Posts by John Dudovskiy

Longleat Adventure and Safari Park, owned by Owned by Longleat Enterprises Limited has been operating from April 1966 and comprises more than “15 fabulous attractions, including the new multi pound Jungle Kingdom and Longleat House, one of the most stunning stately homes in Britain” (About Longleat, 2013, online). The following table illustrates Longleat Safari Park SWOT analysis: Strengths Lack of competition in the UK High quality of customer services Affordable prices for Longleat Hotels Weaknesses Not possible to reach the park by public transport “Mercedes Destroyed by Monkeys at Longleat Safari Park” and some other similar videos on YouTube demotivating people to attend to park Opportunities Increasing ranges of services Possibilities of attracting sponsors Increasing ranges of animals Threats Negative impacts of various environmental groups Visitors being attacked by animals Environmental changes posing risks for animals in Longleat Safari Park

Thorpe Park is one of the most popular theme parks in the UK and it belongs to Merlin Entertainments Group, the world’s second biggest visitor attraction operator with more than 30 million visitors annually and about 13,000 employees (Merlin Entertainment Group, 2013, online). Merlin Entertainments Group management have specified its mission statement as ‘The delivery of memorable experiences to our millions of guests underpinned by the very highest Health & Safety standards’. Besides Thorpe Park, Merlin Entertainments Group portfolio includes a range of famous entertainment brands such as Legoland, Chessington World of Adventures, Madame Tussauds, Heide Park, The London Eye, Warwick Castle, Sea Life, Alton Towers, Gardaland, and London Dungeons (Merlin Entertainment Group, 2013, online). SWOT analysis can be used in order to represent relevant secondary data in an appropriate format to assist in decision-making. SWOT analysis can be explained as a “review that helps planners compare internal organisational strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats” (Boone and Kurtz, 2013, p.46). The following table illustrates Thorpe Park SWOT analysis Strengths Greater ranges of ages of target customers (not only children) A wide range of rides Effective website design World-famous rides such as SAW, STELTH, and COLOSSUS Weaknesses High level of seasonality Geographical location not far from Chessington World of Adventures and Windsor’s Legoland Expensive prices Opportunities Introduction of new, innovative rides Increasing ranges of services Formation of strategic collaborations with other companies in catering and entertainment industry Threats Injuries to customers due to technical or other faults Further increasing influence of indirect competition – video games Negative impacts of relevant government legislations References Boone, L.E. & Kurtz, D.L. (2013) “Contemporary Marketing” Cengage Learning Merlin Entertainments Group (2013) Available at: http://www.thorpepark.com/misc/merlin-entertainments.aspx

Failure of plans in tourism industry, like any other industry is not a rare occasions. Plans may go wrong as a result of the impact of external environment, as well as, mistakes and shortcomings taken place in planning process. Shortcomings during the planning process resulting the in the failure of plans may take place in the following manners: Mistakes may occur during the first stage of planning process, which is study recognition and preparation. For example, management may decide to conduct relevant study on regional levels, when the scope of the study necessitates data collection on the national level, thus compromising the quality of the plan from the outset of the planning process. Moreover, individuals responsible for tourism planning may fail to formulate SMART objectives. In this case, objectives may be too vague and lack deadlines, and it would be not possible to assess the level of achievement of these objectives in an appropriate manner. Shortcomings planning process can also take place during the stage of survey of existing data. Specifically, such shortcomings may involve collection of outdated data, collection of irrelevant data, collection of data from biased and unreliable sources etc. Arguably, implementation of new surveys can be specified as one of the major stages in tourism planning process that accommodates the most mistakes. Such mistakes may be caused due to the incompetence and the lack of previous experiences and they may involve selection of inappropriate data collection tools, sampling mistakes, and others. Analysis of secondary and primary data can be mentioned as another stage in the planning process in tourism where mistakes can happen possibly resulting in the failure of the plan. Mistakes in data analysis may involve failure to identify common patterns within the information provided by survey respondents, failure to achieve a required level of depth…

Planning process for tourism industry comprises the following stages: 1. Study recognition and preparation. The first stage in planning process is associated with the recognition of the need for the strategy in order to obtain and/or increase competitive advantage to contribute to long-term growth. Depending on available budget and a range of other factors, studies may be planned to be conducted on local regional or national levels. 2. Setting of objectives or goals for the strategy. Goals and objectives need to be formulated according to SMART principle, where the acronym stands for specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-bound. 3. Survey of existing data. The survey of existing data or secondary research can be done through analysing relevant information available on wide range of tourism reviews websites, newspapers, magazines, books and other online and offline published materials. The types of data that need to be collected from these sources include, but not limited to patterns of tourist behaviours, availability and quality of accommodation, impacts of environmental factors, social and cultural characteristics of tourism destinations etc. Importantly, the survey of existing data should cover all three directions: the state of issues at present, projected changes in the state of issues, and outline of principles for monitoring for the future. 4. Implementation of new surveys. New surveys are conducted in order to obtain fresh data and/or fill the information gap in relation to the tourism industry. Surveys can be conducted through online or offline questionnaires or interviews. When conducting the survey it is very important to select respondents i.e. sample group members from amongst target customers for tourism destinations. 5. Analysis of secondary and primary data. In case of questionnaires, data analysis can be done through representing collected information in bar-charts, pie-charts etc. In case of interviews, on the other hand, data analysis may involve finding common patterns…

