
Warner Bros. is a subsidiary of Time Warner and during the year of 2012 alone the company has produced 18 films in English language internationally and 23 films in local languages around the globe (Annual Report, 2012). The portfolio of Time Warner along with Warner Bros. comprises a set of famous media and entertainment brands such as Time, New Line Cinema, Sports Illustrated, TNT, People, TBS, Cinemax, HBO and CNN. Time Warner has generated the revenues of USD 28.7 billion during 2012, with operating income amounting to USD 5.9 billion (Annual Report, 2012). Warner Bros. represents Film and TV Entertainment segment of Time Warner and during the year of 2012 Warner Bros. has generated USD 12 billion revenues which accounts to 39% of Time Warner total revenues. Warner Bros. vision is associated with ‘sharing stories from the most talented and creative voices in the industry in a consistent manner’. Core mission of Warner Bros. has been specified as ‘creating and distributing great stories to audiences around the globe’. Warner Bros. produces feature films in two formats: on its own and through co-financing arrangements with other companies. “Warner Bros. feature film strategy focuses on offering a diverse slate of feature films with a mix of genres, talent and budgets” (Annual Report, 2012. p.24). In other words, product differentiation strategy is the main business strategy currently pursued by Warner Bros. strategic level management. Attempts to lead technological changes mark another important aspect of Time Warner and Warner Bros. corporate strategy. Specifically, the company is taking digital efforts to the next level according to its principles of Contents Everywhere, and consumers are being provided with access to service thorough increasing numbers of platforms such as mobile devices in innovative manners. Warner Bros. is one of the leading global entertainment companies that has successfully…

PESTEL analysis can be explained as “a checklist to analyse the political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, environmental and legal aspects of the environment” (Rao et al., 2009, p.115). The framework assists with analysis of the impact of each of these individual aspects of external environment to be used in decision-making by senior management. PESTEL analysis for Warner Bros. is illustrated on the following table: Political Political situation in the US and foreign markets Censorship on media and entertainment in emerging markets Impacts of lobbying groups in film and entertainment industry Effects of industry pressure groups Economical Impact of US foreign trade deficit issue Resign costs of advertising Level of US unemployment Inflation rate in the US Changes in the US taxation system Social Value changes in the US and other market Increasing influence of internet on social life Changes in demographic challenges Increasing importance of work-life balance Acceptance of same-sex marriages by increasing numbers of states in the US Technological Increasing popularity of 3D technology Maturation of films in DVD format Emergence of innovative platforms to consume entertainment products Increasing integration of IT in various stages of film production Technological breakthroughs in film production Ecological Problems associated with global warming Rising environmental concern of people globally Increasing importance of eco-tourism and related issues Increasing importance of corporate social responsibility (CSR) Legal Licensing issues with other organisations in the industry Problems related to intellectual property Legal barriers to enter emerging markets Changes in the US rules and regulations in relation to films and entertainment industry. Warner Bros. PESTEL Analysis References Rao, C.A., Rao, B.P. & Rao, K. (2009) “Strategic Management and Business Policy: Text and Cases” Excel Books

Strengths Warner Bros. has a solid financial position with USD 12 billion revenues generated during the year of 2012 alone with more than USD 1.2 billion operating income (Annual Report, 2012). Moreover, Warner Bros. has produced a series of successful franchises such as The Lord of the Rings, Batman, Harry Potter and Hangover that have immense contributions to the level of profitability of the company. Knowledge and experiences associated with the production of these successful franchises can be specified as strengths of Warner Bros. The agreement of Warner Bros. with Netflix Inc. that allows the company to stream previous sessions of shows’ series shown on CW network can be added to the list of its strengths due to the associated potentials for profit maximisation. Weaknesses Overdependence of Warner Bros. on the home market in the US is its major weakness in global competition. US government debt issues and implications of this issue on consumer spending patterns in the future increases the level of urgency of this weakness on long-term perspectives. Moreover, recent damage to Warner Bros. brand image for being used for infringing Cat Meme Copyright can be listed as weakness for the company that has to be addressed by senior level management. Opportunities There is an attractive profit maximisation opportunity for Warner Bros. through introducing new instalments to its successful franchises such as The Lord of the Rings, Batman, Harry Potter and Hangover. Expansion of digital distribution capabilities represents opportunity for Warner Bros. to strengthen its role as a leader of technological changes in the industry. Moreover, the levels of Warner Bros. revenues can be further increased through higher integration of product placement marketing strategy. Threats Business threats faced by Warner Bros. are diverse and they primarily include further decline of the sales of DVDs due…

