advantages product differentiation strategy provides to the business. Product differentiation strategy increases the level of customer loyalty dramatically by mentioning the statistical data according to which US consumer loyalty to a single brand varies from 30 percent in batteries up to 70 percent in cigarettes. When conducting competitive analysis companies should seek following information: current strategy and future objectives of competitors, assumptions about the industry in which competitors believe, and strengths and weaknesses of competitors. Example: Application of Porter’s Generic Strategies to Warner Bros. According to Porter’s generic strategies differentiation in broad competitive scope marks the main competitive advantage of Warner Bros. The company engages in diversification in two levels:…

Five forces framework introduced by Porter (1980) has been acknowledged as an effective tool used in strategy formulation. Application of the framework is associated with analysis of five separate factors determine the overall level of competitiveness in the industry. Warner Bros. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis can be illustrated in the following manner: Threat of new entrants in film, television, and music entertainment industry has been traditionally moderate due to high levels of cost barriers. However, internet and rapid developments in information technology have increased the threat of new entrants to the industry through providing opportunities to lower cost barriers. Bargaining power of buyers is immense as there are no switching costs for the customers of Warner Bros. Buyer bargaining power is also fuelled by abundance of offers in films and manufacturing industry. Threat of substitute products for products offered by Warner Bros. is significant. Substitutions for Warner Bros. products include a wide range of video games, as well as, increasing popularity of major social networking websites such as Facebook, YouTube and Twitter. Bargaining power of suppliers is greater in films and entertainment industry compared to many other industries. Due to the unique nature of this industry famous actors can be classified as suppliers at the same time as serving as human resources. According to this approach, the success of sequels of famous Warner Bros. franchises such as Lord of the Rings, Batman, Harry Potter and Hangover is possible only through attracting A-list actors and actresses who have great bargaining power. Rivalry among existing competitors in global entertainment industry is intense and major companies competing in the industry along with Warner Bros. include Paramount Pictures Corporation, The Walt Disney Studios, Fox Filmed Industries and others. This portal also contains SWOT and PESTEL analyses for Warner Bros. References Porter, M. (1980) “Competitive…
