Search results for: Ansoff Matrix
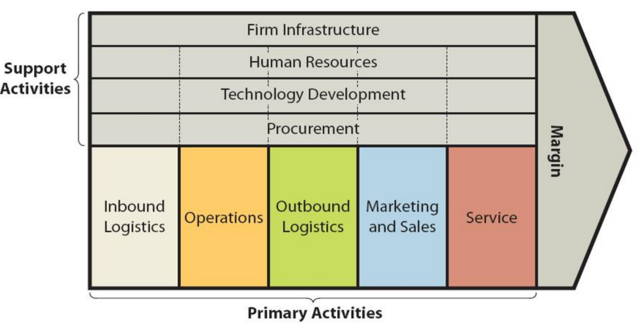
BYD value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of BYD value chain analysis. BYD Primary Activities BYD Inbound logistics BYD inbound logistics is one of the key sources for value creation for the EV behemoth. BYD has more than 11,000 cooperative suppliers, 41% of which are located in Southern China, 34% in Eastern China, 9% in Northern China.[1] The electric automaker aims to produce as many spare parts in-house as possible, thus decreasing dependence on external vendors, at the same time increasing profit margins. For example, for BYD Dolphin only tyres and windows are delivered by suppliers and all other components are produced by the company itself.[2] BYD prioritizes long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, securing stable access to critical materials and components like lithium, cobalt, and semiconductors. This reduces procurement risks and price fluctuations. The company leverages cutting-edge technologies like digital supply chain management systems, artificial intelligence for demand forecasting, and automated warehouse robots. BYD Operations In the operations stage, BYD engages in the manufacturing and assembly of its products. This includes the production of EVs, batteries, solar panels, and energy storage systems. Efficient production processes and quality control measures are crucial in this stage. BYD operations can be divided into the following four segments. Automobile. BYD delivered a total of 1,802,000 vehicles in 2022, with a year-on- year growth of 149.9%, including around 1,788,000 new energy vehicles, with a year-on-year growth of 217,6%.[3] Rail Transit. The company produces medium-capacity “SkyRail” and low-capacity “SkyShuttle” filling the technological and industrial gap in rail transit and providing effective solutions to traffic jams in cities all over the world. Renewable energy. As a provider of integrated renewable energy solutions, BYD produces relevant products like batteries, solar energy…
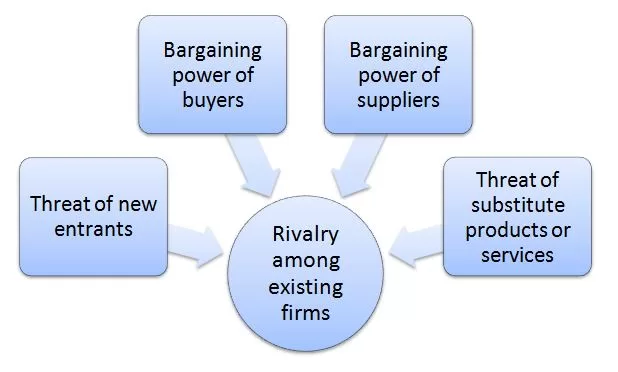
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. BYD Porter’s Five Forces are illustrated in figure below. Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in BYD Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into EV sector is low to moderate. The following are the main factors that determine the intensity of this threat. Massive capital investments Requirement for huge capital investments is a significant entry barrier for potential entrants into the EV market. In order to succeed new players would have to introduce improvements in battery range and life, charging speeds, efficiency or vehicle performance. Any of these achievements would necessitate investments in research and development and it would be hard for new market players to compete with deep-pocketed existing market players in this front. For example, Volkswagen plans to invest €35 billion in EV R&D by 2025[2], while Ford has allocated USD50 billion by 2026 for the same purposes[3]. Possible retaliation from current market players New entrants in the EV EV market can expect varying degrees of retaliation from existing businesses, depending on several factors. For example, established automakers such as Tesla and BYD can reduce prices on their own EVs to undercut new players, increase marketing and advertising efforts to maintain brand awareness or lobby against government policies favouring new entrants. Moreover, oil and gas companies feeling threatened by the shift away from fossil fuel may spread misinformation about the environmental benefits of EVs or pressure lawmakers to delay or limit EV incentives Customer switching costs These are the expenses, efforts, and time involved for customers to switch from their current EV brand to a new one. They can be tangible (financial) or intangible (psychological and time-related). For tangible expenses,…

BYD marketing communication mix consists of various channels to communicate the marketing message to the target customer segment. These channels are print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing. BYD Print and Media Advertising Print and media advertising includes various traditional forms of paid communication used to promote a product, service, or brand through printed or broadcasted media channels. While BYD primarily focuses on digital marketing due to its reach and engagement potential, it still strategically utilizes print and media advertising for several reasons such as: Reaching specific audiences. Print and media offer access to demographics less active on digital platforms, like older generations or local communities. Building brand awareness. High-profile magazine spreads or television commercials can significantly increase brand recognition and visibility. Complementary storytelling. Print and media formats allow for longer narratives and deeper dives into BYD’s values, technology, and environmental commitment, complementing the quick bites of digital marketing. BYD Sales Promotions Sales promotions refer to short-term incentives, activities, or