Search results for: Mckinsey 7s
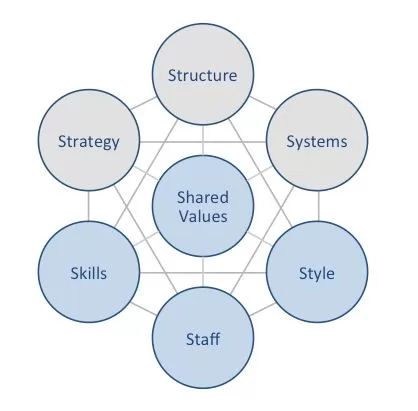
BYD McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in Figure 7 below, shared values are positioned at the core of BYD McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in BYD McKinsey 7S Model Strategy. BYD business strategy integrates cost leadership and extensive vertical integration. This strategy allows lowering dependence on external vendors and optimizing resources within the company and having tighter control over the entire production process ensures consistent quality standards. Moreover, one of the leading rechargeable battery manufacturers in the global arena maintains an accelerated pace of new model development as one of its core competitive advantages. Structure. Organizational structure of BYD is complex and it is difficult to classify it according to conventional categorizations. Nevertheless, it is closer to matrix structure combining functional departments (e.g., R&D, Sales) with product-based divisions (e.g., Dynasty, Ocean, Commercial Vehicles) than alternative structures. Systems. The electric automaker depends on a wide range of systems for its business operations. These include manufacturing systems such as vertical integration, lean manufacturing, robotics and automation, as well as, R&D systems. Moreover, supply-chain management, information, quality management, financial and HR systems are also critrically important for the EV giant. BYD Company Limited Report contains a full analysis of BYD McKinsey 7S Model. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix and Value Chain analysis on…
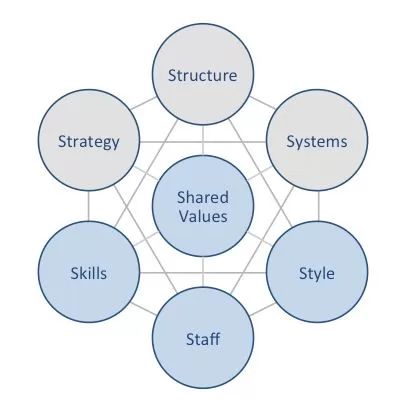
Marriott McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness for the largest hotel chain in the world. According to this framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Marriott McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Marriott McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Marriott International’s business strategy is focused on providing high-quality hospitality services to a wide range of customers. The company has a portfolio of over 30 brands, ranging from budget-friendly to luxury, to appeal to different needs and budgets.[1] The hotel chain pursues asset-light business model and growth through acquisitions business strategy. Moreover, Marriott has been focusing on bleisure travellers as part of its business strategy. Structure Marriott International has a decentralized organizational structure, with each brand operating as its own business unit. This allows the company to tailor its offerings and services to the specific needs of each market. Marriott also has a strong focus on operational excellence, with a number of systems and processes in place to ensure that its hotels are run efficiently and effectively. Systems Marriott International has a number of systems in place to support its business operations, including a reservation system, a loyalty program, and a property management system. The company is also investing heavily in new technologies, such as mobile check-in and self-service kiosks. Marriott International Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Marriott McKinsey 7S Model.…
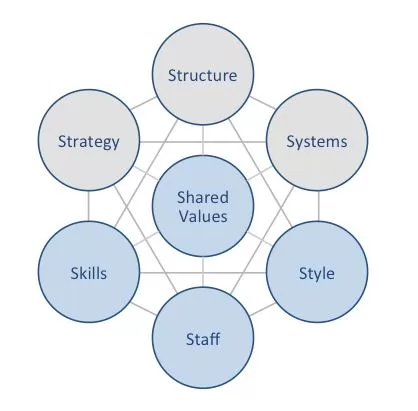
Netflix McKinsey 7S model shows how seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems are hard elements, while shared values, skills, style and staff represent soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in Figure 6 below, shared values are placed at the core of Netflix McKinsey 7S model. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Netflix McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Nvidia business strategy relies on focusing on revenues maximization over membership growth and investing in original content. The entertainment services provider considers its globally successful original content such as House of Cards (2013-2018), BoJack Horseman (2020) and Squid Game (2021) as its unique selling proposition amid intensifying competition. Moreover, the largest streaming service in the world stays away from news and live sports segments, sticking to movies, series, documentaries and games, as part of its business strategy. Structure Netflix organizational structure is flat and unitary. There are considerably less management layers considering the size of the company and scope of its operations comprising 12500 people in offices in over 25 countries.[1] As a result, the flow of information is fast at the on-demand media provider and this contributes to the flexibility of the business to external macroeconomic changes. Systems There is a wide range of systems and processes that are important for the largest streaming service in the world to sustain its business. These systems include employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing, customer relationship management, business intelligence, knowledge management and others. Furthermore, the system of…
