Posts by John Dudovskiy
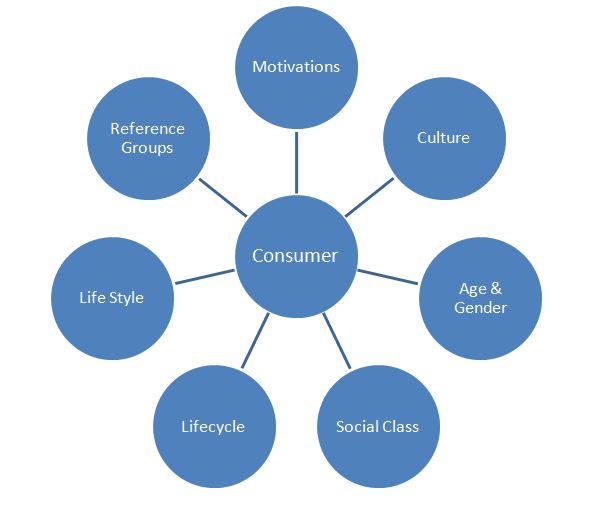
Generally, factors impacting consumer behaviour include motivations, culture, age and gender, social class, lifecycle, life style, and reference groups etc (Arnould et al., 2002, Agwaral, 2006, Hudson, 2008). Full range of factors impacting consumer behaviour can be divided into psychological, situational, and social categories and each of these categories is discussed in more detail further below. Figure 1. Factors Impacting Consumer Behaviour Psychological and Personal Factors Impacting Consumer Behaviour Psychological factors impacting consumer behaviour include lifestyle, interests, occasions for the use of products and services, benefits sought for the use of products and services etc (Batra and Kazmi, 2008). Personal factors affecting consumer behaviour is related to psychological factors and they include attitudes, motivations, perceptions, occupation ect. Lifestyle is one of the most important consumer variables and an important base for customer segmentation (Majumdar, 2010). Therefore, lifestyle analysis is perceived as one of the critical components of marketing research initiatives. Values and lifestyle systems (VALS) represent framework that divide population into different categories according to psychological factors that are found to be correlated with their purchase behaviour (Assael, 2004). An initial VALS or VALS1 specified eight separate psychographic groups: innovators, survivors, thinkers, makers, achievers, strivers, believers and experiencers. According to VALS framework belonging to each group is associated with specific psychological profile and certain lifestyle. According to Hudson (2008) VALS represents a valuable framework in practical level, because businesses can develop products and services that targets unique needs of individual groups within the framework. However, VALS has been criticised on the grounds of being too abstract and too general and this criticism has caused the development of VALS2 that “classifies people into segments based on whether they control abundant or minimal resources” (Arnould et al., 2002, p.126) Figure 2. VALS2 Figure adapted from Arnould et al. (2002) According to VALS2…

Consumer Behaviour can be defined as “the study of why people buy the products they do and how they make decisions” (Hudson, 2008, p.40). The study of consumer behaviour is not new with economists such as Nicholas Bernoulli, John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern initially addressing issues of consumer behaviour about 300 ago. Generally, evolution of consumer behaviour as an important area within the broad field of marketing incorporates the following stages: First stage: economic man approach. The earliest approach to consumer behaviour, economic man approach perceives consumers to be thinking logically and rationally at all times in relation to decision making. According to Arnould et al. (2002) this approach to consumer behaviour has been subjected to criticism due to neglecting irrational aspect of consumer behaviour. Second stage: psychodynamic approach. Psychodynamic approach is mainly based on the work of famous psychologist Sigmund Freud (1856 – 1939) and this approach views consumer behaviour as biological influence of drivers that are beyond rational thinking capabilities of individuals (Blythe, 1997). Specifically, three facets of human psychology are identified as the ID, ego, and superego. Third stage: behaviourist approach. Behaviourist approach to consumer behaviour focuses on the impact of external factors on patterns of behaviour amongst individuals (Neal and Quester, 1997). The majority of literatures discussing behaviourist approach mention experiments conducted by Russian scientist Ivan Pavlov (1849 -1936), where dogs were taught to behave in certain ways in given conditions with organising impact of the same external factor in a repeated manner. Fourth stage: cognitive approach. This approach to consumer behaviour is based on Stimulus – Organism – Response model proposed by Hebb (Bray, 2008). As illustrated in figure below, according to this model once organism is impacted by an external stimulus the response to the stimulus directly affects the nature of the final…
By John Dudovskiy
Category: Consumer Behaviour
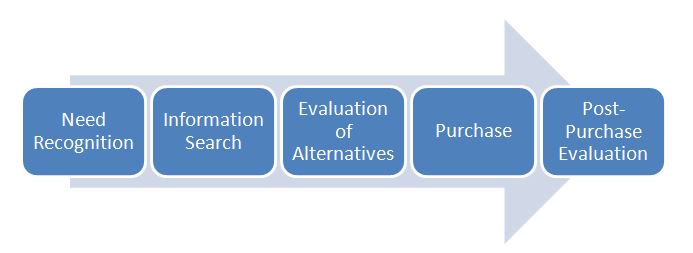
