Search results for: Segmentation, Targeting

McDonald’s marketing strategy is based on the following principles: 1. Think globally, act locally. McDonald’s is a truly global company with 40,031 restaurants in in119 countries.[1] The fast food chain is famous for standardisation of a wide range of business processes. Specifically, the company attempts to adjust its menu, as well as, restaurants settings to the tastes and preferences of local consumers. For example, it serves McSpaghetti in Philippines, Chicken Parm in Australia, Cookie and Cream Pie in Malaysia, Gracoro Burger in Japan and the list goes on. 2. Extensive focus on print and media advertising. The fast food giant focuses on print and media adverting component of marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other components. Specifically, McDonald’s advertising costs totalled USD 82.9 million, USD 329.2 million and USD 81.5 million for 2021, 2020 and 2019 respectively.[2] The marketing message attempts to associate the brand with enjoying tasty food and sharing goods moments with loved ones. 3. Targeting the widest range of customer segment. McDonald’s segmentation, targeting and positioning strategy attempts to appeal to the needs and preferences to the wide range of customers in terms of geographic location, demographic, behavioural, as well as, psychographic traits. 4. Cost leadership strategy. Within the framework of marketing communication mix (also known as 7Ps of marketing) McDonald’s prioritizes price over other elements. In fact, enjoying tasty food served in short duration of time is fast food chain’s unique selling proposition. The tasty food served by the company is often not a healthy one, but this is a separate issue impacting the brand. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value…

McDonald’s Corporation is a global fast food chain that serves more than 70 million customers in 119 countries employing about 200,000 people. McDonald’s operates two types of restaurants – company-owned and franchised restaurants with about 93% of restaurants belonging to the latter category (Annual Report, 2021) McDonald’s had disappointing financial results in 2014 with a sales growth of only 1% and a decline of operating income of 8%. Steve Easterbrook, McDonald’s Chief Brand Officer was promoted as the new CEO and President effective from March 1, 2015 to turn around the business. The list of major changes introduced by Steve Easterbrook includes reducing the use of antibiotics in chicken and massively restructuring the corporation, along with introducing changes in the menu. The turnaround efforts of the new CEO Steve Easterbrook proved to be effective with the company shares hitting record by the third quarter of 2015. However, Mr. Easterbrook was fired in 2019 due to breaching McDonald’s employee code of conduct through engaging in consent sexual relationship with female employees. New President and CEO Mr. Chris Kempczinski has proved to be effective so far, with McDonald’s emerging from COVID-19 pandemic stronger than before. In 2021, global comparable sales increased 17.0%, primarily due to strong sales performance across all segments from continued execution of the Accelerating the Arches strategy, as well as recovery from the impact of COVID-19 in the prior year. In 2021 consolidated revenues increased 21% (18% in constant currencies) to USD23.2 billion. At the same time, the fast food giant has certain weaknesses as well. These include the menu still consisting of primarily unhealthy food and the declining brand image of McDonald’s. Furthermore, the fast food chain has very high employee turnover and the company has attracted increasing negative publicity in the past few years. McDonald’s Corporation Report…