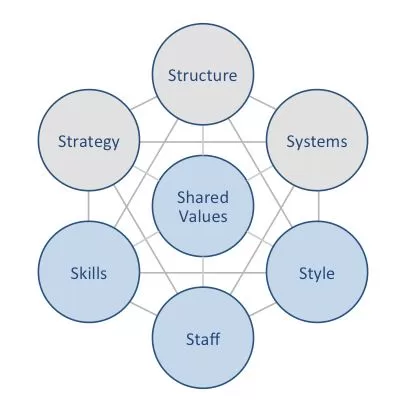
Nvidia McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. The model positions shared values are positioned at the core remaining elements, because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Nvidia McKinsey 7S Model Strategy. Nvidia business strategy benefits from first mover advantage systematically. This has been the case with GPU, Computer Unified Device Architecture (CUDA) and invented deep learning hardware accelerators, such as the Tesla V100 and T4 GPUs and a range of other products. However the sustainability of this strategy in the long-term perspective requires the regular pipeline of new products through effective investment in research and development. Structure. As one of the largest multinational technology companies in the world Nvidia organizational structure integrates the elements of functional and hybrid structures. Within the company business processes are divided into various divisions with highly specialised employees with the relevant skills and competencies attached into respective divisions. Furthermore, the senior management forms temporary project groups to develop new products or for other initiatives and group members report to multiple superiors for the duration of project. Systems. Nvidia depends on a wide range of systems for the business to operate smoothly. These include, but not limited to employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing, customer relationship management, business intelligence and knowledge management. Each system has its KPIs and controls in place and they are monitored systematically. Nvidia Corporation Report contains a full analysis of Nvidia…
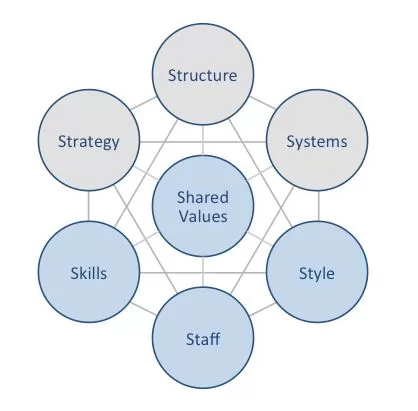
WeWork McKinsey 7S model highlights the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to this model strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses there are strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are placed at the core of WeWork McKinsey 7S model, because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. Hard Elements in WeWork McKinsey 7S Model Strategy. WeWork pursues simplification business strategy. Specifically, co-working giant simplifies the notion of flexible workspace and makes it practical for businesses of all sizes through offering space as service. Furthermore, the company is on the path of digitalizing real estate business on the global scale. Structure. Under the leadership of co-founder and former CEO Adam Neumann WeWork organizational structure was chaotic and ineffective. The current CEO Sandeep Mathrani restructured the company to a great extend to make it more simple and transparent. Currently, global flexible workspace provider has an hierarchical organizational structure. Systems. The workspace provider relies on a wide range of systems for its daily operations. These include employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing systems. Furthermore, customer relationship management, business intelligence, knowledge management systems are also important for WeWork. WeWork Inc. Report contains a full analysis of WeWork McKinsey 7S Model. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Ansoff Matrix and Value Chain analysis on WeWork. Moreover, the report contains analyses of WeWork leadership, business strategy organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of WeWork marketing strategy, ecosystem…
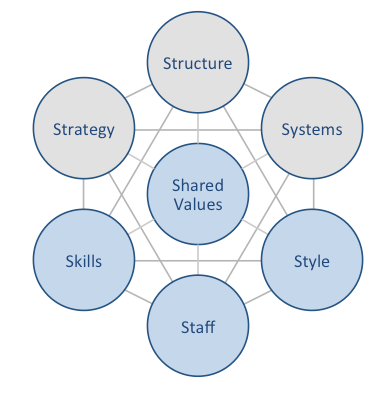