The consumer decision making process is complex and involves all the stages from problem recognition to post purchase activities. It has been noted that “the childhood and the human’s development has a crucial impact on personal decision making process” (Sokolowski, 2011, p.1) and the framework of consumer decision making process is found to be addressed by the majority of authors who have addressed the topic of consumer behaviour. All the consumers have their own needs in their daily lives and these needs make them make different decisions. These decisions can be complex depending on the consumer’s opinion about a particular product, evaluating and comparing, selecting and purchasing among the different types of product. Therefore, understanding and realizing the core issue of the process of consumer decision making and utilize the theories in practice is becoming a common view point by many companies and people. There is a common consensus among many researchers and academics that consumer purchasing theory involves a number of different stages. Depending on the different factors and findings, numerous researchers and academics developed their own theories and models over the past years. However, according to Tyagi and Kumar (2004), although these theories vary slightly from each other, they all lead to almost the same theory about the consumer purchasing theory which states that it involves the stages of search and purchase of product or service and the process of evaluation the product or service in the post-purchase product. Five Stage Model initially proposed by Cox et al. (1983) is considered to be one of the most common models of consumer decision making process and it involves five various stages. These stages are: recognition of need or problem, information search, comparing the alternatives, purchase and post-purchase evaluation. This simple model clearly illustrates and explains how the consumers make…

McDonald’s ecosystem, also referred to as McEcosystem comprises 40,031 restaurants in in 119 countries.[1] As of December 2021 in total 37,295 stores, or 93%, were franchised. The company provides a global brand, operating system, and financial tools to help these franchisees become successful. It has been noted that “franchisees are to McDonald’s as developers are to Facebook or Salesforce”[2]. In other words, franchisees help the fast food chain to develop new products thanks to their experience of dealing with customers on a daily basis on their respective local markets. For example, the most popular items in McDonald’s menu such as Big Mac, Filet-O-Fish, or McMuffin were invented by franchisees. It can be argued that there is a great potential for McDonald’s to further develop an effective ecosystem with positive implications on the bottom line. In order for Macdonald’s ecosystem to be efficient the following points need to be taken into account: 1. Facilitating collaboration. Back in time it cost franchisee-inventors of Big Mac, Filet-O-Fish and McMuffin considerable efforts to convince then CEO Ray Kroc to add their inventions on McDonald’s menu. Once added new meals proved to be hugely successful and they are among best selling items to this day. The fast food chain has expanded multiple times since that time. Accordingly, the potential for additions on the menu invented by franchisees has expanded as well. It is critically important to establish and maintain collaboration with all stakeholders in general and franchisees in particular in order to realize this potential in practice. 2. Promoting knowledge sharing. In order to achieve franchisee contribution to strengthen its ecosystem, McDonald’s needs to ensure knowledge sharing among franchisees efficiently. Such initiatives may include organizing online and offline forums aimed at new product development and rewarding franchisees who contribute to knowledge sharing the most. 3. Effectively using the…
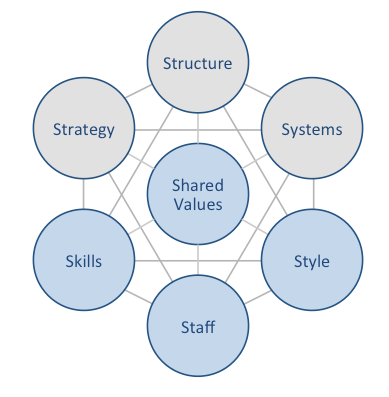
McDonald’s McKinsey 7S framework illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of McDonald’s McKinsey 7S framework, because shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in McDonald’s McKinsey 7S Model Strategy McDonald’s pursues business strategy of cost leadership and an aggressive international market expansion. The company is able to operate with low operational costs due to economies of scale enjoyed to an enormous extent. Moreover, along with operating company-managed restaurants, McDonald’s capitalizes on the high level of brand awareness via franchising. High speed of customer services, universality of the taste and cleanliness of restaurants worldwide also belong to the list of competitive advantages for the fast food giant. Structure McDonald’s has divisional organizational structure and fast food chain’s business operations are divided into four divisions according to geographical locations. These divisions consist of United States, Europe, Asia/Pacific, Middle East and Africa (APMEA) and other countries. The company benefits from divisional organizational structure in a way that managers are free to make decisions taking into account unique aspects of respective markets. Systems There is a wide range of systems that enable McDonald’s operations at a global scale. These systems include but not limited to employee recruitment and selection, team development and orientation, transaction processing and customer relationship management system. Moreover, the fast food chain also relies on advanced business intelligence system and knowledge management system.…
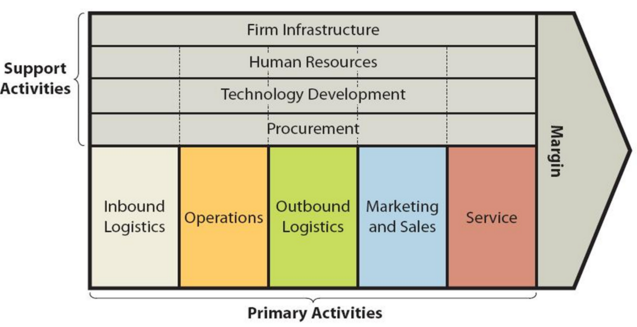
