Posts Tagged ‘IT’
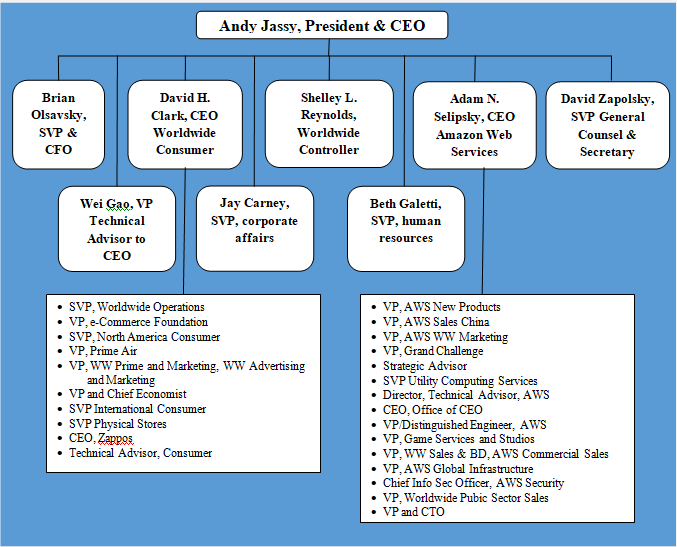
Amazon organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Senior management team include three CEOs and three senior vice presidents responsible for various vital aspects of the business reporting directly to CEO Andy Jassy. Amazon organizational structure has the following four key features: 1. Hierarchical corporate structure. Hierarchical structure at Amazon has developed due to the immense size of the business. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue employs more than 1,3 million people worldwide.[1] 2. Hybrid project groups. Amazon corporate structure integrates hybrid project groups when developing new products and services. Specialists from various departments are attracted according to their skills and competencies required for the project. These employees can be attracted part-time reporting to both, the head of their departments and project leaders, or they can engage in the project full-time reporting to project manager only for the duration of the project. 3. Flexibility of the business. It is important to note that despite its large size, unlike many other companies with hierarchical organizational structure, Amazon remains highly flexible to adapt to frequent changes in the external marketplace. Moreover, the online retail giant leads changes in external business environment; it has caused disruptive innovation in e-commerce and currently it is about to cause a disruptive innovation in global logistics industry. Successful organization of hybrid project groups plays an instrumental role in maintaining flexibility of the business. Amazon organizational structure integrates many small teams that deal with various aspects of the business. Amazon founder and former CEO Jeff Bezos is credited with the introduction of ‘two pizza rule”. According to this rule, meetings should be held in teams small enough that could be all fed with only two pizzas. “Two pizza rule” continues to this day under the new CEO Andy Jassy. 4. Stability in the top management.…

Amazon business strategy can be described as cost leadership taken to the extreme. Range, price and convenience are placed at the core of Amazon competitive advantage. The global online retailer operates with a razor thin profit margin and succeeds due to a combination of economies of scale, innovation of various business processes and a constant business diversification. Founder and first CEO Jeff Bezos believes in focusing as a business strategy on things that do not change. At the outset of the business he reasoned that people always want low prices, selection and fast delivery. Exceeding customer expectations on these points has remained as the core of Amazon business strategy. Innovation and technology the online retail behemoth uses are simply instruments to pursue this core strategy. Moreover, Amazon business strategy is guided by four principles: customer obsession rather than competitor focus, passion for invention, commitment to operational excellence, and long-term thinking.[1] The following four points constitute the cornerstones of Amazon business strategy: 1. Regularly entering into new niches and segments. Started only as an online shop for selling physical books in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online in the global scale. Sophisticated global logistics represents one of the solid bases of Amazon competitive advantage. The tech giant has used this advantage extensively to engage in successful business diversification. Recently, the company launched Amazon Home Services, a simple way to buy and schedule local professional services as a continuation of its diversification strategy.[2] Currently, the tech giant operates in increasing range of industries including e-commerce, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, consumer electronics, entertainment, digital distribution, B2B distribution, self-driving cars and supermarkets. As the largest internet company by revenue in the world, Amazon frequently disrupts the industries it chooses to enter. The e-commerce giant occasionally finds new niches and segments accidentally, while…
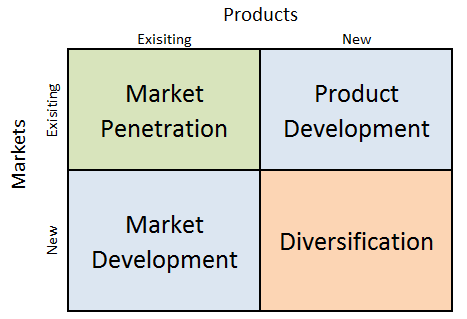
