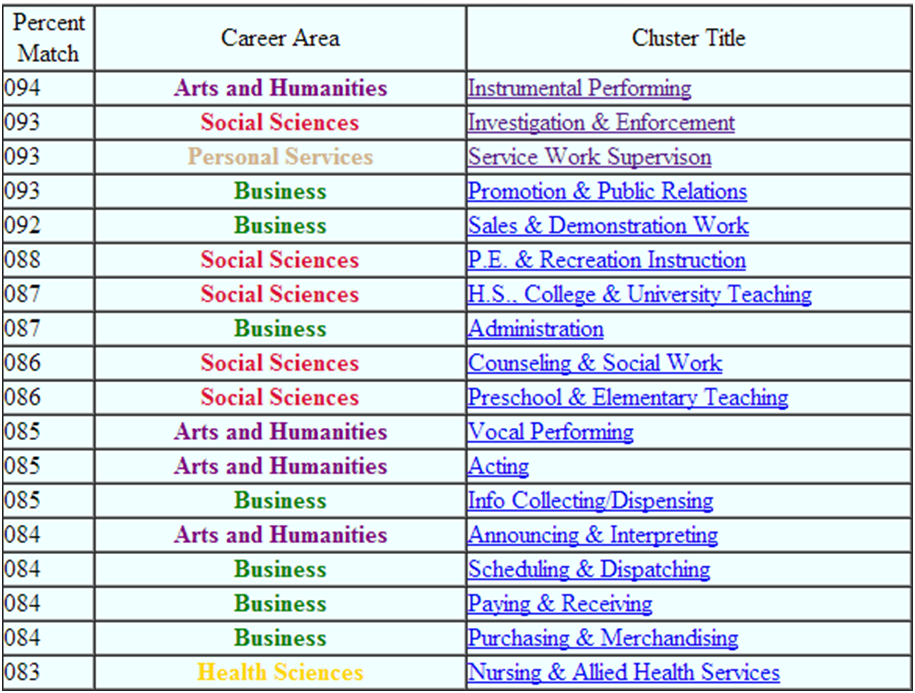
My self-assessment has been completed with the application of Careerlink Inventory, an online skills and interests inventory. This software provides an assessment of five different aspects of individual personality and suggests relevant career recommendations. Specifically, personality aspects assessed consist of aptitudes, interests, temperaments, and physical capacities and working conditions (Careerlink Inventory, 2014, online). The advantages of Careerlink Inventory include practical assistance in making educational and career choices through finding an appropriate match to personal aptitudes, interests, temperaments, and physical capacities. Answers given to Careerlink Inventory multiple choice test questions are analysed by the software and the level of match between responses and a wide range of career areas are represented in percentages. The following table illustrates percentage matches between my skills and interests and a range of career areas and cluster titles according to Careerlink Inventory self-assessment results. Careerlink Inventory self-assessment results Results of Careerlink Inventory self-assessment indicate that there is a 94% match between my skills and interests and Arts and Humanities career area. Report provided by Careerlink Inventory states that this specific career area is closely associated with entertaining audiences and a high level of creativity. Importantly, the same points equally relate to successful event management as well, and from this perspective Careerlink Inventory finds event management as a suitable career choice for me. Moreover, Careerlink Inventory self-assessment has found 93% match between my skills and interests and Social Sciences career area. It is clarified in self-assessment results report that Social Sciences involve serving the public interests in a wide range of manners. In other words, my skills and interests are best applied in serving the interests of public, and this can be done through dealing with various aspects of event management in a successful manner. There is also 93% match between my skills and interests and Personal…