Value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The figure below illustrates the essence of McDonald’s value chain analysis. McDonald’s value chain analysis McDonald’s Primary Activities McDonald’s Inbound logistics McDonald’s inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials and using them to produce its burgers and other items in the menu. Raw materials for the fast food chain include meat, raw vegetables, ketchup, mayonnaise, napkins etc. Economies of scale are the main source of value creation in McDonald’s inbound logistics. The fast food giant has been pursuing backwards vertical integration strategy. This strategy involves companies to expand their roles and capabilities to complete tasks formally fulfilled by other companies in their supply chain. Specifically, McDonald’s “grow their own beef through contracted producers, process their own meat, create their own spices and mixes in factories that they contract, grow their own potatoes and other vegetable through contracted producers, transport their goods on their own.”[1] Backward vertical integration strategy allows the fast food chain to control the quality of their ingredients and reduce the costs of supply. McDonald’s Operations McDonald’s operates more than 40,000 company-owned and franchised restaurants. As of December 2021 in total 37,295 stores, or 93%, were franchised[2]. McDonald’s franchise restaurants have one of the following formats: conventional franchise, developmental license or affiliate.[3] Conventional franchising involves franchisees paying rent and royalties on the percentage of sales along with the payment of initial fees when opening a new restaurant. In this type of franchising, McDonald’s Corporation owns the land and building or secures a long-term lease for the restaurant location and the franchisee pays for equipment, signs, seating and décor.[4] Developmental license involves licensees providing capital for the entire business, including the real estate interest.[5] In developmental license…

McDonald’s CSR is an interesting topic due to the size and scope of the operations of the company. The fast food giant had formulated its 2020 Aspirational Goals that explain the measures of sustainable sourcing of foods and packaging, providing balanced choices to customers, developing and operating environmentally efficient McDonald’s restaurants and supporting local communities to be initiated by the company. By the end of 2020 the fast food giant achieved or substantially achieved the majority of its aspirational goals. The company releases The Good Business Report annually and it includes the details of McDonalds CSR programs and initiatives engaged by the company. McDonald’s Supporting Local Communities McDonald’s claims to be improving the lives of children and their families via the support of Ronald McDonald House Charities (RMHC) and other organizations. According to McDonald’s this support addresses the needs such as education and physical activity The company is also proud to support the network of over 260 local chapters of RMHC spanning over 60 countries and regions that creates, finds and supports programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children and their families. In 2020, the fast food chain announced a five-year, USD10390 million commitment to RMHC. McDonald’s Educating and Empowering Workers McDonald’s Hamburger University, founded in 1961, comprises 8 campuses around the world and provides training for McDonald’s Franchisees, managers and employees In Europe, McDonald’s and participating Franchisees have pledged to offer 45,000 apprenticeships by 2025[1] Labour and Human Rights at McDonald’s The company requires its suppliers to adhere to the Supplier Code of Conduct. The Code clarifies requirements of McDonald’s about issues related to Human Rights, Environmental Management, Workplace Environment and Business Integrity In 2018, the fast food chain introduced McDonald’s Human Rights Policy, which outlines its commitment to respect its people and their…

McDonald’s 7Ps of marketing comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in McDonald’s Marketing Mix (McDonald’s 7Ps of Marketing) McDonald’s restaurants offer a substantially uniform menu, although there are geographic variations to suit local consumer preferences and tastes. The fast food chain sells a wide range of fast food products such as hamburgers and cheeseburgers, Big Mac, Quarter Pounder with Cheese, Filet-O-Fish, several chicken sandwiches, Chicken McNuggets, wraps and french fries. The company also offers salads, oatmeal, shakes, McFlurry desserts, sundaes, soft serve cones, pies, soft drinks, coffee, McCafé beverages and other beverages.[1]Although, the company has long announced its pledge to increase the nutritional value of its meals, McDonald’s foods widely remain to be perceived as unhealthy. Place Element in McDonald’s Marketing Mix (McDonald’s 7Ps of Marketing) There are 40,031 McDonald’s restaurants in 119 countries.