According to Azhar (2003) organizational culture is the combination of important assumptions that are shared in common by each members of an organization and are often unstated. Organizational culture is basically made up by two major common assumptions: values and beliefs. Values are the assumptions that have been forwarded by the leaders of the organization and considered to be ideals that are desired by all the members of an organization. Beliefs on the other hand are the assumptions about the reality and created by experience. Robbins (1986) on the other hand, defines organizational culture as a uniform perception of an organization which has common characteristics. Organizational culture, according to the author is something descriptive and effectively it can distinguish one particular organization from another. It can also integrate individuals and groups of organization systems. Organizational culture is also defined by Rousseau (2000) as a set of commonly experienced stable characteristics of an organization which shows the distinctive features of an organization which differentiates it from others. Similar to the definitions of Azhar (2003) that has been stated above, Rousseau (2000) also define the organizational culture as set of norms and values that are shared by individuals and groups across the organization. Organizational values and beliefs refer to the common ideas about what the shared goals of an organization are, what types of behaviour should the members of an organization follow in order to achieve the common goals of an organization. These organizational values in turn form out the standard norms and guidelines for the organization that makes it distinct from others. Organizational culture is also defined by Schein (2004) as a pattern of shared assumptions that have been accepted by a group of individuals as they solve their problems. Because they have used these assumptions to solve their problems and…

Differences in Aims and Objectives in their Implications on Leadership Practices Differences in organisational aims and objectives have been found to be a significant difference between private and public sector organisations. This difference has implications on leadership practices in public and private sector organisations. In other words, usually there are clear performance indicators to assess the performances of organisational leaders in private sector and these indicators include company share prices, market share, and the levels of revenues. In cases of public sector organisations, on the other hand, performance indicators are vague, because organisational aim and objectives usually involve qualitative rather than quantitative elements. From this perspective, while the level of effectiveness of organisational leaders can be determined within a year or even shorter period of time on the basis of several quarterly performance of the organisation, longer period of time may be necessary to establish the level of effectiveness of leaders in public sector. Differences in Organisational Stakeholder Expectations and their Implications on Leadership Practices The variety and role of organisational stakeholders have been found as another point of a vast difference between private and public sector organisations. Establishing strategic relationships with stakeholders and meeting their expectations at a reasonable extent in private sector necessitates organisational leaders to adopt various roles simultaneously. In order to be successful, private sector organisational leaders need to be perceived as socially responsible by general public, they need to be perceived as dynamic and cost saving by shareholders, and at the same time organisational leaders need to be perceived as caring and motivational by the workforce. Arguably, meeting stakeholder expectations in public sector is less contradicted compared to meeting stakeholder expectations in private sector from leadership viewpoint. This is because in most cases no stakeholder group expects profit maximisation from public sector organisations, and…

Harrison (1972) presents a model of culture, known as Harrison’s Model of Culture that divides organisational cultures into the four categories: role, task, power, and person cultures. Organisations with role culture tend to be reliant on formal rules and regulations. In role culture organisations formal job descriptions of positions are more important than personal traits and characteristics of individuals taking these positions. In task culture organisations, on the other hand, the levels of skills and competencies to deal with tasks in hand are perceived to be the most important factor to exert influence. Task culture organisations tend to operate in project-based manner with specified deadlines for each project. Disadvantages of task culture organisations include conflicts of interests within teams and other relationship problems due to not clearly specified roles and responsibilities for team members. Power culture organisations tend to be highly autocratic, with a top executive exercising great power towards all organisational processes. The advantages of power culture in organisations can be listed as high speed of decision making and implementation of organisational changes. However, power culture is associated with a range of disadvantages as well that may include lack of constructive arguments and discussions, and lower level of employee motivation. In person culture organisations a specific individual serves as a source of influence for group members. This type of organisational culture is the least popular due to the fact that it lacks formal hierarchy, along with other disadvantages.