Amazon Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the e-commerce and cloud computing company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Amazon Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Amazon uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Amazon uses market penetration strategy aggressively. Sophisticated user experience features in general and recommendations feature on e-retailer’s website in particular play an important role in the application of market penetration strategy. Specifically, Amazon focuses on user experience personalization thanks to efficient application of data science and machine learning. The e-commerce giant collects and possesses a vast amount of data related to customers such as age, sex, lifestyle, habits and preferences. The company uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse this data and suggest products that a particular customer is highly likely to buy. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Product development is one of the core strategies used by Amazon. Started by Jeff Bezos selling only physical books online in 1997, today Amazon sells anything that can be sold online. The largest internet retailer in the world by revenue sells more than 500 million products, including products sold by third parties on Amazon platform. Top product categories include clothing, shoes, jewellery, home and kitchen appliances, books, electronic devices, sports and outdoor items and others. The e-commerce and cloud computing company produces increasing number of products under the private label as well. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Amazon is engaged in market development in a systematic manner. Started only in…

Uber corporate social responsibility is attracting a lot of interest among business researchers and practitioners recently. Not paying due attention to CSR aspect of the business has been traditionally one of the weaknesses associated with Uber under previous CEO and co-founder Travis Kalanick. The ride-hailing giant has even lost its license to operate in London in 2017 due to the lack of corporate social responsibility[1]. However, under the new CEO Dara Khowrowshahi the company has fully recognized the importance of conducting sustainable business and this change is communicated to internal and external stakeholders systematically. The largest mobility platform in the world has pledged to become a fully zero-emission platform by 2040, with 100% of rides taking place in zero-emission vehicles, on public transit, or with micro-mobility Uber CSR Programs and Initiatives Uber and Gender Equality and Minorities The company received the maximum score of 100% on Human Rights Campaign 2020 Corporate Equality Index 59,7% of total workforce are man and 40,3% of all workforce are women. In tech jobs, the majority 76,9% of employees are men, whereas women fill only 23,1% of tech positions Black or African American represent only 7,5% of the total workforce Water Consumption by Uber The global transportation technology company used 699,854 cubic meters of water globally in 2019 Mission Bay campus in San Francisco, USA is estimated to save round 2.5 million gallons of water through re-using the water Carbon Emissions by Uber The company has set a goal that 100% rides in US, Canadian, and European cities will be in electric vehicles (EV) by 2030. Uber Green program is being expanded make it easier for riders to choose to travel in hybrids or EVs The ride-hailing giant is committing USD 800 million in resources to help hundreds of thousands of drivers transition to EVs…

Uber is working towards developing its own ecosystem in order to increase customer loyalty with positive implications on company’s revenues. The development of Uber ecosystem has integrated the following key milestones: 1. Request API The development of Request API (application programming interface) has been viewed by industry analysis as the first step towards developing the ecosystem. It has been noted that “Request API gives third party developers the ability to integrate their application into Uber. So if you’re an airline or a restaurant booking application, you can create a situation whereby your flight delay was automatically notified to your Uber driver so that your pickup is correctly rescheduled.”