[2] As of December 2021 in total 37,295 stores, or 93%, were franchised. According to its aggressive expansion business strategy, the company aims to establish its presence in urban, as well as, in rural areas. The company states that “McDonald’s looks for the best locations within the marketplace to provide our customers with convenience. We build quality restaurants in neighbourhoods as well as airports, malls, tollways, and colleges at a value to our customers”.[3]. Generally, major fast food restaurants tend to cluster and in most locations, where there is a McDonald’s, there is also a Burger King right across the street.[4] Price Element in McDonald’s Marketing Mix (McDonald’s 7Ps of Marketing) McDonald’s pricing strategy comprises the following: 1. Economy pricing. McDonald’s follows cost leadership business strategy and accordingly, its foods and drinks are offered for competitive prices. The fast food chain offers customers the possibility to dine for a fraction of costs that are charged…

McDonald’s marketing strategy relies upon an extensive utilization of individual elements of the marketing communication mix. Specifically, McDonald’s marketing communication mix comprises print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing. McDonald’s marketing and promotional efforts focus on value, quality, food taste, menu choice, nutrition, convenience and the customer experience McDonald’s Print and Media Advertising McDonald’s marketing strategy attempts to integrate the elements of creativity and uniqueness in its print and media advertising. For example, the company has launched ‘Easy Morning’ print ads with the tagline “In the morning not everything is as easy as breakfast at McDonalds”, and a humorous attempt has been made to show an appropriate time to eat burger via a print ad. McDonald’s spends considerable amount of financial resources for print and media advertising. These investments amounted to USD 82.9 million, USD 329.2 million and USD 81.5 million for 2021, 2020 and 2019 respectively. Particularly, in 2020 the fast food chain made significant investments in brand communications.[1] The company has launched some controversial marketing campaigns as well. These include commercial in UK that exploits a child’s grief over the death of his father, “Carry On,” campaign referencing public tragedies including 9/11 and the Boston Marathon bombings and others. McDonald’s viral marketing also plays an instrumental role in terms of spreading the marketing message among the members of the target customer segment. The most noteworthy McDonald’s viral marketing campaigns include “Ask McDonald’s YouTube campaign” in Canada, ‘McDonald’s GOL!’ marketing video clip that attracted more than 10 million views and others. McDonald’s Sales Promotions Sales promotion is a popular marketing technique with McDonald’s and other fast food chains. McDonald’s uses the following sales promotions techniques: Competitions. Free breakfast delivery promotion according to mobile nominations[2] Seasonal promotions. “”McPick 2,” a limited-time…
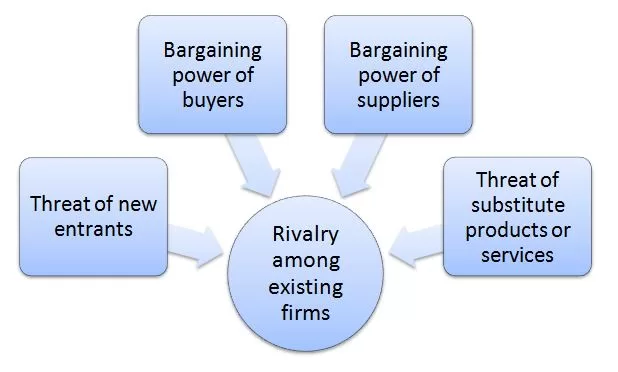
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. McDonald’s Porter’s Five Forces are represented in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in McDonald’s Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into fast food chain industry is moderate. Potential entrants into fast food chain industry have to deal with the following factors. 1. Massive capital investment requirements. Establishing a fast food chain requires huge financial investments to create an infrastructure, secure leases for locations, purchasing equipments and recruiting staff, among others. Securing funding for a new fast food venture can prove to be challenging taking into account high level of market saturation internationally. 2. Economies of scale. Major market players such as McDonald’s, Starbucks Coffee, Burger King, KFC and Subway substantially benefit from the economies of scale with positive implications on their cost structure. New market entrants, on the other hand, cannot benefit from the economies of scale to similar extend and this may prove to be a significant industry entry barrier. 3. Creativity and innovation. Despite fast food industry entry barriers such as huge capital requirements and economies of scale mentioned above, there is still a chance for new companies to successfully enter the industry. They can do so by innovating in terms of foods to offer, as well, as achieving greater technological integration into various business processes. Bargaining power of buyers in McDonald’s Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of McDonald’s buyers is immense. The following set of factors, among others determines customer bargaining power in fast food industry: 1. No switching costs to competition. Customers can switch from McDonald’s to any other fast food chain such as KFC, Pizza Hut, Starbucks and Burger King with no…