It has been noted that “research is a term used literally for any kind of investigation that is intended to uncover interesting or new facts” (Walliman and Walliman, 2011, p.1). The career research process I have used is the one proposed by Morgan (2010) and it consists of the following stages: 1. Assessment. The research process commences with assessment of personal skills and knowledge, as well as, passion in order to be able to identify genuine career aspirations. Specifically, my hobbies and spheres that attracted my interest the most have been deeply analysed during this initial stage of career research process. 2. Collecting Information. Both, primary and secondary data sources have been used to collect the relevant information during the second stage of career research process. Secondary sources of data used in research process comprise industry analyses, industry magazines and newspapers, and a range of books devoted to career management. Primary data sources used during the career research, on the other hand, include individuals already employed in the industry. 3. Presentation. This stage includes improvement of the verbal pitch, and development of a personal marketing plan as a prospective employee. A high level of importance of developing a personal marketing plan can be explained by increasing level of competition in the job marker for graduates with little or no formal job experiences. 4. Project management. Achievement of career objectives is approached as a project management with identification of short-term and long-term goals and organising regular reviews. 5. Interview preparation. Performances in interviews play a great role in the achievement of career objectives, and accordingly interview preparation is identified as a strategic stage in career progression. 6. Project update. This stage in career research process involves career progression monitoring conducted in a regular basis, and strategy modification if necessary. References Morgan, H. (2010) “The…

A wide range of factors have impact upon a brand than a business strategy and generally these factors can be divided into two categories: internal and external. Internal factors affecting brand include business strategy, internal conventions, brand legacy marketing mix and marketing implementation. External factors, on the other hand, include, but not limited to category, cultural, and needs conventions. Crossan and Apaydin (2010) confirm this viewpoint and specify core elements of the brand as expression, perception, and recognition that are subjected to the impact of internal and external factors specified above. Moreover, Fog et al. (2010) argue that regardless of industry and nature of the business brands cannot exist independent of the company, its organisational culture, suppliers, distributors and buyers, at the same time specifying these elements as factors affecting branding aspect of the business. It has been argued that “it can be easier to establish a new brand if there is a history of product or service experience which has already earned trust and credibility” (Davis and Baldwin, 2006, p.29). However, Alessandri (2009) offers an alternative viewpoint claiming that the level of effectiveness of branding strategy depends upon the quality of brand identity, the choice and the level of implementation of communication channels to promote the brand, and the quality of products and services above all. The personality of CEO of the company is considered to be another major factor affecting brands and branding initiatives by Fioroni and Titterton (2009). Moreover, the issues of brand personification have been explained by Fioroni and Titterton (2009) by referring to the example of Virgin Group, where it’s CEO Richard Branson has successfully established himself as a core of the brand. A wide range of secondary data authors share their viewpoints in terms of improving brand image and value in a global scale.…

The process of brand development can be divided into four stages. The first stage involves analysing the current situation. The purpose of this stage relates to the identification of gap in customer satisfaction with specific ranges of products and/or services. The second stage of brand development process relates to the formulation of a brand vision. Specifically brand vision is developed in a way that it is directly associated with eliminating gap in customer satisfaction with great level of effectiveness. The third stage is the combination of strategy and creativity. Regarding this particular stage it has been stated that “strategy alone would not succeed; it must be accompanied by a creative identity that engages the senses appropriately, and enough publicity and advertising to arose demand for the brand” (Healey, 2008, p.16). The fourth stage involves analysing the outcome and introducing necessary changes. By the time this stage is reached firms would have results of the level of acceptance of brand by the firm target customer segment. Accordingly, necessary modifications can be introduced to brand strategy in order to eliminate shortcomings that have been identified. References Healey, M. (2008) “What is Branding?” Rockport Publishers