[1] 2. Uber Eats The launch of food delivery service by the company as UberFRESH in 2015, later renamed as UberEAT in 2015 was an important move for the ride-hailing giant to expand beyond ridesharing. This is a major difference between Uber and its main rival Lyft. Specifically, when Lyft was concentrating solely on taxi services and ride-sharing for a long time before doing anything else; Uber senior management sought to differentiate the business using the same platform early on with positive implications on its ecosystem. 3. Uber Feed The update of app on November 2016 paved a way for further development of Uber ecosystem. Nowadays, Uber app learns from routines of users and scrapes their calendars for the address of their meetings across the town.[2] Particularly, Uber Feed is an important feature and it intends to gain customers attention during the ride. Uber Feed presents a stack of services Uber thinks customers might find useful during their trip. Customers can swipe left on Uber Eats to see which restaurants can deliver to their house in synch with their arrival time. Alternatively, if customers are running late to their destination, they can use…
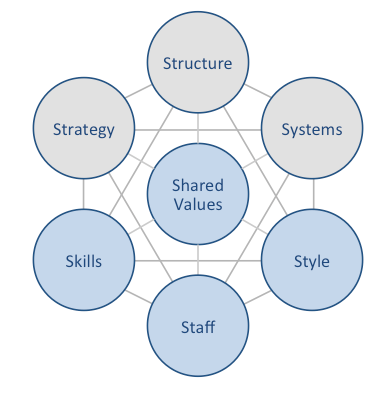
Uber McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Uber McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements Strategy Uber pursues cost leadership business strategy. The ride-hailing giant gains cost advantage thanks to internet-based nature of its business model that disrupted traditional taxi industry in the global scale. The international transportation technology company increases range of its services regularly to cater for the needs of greater numbers of customers. Moreover, Uber business strategy places a great emphasis on a high level of user convenience. Growing the business through acquiring adjacent businesses is another important aspect of Uber business strategy. Structure Uber organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Accordingly, the company is disadvantaged by the shortcomings of hierarchical structure such as ineffective communication across various departments, rivalry between departments that may compromise long-term growth prospects and high level of bureaucracy. Following the failed IPO in 2019, the CEO Mr. Khosrowshahi changed Uber organizational structure to increase his role in operational day-to-day management. As part of these changes, the positions of chief operating officer (COO) and chief marketing officer (CMO) were also eliminated. Systems Systems within McKinsey 7S model refer to daily activities and procedures that Uber staff use to provide ride-haling services to millions of customers worldwide. There is a wide range of various systems that are important for Uber’s long-term…
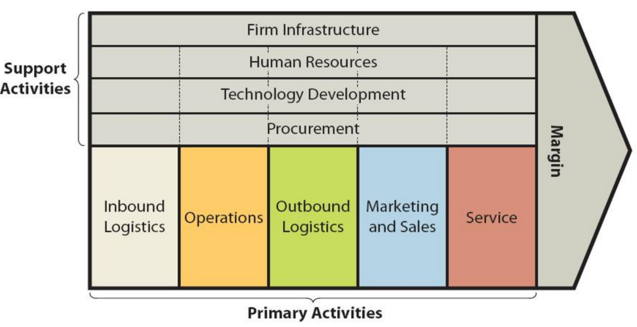
Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis. Uber Value Chain Analysis Uber Primary Activities Uber Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service. Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services. Uber Operations Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. Business operations are divided into four reportable segments: 1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages: a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and…
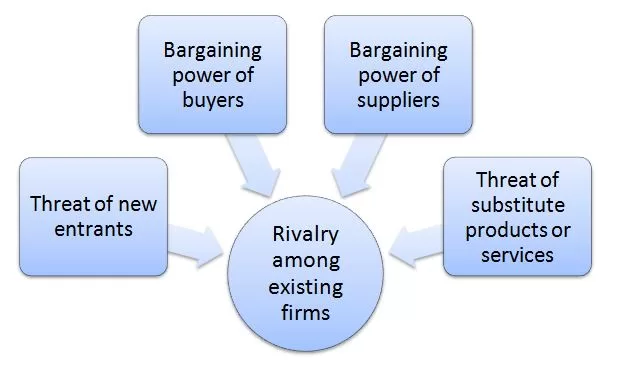
Uber Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework analyses five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in figure below: Uber Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Uber Porter’s Five Forces analysis Threat of new entrants into internet-based ride-hailing sector is significant. The following factors play role in the formation and extent of the threat of new entrants into mobility platform sector: 1. Simplicity of the business model. Nothing about Uber business model or its app is secret. In other words, Uber business model and its app can be replicated by any other company without massive amounts of capital requirements. Thanks to internet-based nature of the business model, new entrants to the market will not have issue to access distribution channels. Furthermore, due to low entry barriers into the ride-hailing industry, the numbers of local and global competitors for Uber have been consistently increasing during the past few years. 2. Scaling issues. While addressing technical aspects of the business such as developing ride-haling app and website may not be difficult, achieving necessary scale in operations is challenging for new entrants. In other words, mobility platform has to attract substantial amount of drivers in order to be successful and this requires time and massive capital investments. 