offers designed to encourage the purchase or sale of a product or service. BYD uses the following sales promotions techniques, among others: New Year Pre-Owned Event. Offering discounts on used BYD EVs alongside free extended warranties and test drives, targeting budget-conscious buyers and promoting their pre-owned program. Summer EV Road Trip Bonus. Providing bonus miles on charging networks alongside travel vouchers and roadside assistance packages, encouraging summer travel and showcasing their partnership with charging infrastructure providers. Back-to-School Family Fleet Package. Offering special discounts and financing options for purchasing multiple BYD EVs for families, catering to the larger vehicle needs of families with children. Tech Upgrade Bonus. For buyers of top-tier models with advanced features, including free software upgrades or subscriptions to connected services, highlighting their technological innovations. Earth Day Sustainability Drive. Offering discounts on models with longer ranges or lower emissions alongside tree-planting initiatives, emphasizing their…

BYD segmentation, targeting and positioning helps the electric automaker identify and reach their target audience effectively. These three components work together to develop a clear marketing strategy. BYD focuses on the following segmentation bases: 1. Geographic Segmentation. Urban vs. Rural. BYD prioritizes urban areas with higher EV adoption rates and developed charging infrastructure. They offer smaller, affordable EVs for city commutes. Developed vs. Developing Countries. In developed countries, BYD competes with premium brands, focusing on advanced features and technology. In developing markets, they offer budget-friendly models with longer range for rural driving. Accordingly, the electric automaker uses multi-segment market positioning. Specific Regions. BYD targets regions with government incentives for EVs and tailors offerings based on local preferences and driving habits. 2. Demographic Segmentation. Age. Millennials and Gen Z are significant targets due to their environmental consciousness and tech-savviness. BYD offers sleek designs and connected features for these segments. Income Level. BYD offers a range of price points across categories, targeting both budget-conscious buyers and those willing to pay more for premium features. Family Size. Larger families with specific needs are catered to with spacious SUVs and MPVs designed for comfort and safety. 3. Psychographic Segmentation. Environmental Consciousness. BYD emphasizes its sustainability features and commitment to green technology, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Technology Adoption. Early adopters and tech enthusiasts are targeted with cutting-edge features and futuristic designs. Lifestyle Preferences. Active lifestyles are addressed with rugged EVs for outdoor adventures, while urban professionals are offered stylish and efficient city cars. 4. Behavioural Segmentation. Driving Habits. Daily commuters receive tailored offerings like fast charging options, while long-distance travellers are targeted with extended range models. Brand Loyalty. Existing customers are offered loyalty programs and upgrade options, while new audiences are targeted with attractive incentives and test drives. Price Sensitivity. Budget-conscious buyers are targeted with affordable models, while those willing to…
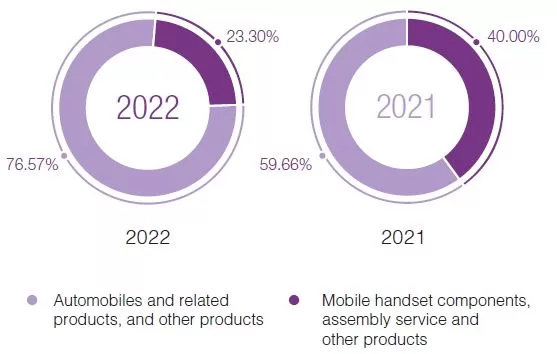
BYD marketing mix (BYD 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence for the one of the leading rechargeable battery manufacturers in the global arena. Product Element in BYD Marketing Mix (BYD 7Ps of Marketing) BYD Group engages in diversified market segments, such as smart phones, tablet computers, smart home devices, game hardware, drones, Internet of Things, robots, communication equipment and medical and health equipment. The table below the complete range of BYD product categories. Product category Products Automobile Vehicles, buses and trucks Rail transit Medium-capacity “SkyRail” and low-capacity “SkyShuttle” Renewable energy batteries, solar energy products, energy storage Electonic Products and services for a wide range of products such as smartphones, tablet PCs, new energy vehicles, residential energy storage, smart home, game hardware, unmanned aerialvehicles, Internet of Things, robotics, communication equipment, health devices etc. BYD Product Categories Despite the diverse product category, automobiles are the biggest source of revenue for the company. Specifically, as illustrated in figure below, the share of automobiles and related products of total revenues increased from 59.66% in 2021 to 76.57% in 2022. This tendency is likely to persist in the longer term perspective. Revenue breakdown by product category[1] Place Element in BYD Marketing Mix (BYD 7Ps of Marketing) In 2022 BYD sold EVs to more than 400 cities in over 70 countries and regions across the six continents of the world.[2] The effectiveness of BYD’s distribution channels is a critical factor in reaching and satisfying the ever-evolving needs of its target audience. Utilizing a combination of authorized dealerships, online platforms, and strategic partnerships, BYD aims to create a seamless experience for customers. A critical analysis of these channels should focus on their efficiency in delivering products to consumers, their contribution…