Ingredient branding, as the name implies “is strategic brand management for materials, components, parts, services, etc” (Kotler and Pfoersch, 2010, p.17). Pride et al. (2011) credit the global microprocessor company Intel for the development of the term of ingredient branding. Namely, the introduction of “Intel Inside” program in 1991 was initiated with the main purpose of marking Intel microprocessors from the products of its competitors and build an effective consumer brand. It has been stated that “an ingredient branding strategy pulls demand from end users through the distribution channel back to the original equipment manufacturers, who feel pressure to use the branded ingredients in the goods they make” (Mohr et al., 2009, p.415). At the same time, some respected marketing scholars argue that “ingredient Branding can start in a later stage of a product life cycle” (Kotler and Pfoersch, 2010, p.19). Moreover, Kotler and Pfoersch (2010) specify general targets of ingredient branding in the following manner: General Targets of Ingredient Branding Source: Kotler and Pfoersch (2010) The issue of relationship between brand role and distributors’ own-brands’ market share has been addressed by Kapferer (2012) who identifies individual functions of branding and their consumer benefits in the following manner: Function Consumer benefit Identification To be clearly seen, to quickly identify the sought-after products, to structure the shelf perception Practicality To allow savings of time and energy through identical repurchasing and loyalty Guarantee To be sure of finding the same quality no matter where or when you buy the product or service Optimisation To be sure of buying the best product in its category, the best performer for a particular purpose Badge To have confirmation of your self-image or the social image that you represent to others Continuity Satisfaction created by a relationship of familiarity and intimacy with the brand that you…

Four main components of branding can be specified as positioning, storytelling, design, price, and customer relationships and each of these components are discussed further below in a greater detail. 1. Positioning Positioning means “defining in the mind of a customer what a brand stands for and how it compares with competing brands” (Healey, 2008, p.8). The origin of the concept of brand positioning can be linked to the idea that consumers form particular opinion regarding each brand they encounter and by engaging in brand positioning companies attempt to influence this opinion in a favourable manner. Brand positioning can be divided into four different components. The first component relates to the class of the product of service, as well as, to the structure of the relevant marketplace. The second component of brand positioning involves segmentation of consumers. Consumer perception in relation to the brand compared to the competitors forms the third component of brand positioning. Final, the fourth component of brand positioning relates to the benefits associated with purchasing products and services of the brand. 2. Storytelling It has been stated that in branding through storytelling “the story is what drives the bond between the company and the consumer” (Fog et al., 2010, p.23). Four elements of storytelling as part of branding can be specified as message, conflict, character and plot. All of these four elements should be present in a branding strategy in order to in order for the strategy to be successful. In order to implement storytelling with an increased level of efficiency companies must communicate the same story to organisational stakeholders through an effective integration of various marketing communication channels. 3. Design It has been argued that “design, in all its varieties, has the potential to bring brands to life in a way that can…

Brand has been defined as “the sum of all associations, feelings, attitudes and perceptions that people have related to the tangible and intangible characteristics of a company, product or service” (Brandeo, 2014). The definition of a brand image has been proposed as “the total, global impression of the information that accumulates in the memory of consumers in relation to a band” (Franzen and Moriarty, 2008, p. 241). The terms of branding in particular has been defined as “the process of continuous struggle between procedures ad customers to define the promise and meaning” (Healey, 2008, p.6). The issues of increasing importance of brands and branding in modern global marketplace have been addressed by a wide range of authors and the most noteworthy contributions to the issue have been made by authors such as Hill et al (2006), Franzen and Moriarty (2008), Clifton and Ahmad (2009), and Kotler and Pfoersch (2010). Interestingly, Okonkwo (2010, p.9) reasons that “the origin of brands comes from the times when early cattle-rearing men stamped their ownership on their livestock by burning a mark of their name or identity on the cattle, to distinguish one cattle-farmer’s stock from another’s”. However, according to Franzen and Moriarty (2008) the importance of branding has seen a significant boost during the past several decades, and reasons for this have been offered as increase in the level of well-being of consumers (Inkpen and Ramaswamy, 2006), increasing role of media (Steers and Nardon, 2008), and innovations in marketing communications (Alessandri, 2009). Abbing (2010) addresses the issues associated with the shift in the role and meaning of branding in a detailed manner and presents his findings in terms of differences in branding in the past and present in the following manner: Brands were previously often referred to as being Brands in current thinking are…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Literature Review

