
Airbnb segmentation, targeting and positioning consists of a set of consequent activities that divide customers into different groups and identify specific groups to be targeted. The accommodation and experience marketplace positions its services in a way that best appeals to the needs and wants of members of this group. Airbnb uses the following types of positioning: 1. Multi-segment positioning. The global lodging company uses multi-segment type of positioning targeting more than one segment with different service packages. For example, the company lists cost-effective apartments for rent for cost-conscious customer segment, whereas Airbnb Plus package targets customers who value advanced quality and design and are willing to pay more. Recently, the platform launched its Airbnb Luxe line of premium apartments that has been positioned as ‘extraordinary homes with five-star everything’ targeting premium customer segment. 2. Anticipatory positioning. Airbnb uses anticipatory positioning, launching services for a market segment that has low turnover with the anticipation that the turnover will increase in the future. Adventures services such as ‘Around the World in 80 Days’ and experiences of “Becoming a Beekeeper” can me mentioned as examples of Airbnb services with anticipatory positioning. The following table illustrates Airbnb segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Airbnb target customer segment Accommodation Experiences & Adventures Geographic Region More than 191 countries and regions and about 100000 cities More than 30000 experiences worldwide Density Urban/rural Urban Demographic Age 18-45 18-60 Gender 54% Females & 46% Males[1] Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Full Nest III Empty Nest I Empty Nest II Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Empty Nest I Occupation Students, employees, professionals, Students, employees, professionals, senior manager, executives Behavioral Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core…

The concept of marketing mix (also known as 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Airbnb marketing mix (Airbnb 7Ps of marketing) below involves the analysis of these elements for the global hospitality service brokerage company. Product Element in Airbnb Marketing Mix Airbnb can be used to find places to stay and various tourism experiences around the globe. It is important to note that Airbnb does not own places or does not host the experiences it offers. It is only a platform between service providers and consumers. The global hospitality service brokerage company has been increasing the range of its services regularly. Started only as s website that can be used to find bed and breakfast type of accommodation in 2008, today Airbnb offers a wide range of hospitality services. These include places to stay for various tastes, purposes and budgets, concerts, adventures, experiences and restaurants. Place Element in Airbnb Marketing Mix There are more than 191 countries and regions and about 100000 cities with Airbnb listings[1]. Airbnb offices are located in 34 cities worldwide.[2] The listings of the accommodation and experience marketplace are not concentrated in any single market. Less than 3% of all active listings are in New York City, London, and Paris. No one city accounts for more than 1% of our listings worldwide.[3] Price Element in Airbnb Marketing Mix Airbnb pricing strategy can be described as economy pricing. Airbnb is widely recognized as the most affordable option of finding an accommodation. The global lodging company charges hosts only 3% booking fee and guests are also charged a service fee (which Airbnb collects directly), and it may collect a VAT (value-added tax) in some jurisdictions. Guests usually have access to common facilities such as their…