3. Expected retaliation from existing market players. Current market leaders such as Uber, Lyft and Curb defend their territories fiercely and they are expected to retaliate against new entrants to the market. Bargaining power of buyers in Uber Porter’s Five Forces analysis The bargaining power of buyers in taxi industry is great. Buyer bargaining power depends on the following: 1. Abundance of offers. Buyer bargaining power is mainly fuelled by the abundance of competition in the industry. Uber customers are highly price sensitive. If…

Uber marketing mix (Uber 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in Uber Marketing Mix (Uber 7PS of Marketing) Uber is a service company and it does not sell products. Uber has clear advantages over regular taxi. These include clear overview of pricing prior to booking, one-tap rides, following drivers on map, cashless convenience and fare splitting, as well as feedback options. The range of services offered by Uber with brief descriptions is illustrated in table below: Service Descrption X Low cost option for the passengers looking for low cost rides for up to 4 riders XL Low cost option for the passengers looking for low cost rides for up to 6 riders Pool Car sharing: riders can bring one other person with them, thus saving on travel costs GO Ride in a hatchback Comfort Newer cars with extra legroom Flash Match with closest Uber Taxi or UberX AUTO Ride in Auto rickshaws, currently available in Bangalore and Pune only Access Taxi service with wheelchair access to cater to the need of elderly and people with disabilities. MOTO Booking bike rides around the city Premium A fleet of stylish vehicles to choose from. Uber Premium comprises Uber SELECT, Uber BLACK, Uber SUV and Uber LUX Green Sustainable rides in electric vehicles Scooters Electric scooters to help people to get around a city Transit Real-time public transit information in the Uber app WAV Rides in wheelchair-accessible vehicles RUSH Courier Package Service EATS Allows customers to order food on the go Uber services and descriptions Place Element in Uber Marketing Mix (Uber 7PS of Marketing) Uber is available in 71 countries around the globe.[1] The service has a high level of geographic concentration. In…

Uber marketing communication mix comprises print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing. Uber marketing communication mix is aimed to associate using Uber services with cost-efficiency, effectiveness and convenience. Uber Print and Media Advertising Uber uses traditional print and media advertising sparingly, mainly concentrating on social media and word-of-mouth marketing channels. Nevertheless, the global taxi technology company still uses TV ads, newspapers and magazine ads, posters and banners in selected locations. The ride-hailing giant is known for unconventional advertising techniques. These include putting ads on drones and having them taunt drivers stuck in traffic in Mexico City.[1] Marketing campaign “Boxes” as metaphor for excessive traffic jams in Asian cities, where the ad proposes ridesharing as a key part of the solution has been praised as innovative and appealing.[2] At the same time, Uber’s use of advertising has proved to be controversial in several instances. For example, a billboard in Egypt which says “I escaped from driving my mother-in-law home 64 times” was found to be offensive by local people[3]. In France, campaign offering men free rides with ‘incredibly hot chicks’ has been criticized as sexist, resulting in an apology from Uber France.[4] Recently, the largest mobility platform in the world started advertising Uber Eats services through selected radio channels in selected locations promoting earning potential through the service. Uber also uses celebrity endorsement in print and media advertising in an occasional manner. For instance, in 2018 the company signed an endorsement deal with Virat Kohli, captain of India’s cricket team to serve as Uber brand ambassador in India.[5] Uber Sales Promotions Uber uses various sales promotions techniques in an integrated manner. For the largest mobility platform in the world discounts, loyalty programs, promotions, refunds, and credits provided to end-users who are not customers totalled USD…