McKinsey 7S model is a tool for analyzing organizational design. The model aims to illustrate how organizational effectiveness can be achieved through alignment of seven key elements. The model divides elements into two categories – hard elements and soft elements. Strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. Shared values are placed at the core of McKinsey 7S model because they are cornerstone to the development of all other elements Hard Elements Strategy. Strategy is a plan to generate profit sustainably on the basis of competitive advantage(s). Answers to the following questions uncover company’s strategy: How company plans to maximize its profits? How company deals with competitive pressures? How the business deals with changes in customer demands, tastes and preferences? Structure. Structure refers to the organization of the business, organizational chart depicting the chain of command. Companies can look for answers to the following questions to identify the pattern of their structure: How divisions/teams are divided? What is the hierarchy of the company? How activities of various divisions are organized? What is the level of autonomy in decision making in various departments? Are the lines of communication explicit or implicit? Systems. Activities and procedures employees use daily to complete their job. The following questions can be used in regard to systems within companies: What are the main systems that maintain performance? How systems are controlled and evaluated? What are benchmarks are used to keep systems on track? Soft Elements Skills. Skills relate to company’s core competencies and capabilities that enable employees to perform efficiently. The following are the main questions related to skills: What are the main important required skills for the company to succeed? Are there any gaps in required skills? What are the skills monitoring and control practices? Staff.…
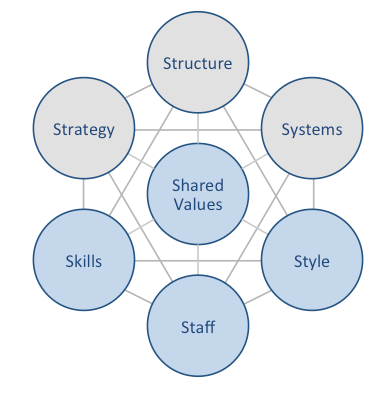
Starbucks McKinsey 7S model is used to highlight the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to this model, strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements. At the same time, shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements. Specifically, a change in one element causes changes in other elements. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Starbucks McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Starbucks business strategy is based on product differentiation with the focus on the quality of products and services. Moreover, the coffee chain giant effectively positions Starbucks stores as a ‘third place’ away from home and work, where customers can meet friends, relatives or spent time alone. Currently Seattle-based international coffee chain is positioning itself as a digital third place as well. Technological innovations and intensive integration of technology into various business processes in general and ordering process in particular represent another important aspect of Starbucks business strategy. The launch of Mobile Order & Pay feature, which allows customers to buy without getting in line, the launch of voice ordering app and “sending text message notifications to customers in the Seattle area when their mobile orders are ready”[1] can be mentioned to illustrate this point. Structure Starbucks Corporation has a hybrid organizational structure which combines geographic, brand-based and functional hierarchy structures. Operations are divided into North America (USA and Canada) and International (China, Japan, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa, Latin America and Caribbean) divisions. Brand-based divisions, on the other hand, consist of Starbucks, Teavana®, La Boulange®,, Evolution Fresh™, Seattle’s…
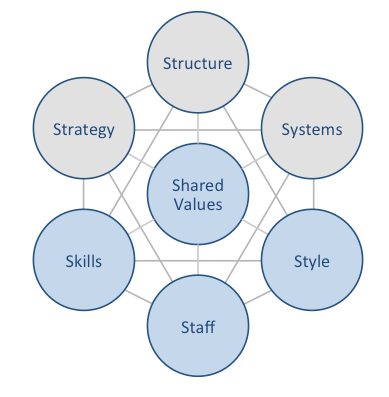
IKEA McKinsey 7S model explains how individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. McKinsey 7S framework considers strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are accepted as soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values represent the core of IKEA McKinsey 7S framework. This is because shared values guide employee behaviour with effects on their performance and ultimately on the bottom line for the business. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in IKEA 7S Model Strategy IKEA business strategy is based on the IKEA Concept, which is built upon the combination of function, quality, design and value – always with sustainability in mind. Moreover, the Swedish furniture chain offers cost advantage value for customers. Accordingly, IKEA business strategy involves offering increasing variety of products for the lowest prices. Regular engagement in new market development and benefiting from strategic alliances constitute additional pillars of IKEA business strategy. Structure IKEA organizational structure is unique and highly complex. The home improvement and furnishing chain maintains uniqueness and complexity its corporate structure in order to pay less taxes. The company can be divided into three large groups: franchise, range and supply and industry. Large scale of the business that integrates 11 franchisees operating in more than 500 locations in 63 countries[1] necessitates hierarchical organizational structure. Nevertheless, the Swedish furniture chain has proved to be successful in overcoming common weaknesses of hierarchical organizational structure such as high level of bureaucracy and lack of flexibility of the business. Systems IKEA business relies on a set of systems. These include employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation…
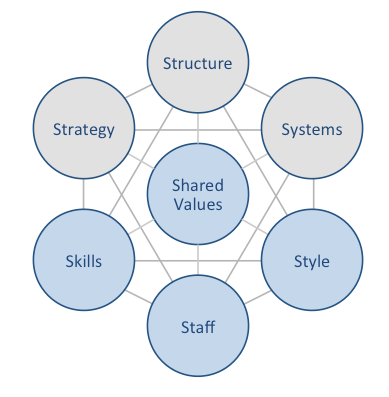
McDonald’s McKinsey 7S framework illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of McDonald’s McKinsey 7S framework, because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in McDonald’s McKinsey 7S Model Strategy McDonald’s pursues business strategy of cost leadership and an aggressive international market expansion. The company is able to operate with low operational costs due to economies of scale enjoyed to an enormous extent. Moreover, along with operating company-managed restaurants, McDonald’s capitalizes on the high level of brand awareness via franchising. High speed of customer services, universality of the taste and cleanliness of restaurants worldwide also belong to the list of competitive advantages for the fast food giant. Structure McDonald’s has divisional organizational structure and fast food chain’s business operations are divided into four divisions according to geographical locations. These divisions consist of United States, Europe, Asia/Pacific, Middle East and Africa (APMEA) and other countries. The company benefits from divisional organizational structure in a way that managers are free to make decisions taking into account unique aspects of respective markets. Systems There is a wide range of systems that enable McDonald’s operations at a global scale. These systems include but not limited to employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing and customer relationship management system. Moreover, the fast food chain also relies on advanced business intelligence system and knowledge management system.…
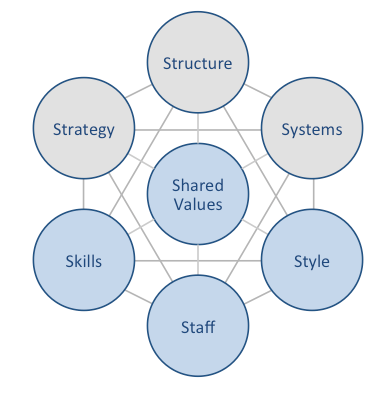
Amazon McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven key elements of businesses can be united to increase effectiveness. According to this model strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements. Specifically, it argues that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Amazon McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Amazon McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Amazon adheres to cost leadership business strategy. Three main pillars of Amazon business strategy are competitive prices, great range and speed of delivery. The largest internet retailer in the world has been able to sustain this strategy thanks to economies of scale, innovation of various business processes and regular business diversification. Moreover, Amazon business strategy places a great emphasis on encouraging communication among various components of its ecosystem. These components of Amazon ecosystem include merchants, writers, reviewers, publishers, apps developers, and the information market of commentators, analysts, journalists and feature writers. Additionally, customer obsession and focus on Amazon leadership values represent important cornerstones of Amazon business strategy. Structure Amazon organizational structure is hierarchical. It is difficult for the company to adapt an alternative structure such as divisional or matrix due to its gigantic size. Specifically, the e-commerce giant employs approximately 1,3 million people who serve hundreds of millions of customers worldwide.[1] The key features of Amazon corporate structure include flexibility of the business; which is unusual for a company of such a big size and stability in the top management, i.e. little turnover in the senior management team. Reliance on hybrid project…