Airbnb brand proposition is rooted in travel, communities, people and experiences and this proposition is placed at the core of Airbnb marketing strategy. Moreover, Airbnb marketing strategy is based on the following three principles: 1. Successful brand partnerships. The travel company has engaged in a number of mutually beneficial partnerships with other brands in order to achieve global brand exposure and create a buzz on the social media. The list of successful Airbnb partnerships include KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, UK bookstore chain Waterstones and even the French government.[1] 2. Celebrity endorsement and social influencers. The peer-to-peer lodging company has been quick to leverage the use of its services by celebrities. The list of celebrities who contributed to spread the word about Airbnb include Mariah Carey, Grande, Lady Gaga, Britney Spears, Channing Tatum and others. The company has been also effective in initiating publicity stands to attract the attention of social media influencers such as journalists, bloggers, YouTubers, podcasters and Instagram stars. For example, Airbnb has sailed a full-size floating size along the Thames River in 2015 to celebrate new rules to support home sharing in London.[2] This particular campaign generated hundreds of press coverage in the UK with positive implications on the level of Airbnb brand awareness. 3. Developing and strengthening the community. From early on, the global hospitality service brokerage company focused on developing its community consisting of both types of customers – hosts, as well as, guests. Airbnb encourages regular communication, detailed profiles and strong reviews in the community. Airbnb Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Airbnb marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Airbnb. Moreover, the report contains analyses of…
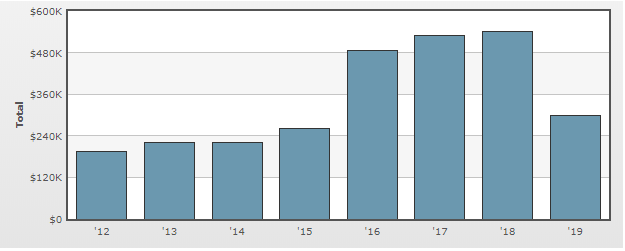
Airbnb PESTEL stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors effecting the peer-to-peer lodging company. It is an important analytic tool used to analyse external factors affecting businesses for strategy development. Political Factors in Airbnb PESTEL Analysis There are some political factors at the local and global scales that affect Airbnb revenues in direct and indirect manners. Issues with governments over the taxes and opposition from local governments and residents are the most important political factors for the peer-to-peer lodging company. Issues with governments over the taxes In the US, there is a dispute between a number of local governments and Airbnb over the allocation of responsibility to collect and pay occupancy taxes. A number of local and foreign governments have criticised Airbnb for not paying housing and/or other relevant taxes and they have been trying to take action with varying levels of success. It has been noted that in the US, “from Nashville to New Orleans to Honolulu, Airbnb is battling local officials over requests to collect occupancy taxes and ensure that the properties listed on its site comply with zoning and safety rules.”[1] The company lobbies its interest hiring firms such as KDCR Partners and Fulcrum Public Affairs in attempt to decrease government oppositions to the business. As illustrated in figure below, Airbnb annual lobbying budget is not massive though, compared to other multinational companies and in 2018 it amounted to USD 540,000.00. Annual Lobbying by Airbnb Opposition from local governments and residents Airbnb has faced opposition from local governments and protests from local residents due to perceived negative impact of the global hospitality service brokerage company to neighbourhoods. One of the major points of concerns in local communities relates to negative impact of the travel industry disruptor on local housing prices. There…
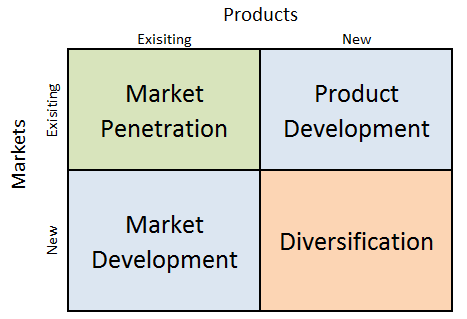
Airbnb Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the global hospitality service brokerage company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for companies. These consist of market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Airbnb Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Airbnb uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration involves the sales of existing products to existing markets. The accommodation and experience marketplace uses market penetration strategy extensively. Airbnb marketing strategy and exceptional customer services play instrumental role in engaging in market penetration by Airbnb. 2. Product development. This strategy is associated with developing new products to sell to existing markets. Product development is one of the main growth strategies for the global rental and experiences platform. Specifically, starting only as a short-term accommodation provider in 2008, Airbnb consequently increased its service portfolio to include experiences, adventures and restaurants services. 3. Market development. Market development strategy refers to finding new markets for existing products. The global rental and experiences platform aggressively engages in market development. Airbnb started its operations in San Francisco, California and today it has more than 6 million listings in more than 191 countries and regions worldwide.[1] Moreover, there are about 100000 cities with Airbnb listings.[2] 4. Diversification. Diversification can be explained as developing new products to sell to new markets. The global lodging company has engaged in diversification business strategy a number of times. Entering the industry as cost-effective accommodation provider for cost-conscious travellers, Airbnb has diversified the business to also serve premium market segment with respective offerings such as villas, mansions and even castles. Airbnb Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Airbnb Ansoff Matrix. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks…
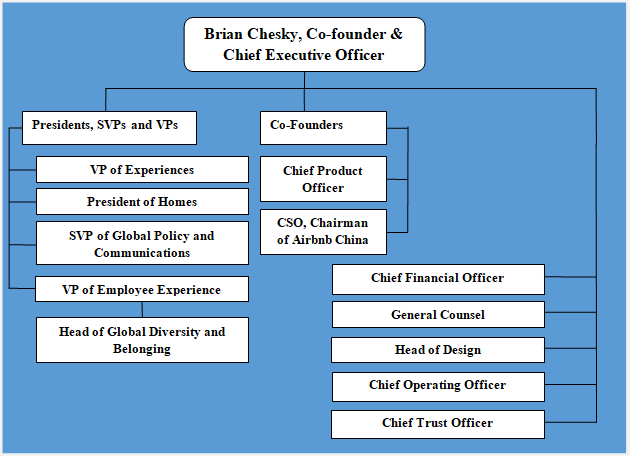
Since its founding in 2008, Airbnb organizational structure has been subjected to changes a number of times to adapt to the growth of the business in at a rapid pace. Furthermore, diversification of the business beyond home rentals to include experiences, adventures and restaurant services necessitated massive changes in its organizational structure. One of the main features of an effective organizational structure is to ensure a rapid flow of information across the company. In order to achieve this, Airbnb CEO Brian Chesky turned to executives from Apple, Facebook, Google and Amazon for advice on how to better organize the company.[1] The latest corporate restructuring at the peer-to-peer lodging company gave more decision making powers to its new business development teams. Holacracy is another important feature of Airbnb organizational structure. Holacracy can be explained as a type of organizational structure where “power is distributed throughout the organization, giving individuals and teams more freedom to self-manage, while staying aligned to the organization’s purpose.”[2] Airbnb organizational structure can be also branded as inter-supportive matrix structure. Airbnb corporate structure integrates many small teams of up to 10 people. The global rental and experiences company promotes the principle of village ecosystem in relationships between its teams. Specifically, if team members need a capability or resource, they can ask other team that has it ask them to share or cooperate. In other words, rather than operating as a separate identities, individual groups within the global lodging company cooperate and support each-other to a great extent and this feature can be specified as one of the main advantages of Airbnb corporate structure. Airbnb Organizational Structure Airbnb Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Airbnb organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five…