Square Inc. is a global financial services and digital payments company based in San Francisco, USA. Founded by co-founder of Twitter, Jack Dorsey and Jim McKelvey in 2009, the company started with selling card readers that enabled small businesses to accept credit cards. Since that time Square has evolved into an international financial services and mobile payments platform providing an ecosystem of integrated products and services. In 2019 Square processed USD106.2 billion of Gross Payment Volume (GPV), which was generated by nearly 2.3 billion card payments from 407 million payment cards. At the end of 2019, Square point of sale ecosystem had over 180 million buyer profiles and approximately 230 million items were listed on Square by sellers. The financial unicorn generated net income of USD375.4 million in 2019, employing 3,875 people full-time. Square business strategy is based on simplification of financial transactions and the company has developed an expanding ecosystem of products and services. The finance sector disruptor has certain business advantages such as the first mover advantage and strong leadership by CEO Jack Dorsey. At the same time, there are certain weaknesses associated with Square. These include lack of global presence, high employee turnover and dependence on payment cards networks. The payments company faces a set of potential threats as well such as increasing complexity of the business, cyberattacks and emergence of new competitors. Leadership style at Square can be classified as purpose-driven leadership and the payments company has a purpose to make it easier for everyone to participate in the economy. Furthermore, Square leadership appreciates teamwork and focuses on benefiting from team effort to a great extent. Square Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S…
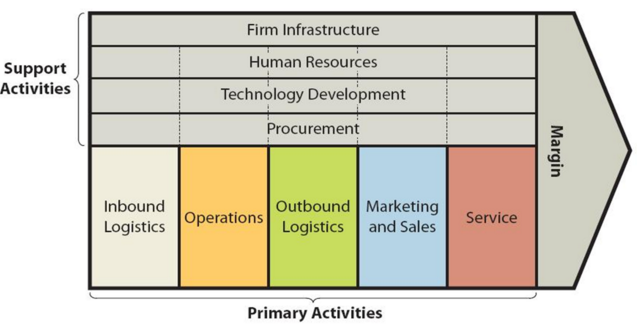
Tesla value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the electric automaker. Figure below illustrates the essence of Tesla value chain analysis. Tesla value chain analysis Primary Activities in Tesla Value Chain Analysis Tesla Inbound logistics Tesla inbound logistics involves the receipt and storage of raw materials to build electric vehicles, energy storage systems and solar panels. Along with a standard set of raw materials, Tesla uses a range of scarce materials such as aluminium, steel, cobalt, lithium, nickel and copper. In the US, the company receives parts at its Fremont automotive factory from thousands of suppliers worldwide, including from its very own Gigafactory in Sparks, Nevada. The electric automaker leases three warehouses totalling a massive 1.3 million square feet in the Oaks Logistics Centre in Livermore, California., just 20 miles northeast of the Fremont factory as a storage for raw materials. Additionally, in 2019, Tesla constructed 870,000-square-foot facility in Lathrop, California as a massive spare parts storage.[1] Currently, highly sophisticated inbound logistics practices are not one of the main sources of value creation for the electric automaker. Tesla works primarily on a build-to-order basis, which means bottlenecks in parts supply could be a big headache.[2] Accordingly, it is critically important for Tesla to establish long-term strategic relationships with suppliers. Tesla Operations Tesla conducts vehicle manufacturing and assembly operations at its facilities in Fremont, California; Lathrop, California; Tilburg, Netherlands and Shanhhai, China. Generally, Tesla operations can be divided into two segments: 1. Automotive. This segment comprises design, development, manufacturing, and sales of electric vehicles. The company produced and delivered approximately half a million vehicles in 2020.[3] The electric automaker started Model Y production at Gigafactory Shanghai in December 2020. The table below illustrates annual production capacities…

W.W. Grainger marketing strategy was traditionally limited to its famous product catalogues and print and media advertisement. The company CEO D.G. Macpherson admitted in 2019 that marketing was a new skill for the global industrial supply company, but the company was learning very quickly.[1] The necessity for improvement of Grainger marketing strategy is fuelled by intensifying competition in general, and competition from Amazon business in particular. Grainger’s total advertisement expense totalled to USD316million, USD241 million and USD187 million for 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.[2] Grainger unique selling proposition is associated with extensive range of MRO products and deep knowledge of company’s sales force regarding main product categories. Moreover, competitive advantages of industrial products distributor include advanced customer services and omni-channel sales strategy. Grainger 7ps of marketing has traditionally focused on product element of the marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other elements. The B2B distributor boasts an extensive product range that includes about 1,7 million types of products supplied by about 5000 suppliers worldwide. [3] Starting from a few years ago, however, Grainger marketing strategy had to change to a certain extent to increase its focus on the price element of the marketing mix. Specifically, due to the increasing threat from Amazon Business, Grainger had to cut profit margin in 2017 to decrease the prices of many products. Segmentation, targeting and positioning practices is an integral part of Grainger marketing strategy and the B2B distributor pursues multi-segment type of positioning. Specifically, the industrial supply company appeals to MRO products needs of all types of customers – small, large and medium. The company targets small and medium businesses through Zoro and MonotaRO websites, whereas large customers with more complex needs are targeted via maintaining face-to-face direct relationships with numerous Grainger sales force representatives. W.W. Grainger Report contains the above analysis…