Attendance of the module and completion of the report has deepened the level of my knowledge in a number of areas. First of all, I learned about the importance of branding from practical and theoretical viewpoints. Moreover, I learned about the potential contribution of effective product design and innovation in products design and its key features in successful branding. During the research process for the report I gained an in-depth knowledge about all stages of the designing process of products and services. I feel very optimistic about applicability of this knowledge in practice in the future as a manager. My knowledge has also increased in the areas of patenting, trademarks and protection of intellectual property. Studying a set of case studies from IMSS has helped me to learn about the types current global trends and assess their implications on businesses within the settings of real life business situations. The module and assessment gave me some ideas about innovation and design. Before attending the module and completing the assessment I thought of design as a static issue and did not duly understand its highly dynamic character. However, thanks to effective teaching method of the tutor, adequate materials and individual learning efforts, now I do understand that product design needs to be perceived as an integral component of new product development efforts and design needs to be based on appropriate integration of simplicity and convenience. Moreover, central idea of the module has been associated with innovation in product design and functionality as a source of competitive advantage and I have obtained an in-depth knowledge about the value of innovation in product design and functionality to be used in the future during my career. The role of branding and effective marketing communication is another area of knowledge that I have gained through attending…
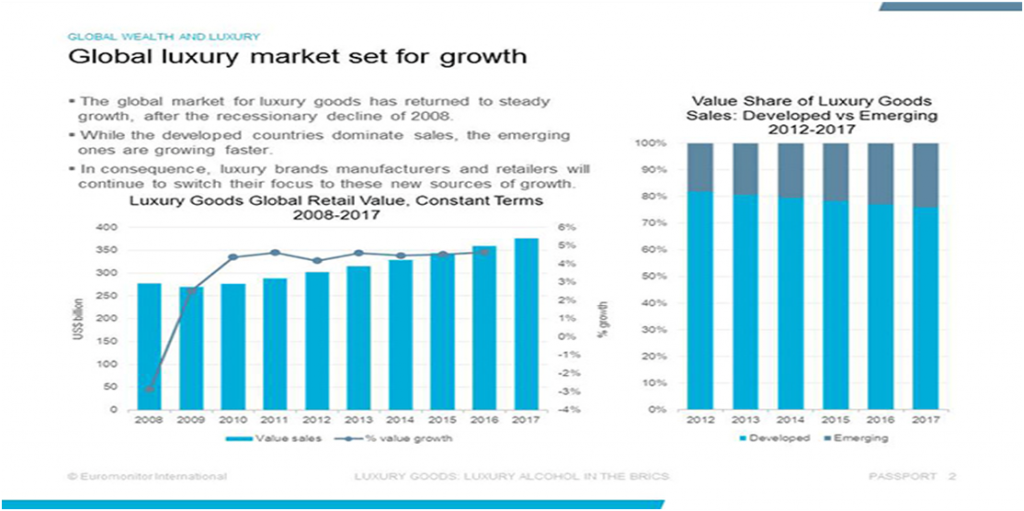
The term luxury has been defined as “something inessential but conductive to pleasure and comfort” (The Free Dictionary, 2014) and “great comfort, especially as provided by expensive and beautiful things” (Cambridge Dictionaries, 2014). Accordingly, luxury industry can be defined as an industry where consumer perceived value about products and services plays greater role and the actual benefits offered by those products and services. Moreover, luxury industry is closely associated with intangible aspects of products and services. In order to establish our luxury clothing brand, we have to make sure that there is a growing marketplace and ever growing demand for luxury clothes in the countries we wish to have our presence. According to market research analysis, there is a growing demand for luxury clothes both in the UK and worldwide. Although there is a common consensus that luxury brands suffered significant losses during and after recession, the market data discovered in this business plan proves the opposite. The Figure 1 shows that demand and growth of the marketplace for luxury clothes have been consistently rising for the last 5-6 years. Although there is a slight shift of growth for luxury marketplace to the emerging markets such as China, overall snapshot for the luxury clothes worldwide tends to be growing at significantly fast rate of around 7-8% for the next few years. The most obvious of these reasons is that there have been more people who have a large amount of disposable income from whom we have seen an increased desire for luxury goods. Brands that manufacture luxury goods have noticed this increase in demand, and have responded by tailoring their particular strategies to making sure that this demand is met in more areas of the world by opening stores in major cities that are entirely dedicated to the sale of…
By Helena Mullock
Category: Industry Analysis