Airbnb leadership practices are contradictory to leadership principles taught in famous business schools worldwide. Nevertheless, the global success of the peer-to-peer lodging company is an undisputed indication of high level of efficiency of Airbnb leadership by CEO Brian Chesky. Airbnb leadership style is integrates the following elements: 1. Going to the source. Airbnb founders Brian Chesky, Joe Gebbia and Nathan Blecharczyk had little or no traditional management experience when they founded the global hospitality service brokerage company. Particularly, Brian Chesky had no business or entrepreneurial experience whatsoever. He dealt with the challenge using the method he calls ‘going to the source’ that is getting advice from top experts in the field. Sources for Airbnb CEO included the likes of Mark Zuckerberg, Reid Hoffman, Marc Andreessen, Jeff Weiner and Jony Ive. Going to the source remains a popular practice at Airbnb to these days and is likely to remain so for the foreseeable future. 2. Managing by visibility. Hands-on approach can be specified as one of the main aspects of Brian Chesky management style. For example, CEO is known to send emails to all employees each Sunday with “whatever is on his mind, which leads to staff replying to him and opening dialogues about various elements of the business”[1] Immersing himself into important details of various business processes allows Chesky to address root causes of the problem and to find innovative solutions to them. 3. Not leading in consensus during the crisis. In 2011 a female host’s apartment was destroyed, the renter took her valuables, and stole her identity while she was travelling for business.[2] While the Chesky gave a response to the incident, the host rebutted in a blog post his claims that the company had done everything it could to help her[3]. Opinions differed within Airbnb senior…

Airbnb, the lodging colossus, has been prudent from the financial point of view. It is important to note that the company hasn’t raised any money from investors since March 2017, when it raised USD448 million. CEO Brian Chesky has pledged to hold an IPO for the 10-year-old company before 2020 when some employee stock grants expire.[1] At a close look, Airbnb business strategy consists of the following three elements: 1. Following a platform business model. A platform business model can be defined as a “business model that focuses on helping to facilitate interactions across a large number of participants”[2] In case of Airbnb, participants are host who offer their properties or organize experiences for guests and travellers who use their services. Airbnb does not own any real estates it lists, not does it host events and experiences it offers. It serves as a broker between suppliers and consumers, receiving a commission of 9% to 15%. 2. High level of technology integration into various business processes. It is a cornerstone of Airbnb business strategy. The company uniquely leverages technology to economically empower millions of people around the world to unlock and monetize their spaces, passions and talents to become hospitality entrepreneurs.[3] The travel industry disruptor currently uses machine learning to improve search, prevent fraud, help hosts optimize pricing, match users with the most relevant listings and other practices vital for the business. Moreover, Airbnb is exploring machine learning algorithms and AI to build a deeper understanding of images, improve reviews using natural language processing (NLP) and support more advanced search using NLP. 3. Focus on community and trust. Cultivating community and maintaining trust among stakeholders is one of the solid bases of Airbnb competitive advantage. The global lodging company maintains a community centre as a place to connect…

Airbnb Inc. is a global hospitality service brokerage company. It is an online marketplace for peer-to-peer lodging, as well as, tourism and experiences services. Founded in 2008 in San Francisco, USA, Airbnb has become a lodging colossus and travel industry disruptor with more than 6 million listings in more than 191 countries and regions worldwide. There are about 100000 cities with Airbnb listings and 500 million Airbnb guest arrivals all-time. Moreover, more than 2 million people on average stay on Airbnb each night and there are more than 30000 Airbnb experiences worldwide. The company employs about 5000 employees worldwide. Airbnb’s business has doubled almost every year of its existence. It became profitable in 2017, with a profit of USD93 million on revenue of USD2.6 billion. This is a stark contrast from heavily loss-making sharing companies such as Uber and Lyft. It is estimated that in 2018 Airbnb surpassed the performance of the previous year and by 2020, its revenue is projected to be as much as USD8.5 billion. The peer-to-peer lodging company is valued at about USD 31 billion. The company’s mission is to create a world where anyone can belong anywhere, providing healthy travel that is local, authentic, diverse, inclusive and sustainable. Airbnb business strategy effectively contributes to this mission. Airbnb business strategy is associated with platform business model and accordingly, instead of owning the services it offers, the company engages as a broker between suppliers and consumers, receiving a commission of 9% to 15%. Moreover, increasing level of technological integration into various aspects of the business can be specified as one of the critical features of Airbnb business strategy. The global hospitality service brokerage company also places its community and trust among organizational stakeholders at the forefront of its business strategy. The travel industry disruptor has certain weaknesses…