Founded in Illinois, US in 1928, W.W. Grainger Inc. is a B2B distributor of maintenance, repair and operating (MRO) products and services. The global industrial supply company has more than 3,5 million customers and about 25000 employees worldwide. (Fact Book, 2020). The global MRO products distributor works with approximately 5000 suppliers internationally. In 2019 Grainger generated revenues of USD 11,2 billion, 3% increase compared to the previous year (Annual Report, 2019). Grainger pursues differentiation business strategy. Specifically, the B2B distributor differentiates on the basis of products, offering the widest range of MRO product categories. Grainger’s use of differentiation business strategy also extends to differentiated sales and services. The company delivers its products with high level of speed and convenience and employs highly qualified sales representatives with deep technical knowledge. Grainger has hierarchical organizational structure and its organizational culture is based on diversity and inclusiveness and value for technology and innovation. Moreover, focus on teamwork can be highlighted as one of integral components of Grainger organizational culture. Business development strategy for the B2B distributor integrates market penetration, product development and market development strategies. The industrial products distributor immensely benefits from the economies of scale and the company has an extensive experience and knowledge in selling MRO products. At the same time, Grainger has certain weaknesses that can have negative implications on long-term growth prospects of the business. High level of indebtness is a major issue for the company and as of December 2019, Grainger’s consolidated debts amounted to USD 2,4 billion. Moreover, with total 72% of revenues generated in the US in 2019 (Fact Book 2020), the B2B distributor is over-dependent on the home market in the US. W.W. Grainger Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces,…

Amazon.com Inc. was founded in 1994 in Washington and Amazon.com as a website became first active in July 1995 to become the largest online retailer in the world to offer Earth’s Biggest Selection in less than two decades. The e-commerce and cloud computing company generated revenues of USD 386 billion and earned a net income of USD 21.3 billion in 2020 alone (Annual Report, 2020) The e-commerce giant employs approximately 1,3 million full-time and part-time employees referred to as Amazonians (Annual Report, 2020). Amazon has declared its adherence to four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence and long-term thinking. These principles represent sources of Amazon’s competitive advantage. Amazon business strategy is a hybrid of cost leadership and business diversification. The online retailer also benefits from encouraging communication between various elements within its ecosystem and promotion of its leadership principles consisting of 16 points discussed in this report. The founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos prefers to base business strategy on things that do not change. Specifically, consumers will always want low prices, variety and speedy delivery of their orders. Amazon focuses on these facts via effective integration of information technology into various business processes. Combination of pragmatist, visionary and autocratic leadership styles are exercised at various levels at Amazon. The company has a hierarchical organizational structure. Nevertheless, it remains highly flexible to adapt to frequent changes in the external marketplace. Amazon organizational culture, on the other hand, is based on the principles of high level of cost-consciousness, constant reinvention and improvement of organizational culture and customer obsession. Major weaknesses associated with Amazon include seasonality of the business, low profit margins and lack of focus on specific product or service categories. Moreover, a weak competitive position of Amazon’s Fire Phone and damage to…