BYD marketing strategy is constantly evolving as the EV market landscape changes. They are adapting to new customer demands, emerging technologies, and competition from established and new EV players. BYD marketing strategy is attempts to communicate the brand’s unique selling proposition (UPS) to the target customer segment. BYD’s USP isn’t just a single thing, but rather a powerful combination of several key factors that set it apart from other EV manufacturers. Here are some of the most prominent elements: 1. Vertically Integrated Powerhouse. BYD controls almost every aspect of its EV production, from mining raw materials to assembling the final vehicle. This gives them a significant advantage in controlling costs, ensuring quality, and driving innovation throughout the entire process. 2. Blade Battery Advantage. Their proprietary Blade Battery technology is a game-changer. It offers higher range, faster charging, and enhanced safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This technology is a major competitive advantage and a key selling point for BYD customers. 3. Technology for Everyone. BYD strikes a unique balance between offering technologically advanced EVs at competitive prices. This makes them appealing to a wider range of consumers, not just those with deep pockets. Their price competitiveness often puts them at the forefront of accessible EV options. 4. Sustainability Champion. BYD is fully committed to promoting sustainable transportation solutions. Their entire focus is on EVs, unlike traditional car manufacturers offering both EV and gas-powered options. This clear commitment to clean energy resonates with environmentally conscious consumers. 5. Beyond Cars. BYD doesn’t limit itself to cars. They offer a diverse product portfolio including buses, trucks, taxis, and even forklifts. This caters to various transportation needs and allows them to tap into different market segments. 6. Innovation Engine. BYD constantly invests in research and development, pushing the boundaries of EV technology.…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. BYD PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects of the electric automaker. Political Factors in BYD PESTEL Analysis Favourable government policies for EV and renewable energy In 2022, global EV sales soared by 68%, reaching a record 10.6 million units. This meteoric rise coincides with a wave of supportive government policies. China, the world’s largest car market, offers generous purchase subsidies and tax breaks for EV buyers. These incentives have propelled China to become the undisputed leader in EVs, accounting for over half of global sales. Likewise, European countries like Norway and the United Kingdom have implemented ambitious carbon reduction targets, coupled with EV purchase incentives and charging infrastructure investments, contributing to their impressive EV uptake rates. The impact of favourable policies extends beyond the realm of personal transportation. Renewable energy sources, once relegated to the fringe, are now experiencing a golden age thanks to supportive government initiatives. In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 offers tax credits for renewable energy projects and EV manufacturing, a move projected to inject USD370 billion into clean energy over the next decade. Similarly, India, the world’s third-largest carbon emitter, has set a goal of achieving 50% renewable energy capacity by 2030, backed by ambitious solar power targets and financial incentives for renewable energy developers. These policy shifts are not driven solely by environmental concerns. Governments are increasingly recognizing the economic benefits of a green transition. EVs create new jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, with estimates suggesting that the global EV industry could create 30 million jobs by 2030. Renewable energy is also attracting substantial…
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates BYD SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Vertical integration and cost advantage 2. Market leadership at the global scale 3. Leadership in technological capabilities 4. Massive manufacturing scale Weaknesses 1. Brand image associated with the perception Chinese quality being low 2. Overdependence on domestic market 3. Too broad range of business 4. Dependence on Chinese government EV subsidies Opportunities 1. International market expansion 2. Formation of strategic partnerships 3. Increasing relevance and popularity of EV 4. Technological advancements Threats 1. Intensifying competition 2. Trade conflicts between China and USA 3. Issues in sourcing key components 4. Global economic slowdown BYD SWOT Analysis Strengths in BYD SWOT Analysis Vertical integration and cost advantage The bedrock of BYD’s cost leadership lies in its deep vertical integration. Unlike