The term of tourism can be defined as “the temporary movement of people to destinations outside their normal places of work and residence, the activities undertaken during their stay in those destinations, and the facilities created to cater to their needs” (Gunn, 2002, p.9, as taken from Mathieston and Wall, 1982), and tourism has been assessed as the largest industry in the global scale. Tourism provides both, economic and non-economic benefits to any given country. Economic benefits of tourism to a national economy is straightforward and it is associated with creation of new jobs, decrease in the levels of unemployment, stimulation of production of products and services to be consumed by tourists and others. Non-economic benefits of tourism, on the other hand, include facilitation of cultural exchanges, contribution to the levels of knowledge, and facilitation of communication. Strategy can be defined as “the determination of the basic long-term goals and objectives of an enterprise, and the adoption of courses of action and the allocation of resources necessary for carrying out these goals” (Campbell et al., 2012, p.12, taken from Chandler, 1962). Accordingly, strategic planning can be explained as “the process of developing approaches to reach a defined objective” (Axson, 2010, p.25). Tourism industry has become more competitive than ever before, and therefore the importance of strategic planning for tourism industry is greater than ever before. The primary aim of the tourism industry relates to the achievement of adequate balance between the interests of public and private sectors. Three general principles of planning for tourism can be specified as anticipation, regulation and monitoring. Anticipation involves making projections about the future state of the tourism on the basis of relevant secondary and primary data. Regulation, on the other hand, is closely associated with the levels of regulation of tourist and affiliated organisations…
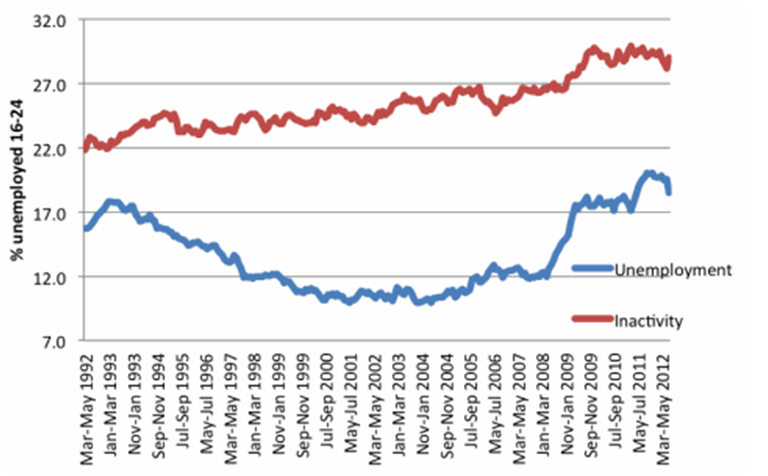
Unemployment is serious social and economic issue for the society, and unemployed individuals in many levels. Unemployment amongst young people is considered to be a special case as “young people between their required school life and their first job are very susceptible to unemployment” (Kurten, 2007, p.3). Moreover, a high level of youth unemployment has massive negative implications for the government on short-term and long-term perspectives. According to International Labour Office (2012), individuals aged between 16 – 25, who are available for work in 15 days, not currently employed, and are looking for employment opportunities in an active manner can be classified as young unemployed. However, in the UK, the age range of young unemployed individuals is specified as 16 – 24 years old. The level of youth unemployment has been consistently rising in the UK during the past several years (Figure 1). Moreover, it has been estimated that the numbers of young individuals who have not been working for more than 2 years have increased from 40,000 to more than 100,000 during the last four years, amounting to the increase of 168 per cent, and the numbers of Job Seeker Allowance claimants amongst young people have increased 315 per cent during the last six month (Al-Katib, 2012). Figure 1 Youth unemployment and inactivity statistics Source: Office of National Statistics (2012) The lack of skills and experience amongst young people in the UK is considered to belong to the list of major reasons behind increasing level of unemployment. Moreover, continuing economic problems in the EU and the UK have been found to have negative implications on the local job market in UK in general, and the job market for young people in particular. There is a stark difference on the levels of employment amongst young people who are engaged in…