Search About us Number of ebooks 300+ Started in 2011 by John Dudovskiy, research-methodology.net is an educational portal that offers knowledge, resources and practical insights for conducting business studies. John Dudovskiy is a seasoned dissertation adviser and he has experience in assisting hundreds of students with their dissertations, reports and essays in business discipline. All materials published at research-methodology.net are designed to support and inspire professionals and students at all levels to conduct studies in the area of business. read more Business Analytical Tools SWOT is a strategic analytical tool for assessing strengths and weaknesses of a business, analyzing available opportunities and threats faced by the business. SWOT analysis can be used at organizational and personal levels. Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the e-commerce and cloud computing company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool used to assess external factors affecting businesses. PESTEL acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors impacting companies. PESTEL has recently evolved from PEST analysis once intensifying forces of globalization and intensifying forces of competition in the marketplace coupled with other set of factors increased the importance and potential impact of environmental and legal factors on businesses. The concept of marketing mix (also known as 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Companies manipulate with each element of the marketing mix according to its marketing strategy, as a part of its business strategy. Segmentation, targeting and positioning involves a set of consequent marketing decisions that constitute the core of company’s marketing strategy. Segmentation refers to dividing population into…

Airbnb Inc. is a global hospitality service brokerage company. It is an online marketplace for peer-to-peer lodging, as well as, tourism and experiences services. Founded in 2008 in San Francisco, USA, Airbnb has become a lodging colossus and travel industry disruptor with more than 6 million listings in more than 191 countries and regions worldwide. There are about 100000 cities with Airbnb listings and 500 million Airbnb guest arrivals all-time. Moreover, more than 2 million people on average stay on Airbnb each night and there are more than 30000 Airbnb experiences worldwide. The company employs about 5000 employees worldwide. Airbnb’s business has doubled almost every year of its existence. It became profitable in 2017, with a profit of USD93 million on revenue of USD2.6 billion. This is a stark contrast from heavily loss-making sharing companies such as Uber and Lyft. It is estimated that in 2018 Airbnb surpassed the performance of the previous year and by 2020, its revenue is projected to be as much as USD8.5 billion. The peer-to-peer lodging company is valued at about USD 31 billion. The company’s mission is to create a world where anyone can belong anywhere, providing healthy travel that is local, authentic, diverse, inclusive and sustainable. Airbnb business strategy effectively contributes to this mission. Airbnb business strategy is associated with platform business model and accordingly, instead of owning the services it offers, the company engages as a broker between suppliers and consumers, receiving a commission of 9% to 15%. Moreover, increasing level of technological integration into various aspects of the business can be specified as one of the critical features of Airbnb business strategy. The global hospitality service brokerage company also places its community and trust among organizational stakeholders at the forefront of its business strategy. The travel industry disruptor has certain weaknesses…

Established in 1977 in California, Apple Inc. is a global designer, manufacturer and marketer of mobile communication and media devices, personal computers, and portable digital music players. Apple is the largest IT company in the world by revenue and total assets and the second-largest mobile phone manufacturer. The company also sells a variety of related software, services, accessories, networking solutions, and third-party digital content and applications. Apple’s ability to design and develop its own operating systems, hardware, application software and services to provide its customers products and solutions with innovative design is placed at the core of its business strategy. As of September 2022, Apple had approximately 164,000 full-time equivalent employees . The net sales of the world’s largest IT company by revenue increased 8% or USD 28,5 billion during 2022 compared to 2021. Higher net sales in Services and Wearables, Home and Accessories categories played an instrumental role in achieving such a growth. Apple business strategy comprises focusing on design and capabilities of products and ever-strengthening the company’s ecosystem. The first company ever to be valued at USD1 trillion purposefully cultivates a reputation for not paying dividends to investors. In short-to-medium term perspective, Apple is working towards decreasing dependence of the business on the sales of iPhones. Leadership style at Apple is known to be democratic. CEO Tim Cook practices ‘quiet leadership’ and he is widely recognized as an effective leader. At the same time, a number of industry watchers and analysts criticize Tim Cook for the lack of innovative genius his predecessor legendary Steve Jobs used to possess. Apple has hierarchical organizational structure. Moreover, the company’s organizational structure also integrates product-based grouping with a focus on collaboration between different groups and divisions. Organizational culture of the multinational technology company, on the other hand, fosters creativity and innovativeness coupled…