Business turnaround can be defined as financial recovery of the company after the period of poor performance. The financial recovery can be achieved through implementing a specific set of strategies by the senior level management. The most popular turnaround strategies include the following: Re-building around a profitable core business Re-branding Changing organisational culture. New product development Cost reduction through human resources downsizing and other measures The choice of turnaround strategies listed above by a company depends on a wide range of factors such as situation in the marketplace, availability of resources, the present pattern of organisational culture and others. Apple’s primary turnaround strategy relates to rebuilding around a profitable core business. Manufacturing of IPhone and IPad have proved to be highly profitable core business for Apple and the management is further increasing its focus on these core businesses through the introduction of IPad Mini, development of lower cost Iphones for emerging markets such as India and China, and committing to investment for further developments of IOS platform. Changing organisational culture can be specified as another turnaround strategy currently in use by Apple CEO Tim Cook. Under former CEO Steve Jobs, Apple organisational culture was famous for being overly harsh, competitive and even exploitative of employees. However, having a reputation for being a ‘nice guy’, Tim Cook is believed to be leading a ‘quiet cultural revolution’ to foster more communication between various levels of management and to make Apple nicer workplace in general. Specifically, the micro-management practice of former CEO Steve Jobs has been abandoned and the level of involvement of employees in strategic decision making has been increased. Moreover, new product development has been employed by Apple CEO as additional turnaround strategy. Apple is believed to be developing watches and television that might have the same impact on respective products…

The theoretical framework of Cultural Dimensions introduced by Geert Hofstede as a result of assessing the values of more than 100,000 IBM workforce from 50 countries represent one of the most significant contributions to the development of cross-cultural studies. Hofstede differentiates cultures on the basis of following dimensions: individualism versus, collectivism, power distance, uncertainty avoidance, masculinity versus femininity, and long-term versus short-term orientation. Individualism versus Collectivism Individualism “describes the tendency of people to see themselves as individuals rather than as members of a group” (Velo, 2012, p. 26), whereas collectivism is associated with preference for group thinking and prioritising advantages of the group over individualistic advantages. In organisations where collectivistic culture prevails employees consider decision making to be the responsibility of superiors. Similarly, Andrews (2009) argues that employees in highly individualistic work cultures feel motivated to engage in decision making in an individual manner. Power Distance Power distance is an extent to which group members are willing to accept unequal distribution of power. In societies with high power distance unequal distribution of power is tolerated by group members to a great extent. Such societies managers are not generally approachable and the most popular form of communication is downward communication. In societies with low power distance, on the other hand, members of society are perceived to be more or less equal. Managers in low power distance organisations are viewed as peers by subordinates and there is usually two-way communication in such type of organisations. Uncertainty Avoidance Uncertainty avoidance dimension of culture refers to the degree of tolerance towards ambiguity and unexpected events and unstructured situations. Societies with high levels of uncertainty avoidance prefer to operate within highly structured environment and generally they have negative approach towards uncertainties. Bhattacharyya (2010) recommends the development of clear procedures and directives when…