This paper represents a business plan sample for Product Placement Opportunities®, a marketing services company that provides a platform for medium sized businesses to engage in product placement in a cost-effective manner through its website www.pp-opportunities.com. The business plan is built upon the gap in the in the marketing services industry that relates to allowing media, special event and computer games businesses to utilise their product placement opportunities in a direct manner, without using the services of marketing agencies. The comprehensiveness of the business plan is ensured by explaining mission statement, business strategy and objectives in a detailed manner. The main source of revenue for Product Placement Opportunities® relates to charging media, special event and computer games and other businesses for advertising their product placement opportunities on www.pp-opportunities.com. Price skimming pricing strategy has been chosen as the most suitable for the business. Analysis of principal personnel qualifications and experience contained within the plan highlights the ways in which competitive advantages are going to be derived. Moreover, cash flow forecast, profit and loss accounts forecast and balance sheet associated with the business plan have been developed on the basis of situational analysis and analysing market size for Product Placement Opportunities® services. The business plan also contains discussion related to relevant legal requirements, such as the company’s legal structure, commercial dealings, insurance and others. Glossary of Terms 1 1. Description of Business 2 2. The Mission and Vision Statement 3 2.1 Business Idea 3 2.2 Trading Status 4 2.3 Management & Ownership 4 2.4 Business Objectives 5 2.5 Business Strategies 5 3. Product and/or Service Plan 6 3.1 Product Placement Opportunities® service description 6 3.2 Product Placement Opportunities® Unique Features 7 3.3 Pricing Strategy& Value Issues 7 4. The Market Plan 8 4.1 Market Research Methodology 8 4.2 Secondary Research 8 4.3…

This paper represents a case study report devoted on the issue of increasing levels of youth unemployment in the UK. The report starts with a brief description of relevant existing key policies. This is followed by the identification of gaps on youth unemployment that need to be addressed. The report also contains discussions about relevant policy goals and the extent of their alignment with government preferences. Moreover, relevant policy options analyses are included in this report with detailed explanations of two the most suitable and appropriate policy options taking into account present economic and political circumstances in the UK. The report is concluded by making recommendations regarding the implementation of a specific policy option with detailed explanations provided. Youth unemployment is proving to be a serious challenge in the UK with highly negative short-term and long-term economic and social implications. Specifically, nearly 1.5 million, or more than 20 per cent of young people in the UK are found to be not engaged in education, employment or training (ACEVO, 2012). Moreover, according to estimations, the net present value cost of youth unemployment for the next ten years is going to amount to £28 billion (ACEVO, 2012). A wide range of negative implications of youth unemployment include negative impact on national economy for short-term and long-term perspectives, negative impact on future earning potentials of youth involved, detrimental impacts on mental and individual health of young individuals involved (Gregg et al., 2011), and increase in the level of anti-social behaviour within the society (Howell, 2005). The major reasons for increasing levels of youth unemployment in the UK have been specified as the recent global economic and financial crisis, failure in the UK immigration policies (Sunley et al., 2011), and systematic employment policy failures (Furlong, 2012). 1. Introduction: Nature of the Problem 1 2.…

It has been justly stated that Human Resource Development (HRD) is becoming a unique philosophy in organisations and central to bringing about effective change. Intensifying levels of competition in the market has caused the profile of HRD to increase for organisations in both sectors, private, as well as, public. HRD can be defined as “the process by which corporate management stimulates the motivation of employees to perform productively” (Roussel, 2006, p.195). In simple terms HRD can be explained as a set of initiatives and programs introduced by organisations with the aims of equipping its members with necessary skills and competencies to be able to meet the demands of their jobs. HRD can have a substantial positive impact on the level of implementation of organisational changes, as well as, on the overall outcome of change initiatives. As it has been briefly mentioned above, this impact can be maximised by organising relevant employee training and development programs that aim to increase the level of knowledge of employees about the importance of change and teaching employees about the ways of dealing with the change. Employee training and development programs offer a range of significant benefits at various levels that include positive implications on the level of employee productivity, higher level of employee motivation and job satisfaction and improvement on the quality of work.

There are several principal differences between public sector and private sector organisations, and these differences include organisational aims and objectives, organisational stakeholders and stakeholder expectations, the levels of public scrutiny, the levels of impact by political factors and others. Organisational Aims and Objectives Private sector organisations pursue the main objective of profit maximisation. Top level executive and marketing management in private sector organisations may attempt to create an image of pursuing other objectives as well such as protecting the environment, making the lives of people more convenient, and creating value for people in many other ways. However, these objectives for private sector organisations are secondary, and they have been developed only to aid the primary objective of profit maximisation. Public sector organisations, on the other hand, usually pursue aims and objectives other than profit maximisation. Moreover, objectives of public sector organisations in the UK may relate to a wide range of areas such as policing, providing education, providing healthcare etc. Organisational Stakeholders and Stakeholder Expectations Customers and shareholders are the most important organisational stakeholders for private sector organisations and their expectations are straightforward. Specifically, customers expect to get the best possible deal from the business, whereas the expectations of shareholders are closely associated with increasing profitability in short-term and long-term perspectives. In case of public sector organisations, on the other hand, stakeholder expectations are closely associated with the delivery of products and services in an adequate manner. It can be stated that population is the most important stakeholder group for public sector organisations. The Levels of Public Scrutiny Public sector organisations are generally subjected to scrutiny to a greater extent compared to private sector organisations in the media and from the government. Moreover, the main reason behind this difference relates to the sources of funding of these…