This report has been prepared for the senior management and Board of Directors of children’s cancer charity in Northern Ireland and the report explains the concept of administrative management and how this role underpins all other functions. Moreover, the report explains the contribution of administrative management in meeting the needs of various stakeholder groups and assesses communication models used by administrative managers. The report is completed by explaining the need to redevelop various organisational systems in order to accommodate organisational change. Role of administrative managers are important for both, private and public sector organisations, however, the level of importance of this role is often underestimated by senior level management for a wide range of reasons. This reason may relate to the fact that unlike other organisational practices such as marketing and finance, the output of administrative management is not directly tangible. 1. Introduction 1 2. Role of Administrative Management 1 3. Contribution of Administrative Management in Meeting the Needs of Customers and Stakeholders 3 4. Communication Models Used by Administrative Managers 5 5. Need to Re-develop Systems to Accommodate Organisational Change 7 6. Conclusions 9 Apple BP General Motors Toyota Motor Corporation How do I receive the report? Once payment is made you will receive a link to you e-mail you have registered with on Pay Pal or the e-email you have entered when specifying bank details to download the report. The report is downloaded in PDF format. The link will stay active for 7 days. How can I use the report to complete my academic assignment/research? Reports and essays offered by research-methodology.net are professionally written samples in their respective areas. Reports and essays are intended to be used as guides and sources of secondary data for reference purposes. I did not receive the link/I can not download the report?…

Branding is one of the success factors in business and the segment of social networking services is not an exception. Branding can provide a number of advantages to products and services, including social networking services such as increasing the levels of product recognition, assisting with new products positioning, and formation of strong brand equity. Due to the highly intangible nature of social networking services, their brand value can be stated to be highly subjective. Specifically, when Facebook went public in May 2012, its share has been priced as USD38, causing the company to be valuated at USD104 billion, the highest valuation for a newly listed public company to date. However, its share price has been reduced to USD18 after only several months by August 2012 (Miller, 2013). Social networking service is a highly competitive area and the major players in this market include Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, Twitter, Pinterest, Google+ and others. Social networking site Estimated unique monthly visitors Alexa Rank Facebook 750,000,000 2 Twitter 250,000,000 9 LinkedIn 110,000,000 14 Pinterest 85,500,000 36 My Space 70,500,000 138 Google Plus+ 65,000,000 N/A Comparisons of various aspects of social networking sites as of July 2013 Source: eBizMBA Interestingly, assessment of popularity of social networking sites is not a straightforward matter. For example, opening a Google Mail (Gmail) account automatically registers a new Google+ social networking profile, and for this reason Google has been subjected to criticism in terms of proving inaccurate data of the popularity of its social networking platform. All of the successful social networking service provides listed above target specific customer segment among population. For example, LinkedIn is mainly aimed at professional aiming to establish and sustain professional networks whereas Pinterest positions itself as an informal social networking site. However, a certain tendency can be observed in this regard in a…

Key features of social networking service design elements are associated with high levels of intractability, high levels of personalisation to the user, at the same time when maintaining high levels of simplicity. Design elements can be specified as one of the most important critical success factors for social networking sites. Generally, design elements for social networking websites include personal profile, news feed, navigation features, advertisements and others. The majority of social networking sites offer customers the possibilities of customising design of their personal profiles to varying extents. Moreover, enabling an adequate extent of design customisation for users can be specified as one of the most important critical success factors for social networking services. This point can be illustrated by referring to the case studies of My Space and Facebook. Although, Facebook was launched more than one year after the launch of MySpace, the former social networking site has become more popular than the latter in a matter of few months due a range of reasons including an adequate balance between fixed service design and customisation. In other words, while MySpace offered an excessive level of design customisation to customers, creating a visual clutter, Facebook offered more simplistic and standard design features and offered more limited design customisation, and this difference has played certain role in higher level of popularity of Facebook compared to MySpace. Effectiveness of Facebook’s approach to design has been further confirmed when a similar design template has been followed by Google in its Google+ social networking site launched in 2011. Relevance of Social Networking Service Key Features to Customer Needs The relevance of key features of social networking services to customer needs is not a straightforward issue. While social networking services aim to satisfy a set of customer needs such as communication, self-expression and recreation, innovations…