traditional automakers who rely on a constellation of external suppliers, BYD owns and operates its entire supply chain, from battery production to semiconductors, electric motors, and even key vehicle components. This single-source approach empowers BYD with several advantages. Firstly, it eliminates the markups and negotiation complexities associated with external suppliers, offering greater cost optimization. Secondly, it enables streamlined communication and collaboration across the entire production chain, allowing for quicker problem-solving and flexibility in adapting to market demands. Analysts estimate this vertical integration translates to a 25-30% cost advantage over competitors, a significant edge in the fiercely competitive EV market. But vertical integration goes beyond mere cost-cutting. It empowers BYD with unparalleled control over quality and consistency. By managing every stage of production, BYD can ensure strict adherence to its own exacting standards. This reduces the risk of defective components or production bottlenecks, further contributing to lower overall costs. The Blade Battery, a BYD innovation, exemplifies this. Its unique design…

BYD organizational culture integrates the following three key elements: 1. Meritocracy. BYD promotes a culture of meritocracy, where performance and results are rewarded. BYD’s culture strongly emphasizes performance and achieving concrete results. Promotions, bonuses, and other rewards are heavily tied to individual contributions and exceeding targets. Such an approach incentivizes employees to constantly strive for excellence, pushing themselves and the company forward. 2. Cost-cutting. Reducing expenses whenever possible is a crucial element of EV maker’s organizational culture, woven into its fabric and contributing significantly to its success. BYD famously controls almost every aspect of its production, from battery cells to vehicle assembly. This reduces reliance on external suppliers and cuts down on costs significantly. For instance, they manufacture their own semiconductors, a major expense for EV production. The company encourages a culture of resourcefulness and frugality among its employees. They’re empowered to find creative solutions to save costs, from reusing materials to optimizing energy consumption. For example, employees developed a system to recycle scrap metal from the production process, saving millions of dollars annually. 3. Value-driven culture. The EV giant promotes the values of excellence, pragmatism, passion and innovation. These values go beyond mere slogans and posters, influencing every aspect of the company’s operations and employee behaviour. BYD empowers employees at all levels to take ownership and make decisions aligned with the core values. A strong community spirit is present at the company fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration, where employees feel valued and invested in the company’s success. BYD Company Limited Report contains the above analysis of BYD organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on BYD. Moreover, the report contains analyses of BYD leadership, organizational structure and business strategy. The report also…
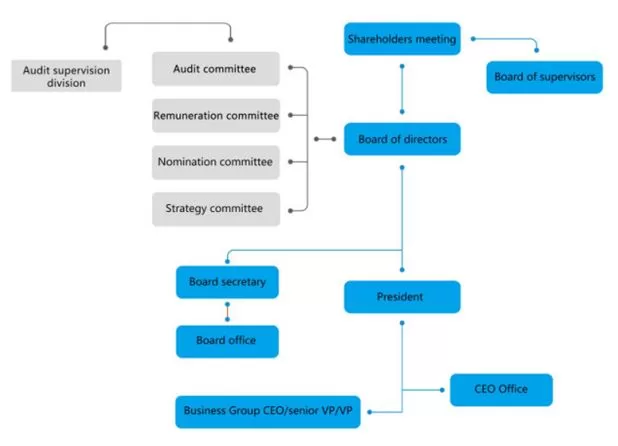
BYD organizational structure has the following characteristics: – Matrix Structure. BYD corporate structure is matrix, combining functional departments (e.g., R&D, Sales) with product-based divisions (e.g., Dynasty, Ocean, Commercial Vehicles). This fosters collaboration and flexibility while maintaining focus on specific product lines. The matrix structure enables quick decision-making and adjustments to market dynamics – Independent Brands. Recent moves towards independent operations for brands like Dynasty and Ocean indicate a strategy to cater to distinct market segments with tailored brand identities and marketing efforts. In other words, independent brands allow for targeted approaches. – Emphasis in R&D. BYD prioritizes internal R&D, with dedicated institutes for each brand and separate units for core technologies like DM-i hybrids and intelligent driving. This fosters innovation and control over key components. – Vertical Integration. The EV behemoth vertically integrates key aspects of its supply chain, including battery production and some vehicle components. Such an approach enhances cost control and quality assurance. Vertical integration expands BYD organizational structure. – Regional Variations. The electric automaker’s structure adjusts to regional needs, with separate sales divisions and local leadership teams managing specific markets. Regular variations approach ensures responsiveness to diverse customer preferences and regulations. The Figure below illustrates BYD corporate structure at the senior level. BYD Company Limited Organizational Chart BYD Company Limited Report contains the above analysis of BYD organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on BYD. Moreover, the report contains analyses of BYD leadership, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of BYD marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.
