
It is acknowledged by secondary data authors that online retailing in its various forms, including retailing of food and grocery products is considered to be a component of e-commerce. E-Commerce can be defined as “conducting business transactions – generally financial transactions – via communications technology” (Morley and Parker, 2010, p.431) Laudon and Traver (2009) inform that internet boom in general, and e-commerce in particular that has started towards the end of the last century had transformed the various aspects of lives of people significantly in a global scale. Authors offer different viewpoints about the nature of that affect but agree on the idea that “with the introduction of e-commerce, we have come to expect 24-hour delivery of products from across the world, and home delivery of groceries from the local Tesco at a time of our choosing” (Gustafsson, 2006, p.39) Hall (2008) mentions a survey conducted in 2008, which revealed that sixty-five percent of food companies were engaged in selling specialty food via internet. The following table illustrates the findings of the survey in a more detailed way: Internet Sales as Percent of Gross Sales Internet Sales as Percent of Total Sales in 2007 Internet Sales as Percent of Total Sales in 2008 Less than 10% 40.0 37.5 11-20% 10.0 10.0 21-30% 1.0 10.0 31-40% 2.0 2.5 41-50% 0.0 0.0 51-60% 2.5 0.0 More than 60% 2.5 2.5 No response 22.5 27.5 However, some authors (May, 2000, Kozami, 2002, Ashley, 2004, and others) dismiss the idea that purchasing food and grocery products through internet is an entirely new thing. They justify their stand by stating that “we should be suspicious of claims that internet provisioning is something entirely new. There are obvious continuities with existing telephone and television shopping, even if the service has become widespread and notionally democratized”…

For the last two or three decades, the principal target of economy has been the control of inflation (Delong, 2002). Both politicians and economists say that this is the first economic duty of any government. And they tend to assume that other economic goals such as economic growth and low unemployment will be achieved only if the inflation is held under control. According to Frank and Bernanke (2001), as economic growth and low unemployment is achieved through successful controlling of inflation, then there is a relationship between inflation and economic growth. There were many researches and investigations to identify and analyse the relationship between inflation and economic growth which were carried out by Barro (1995) Li (2000), Gokal and Hanif (2004), and they all identified the relationship between two variables. They all tend to conclude that a consistent economic growth can be achieved with low consistent inflation rates; however, higher inflation rates distort the economic growth consistency of any country. Like many other developing and emerging groups, CIS countries also aim to achieve low sustainable inflation together with high economic growth which is of great importance for any country. Malik, (2005), indicates that one of the determinants of macro-economic stability is inflation, and long term economic growth requires macroeconomic stability which will be achieved through low inflation along with sustainable budget deficits, realistic exchange rates and appropriate real interest rates. He points out that the stability of inflation rates has an enormous impact on the economic growth of the country. Khan and Senhadji (2001) state that first researchers to study and detect the nonlinear inflation and economic growth relationship were Fischer (1993). Later, Sarel (1996) examined the data of 87 countries and covered the period of 1970-1990. He actually found structural break point of the relationship between inflation and economic…

The nature and level of utilisation of marketing strategy by Illy in general and ‘Illy’s and Boos Cupcakery’ in Bristol in particular can be effectively explained by utilising the concept of marketing communications mix. Kotler and Keller (2006) divide elements of marketing communication mix into large six groups that consist of advertising, sales promotion, events and experiences, public relations and publicity, direct marketing and personal selling. Marketing strategy developed by Illy aims to communicate Italian origins of the brand and perceived high quality of products through integration of various marketing communication channels as explained below in a greater details. Advertising Generally, any form of external communication of a business entity can be categorised as advertising. Indoor and outdoor posters, and attractive displays at the point of purchase are the most popular advertising methods used by ‘Illy’s and Boos Cupcakery’ in Bristol. Illy advertising strategy makes an extensive use of print and broadcast advertising in a global scale. Popular social networking site YouTube is one of the main platforms for Illy media advertisements. Sales Promotions The main objectives behind sales promotions can be specified as offering short-term price incentives to customers in order to increase the volume of sales. ‘Illy’s and Boos Cupcakery’ in Bristol engages in sales promotions in a regular manner through temporarily reducing prices for different products. Moreover, Illy engages in occasional sales promotion campaigns through sending promotion offers to customers’ e-mails, including complimentary item with the purchase of specific range of products. Also, unlike many other coffee chains, barristers at Illy are taught to welcome occasions when they are asked for a coffee sample for free. Events and Experiences ‘Illy’s and Boos Cupcakery’ in Bristol does not engage in events and experiences due to the small size of the venue and budget limitations. However,…

Gap Model of Service Quality consists of the following gaps: Gap 1: customer expectation – management perception gap: the difference between the service the customer expects and the service level the supplier thinks that customer wants. Gap 2: management perception-service standard gap: the difference between the service specification that is set and the supplier management assessment of customer service requirements. Gap 3: service standard-service delivery gap: the difference between the actual service that is provided and the planned level of service based on the service specification that has been set. Gap 4: service delivery-external communication gap: the difference between the actual service that is provided and the promised level of service that was communicated to the customer. Gap 5: actual service – perceived service gap: the difference between the service that the supplier is providing and the service that the customer thinks is being received.
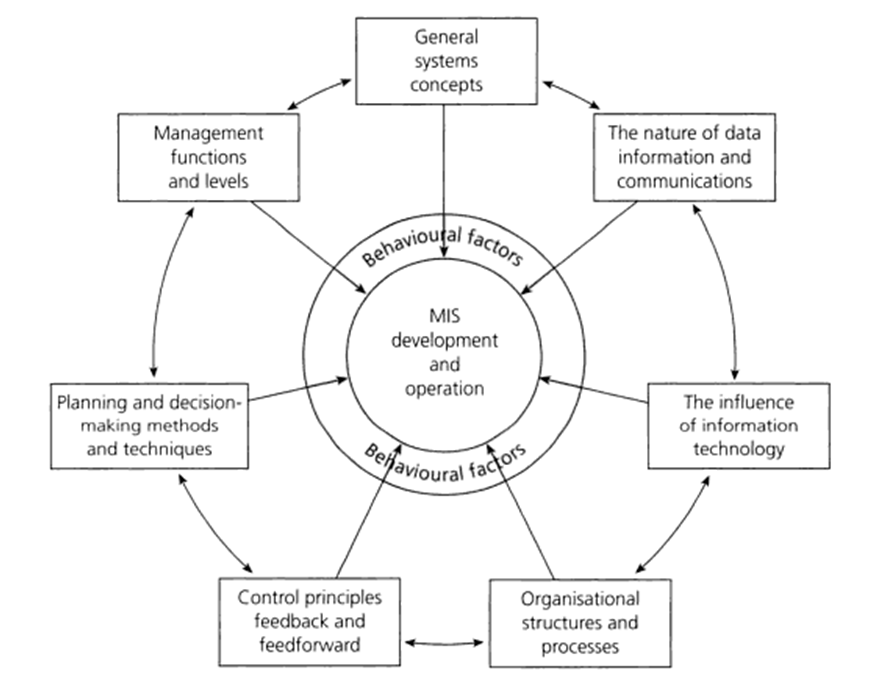
Management Information System can be defined as “a system to convert data from internal and external sources into information and to communicate that information, in an appropriate form, to managers at all levels in all functions to enable them to make timely and effective decisions for planning, directing and controlling the activities for which they are responsible” (Lucey, 2004, p.2). Alternatively, Management Information System can be defined as “a computer-based system that provides information and support for managerial decision making” (Daft et al, 2010). In simple terms, Management Information System represents a system used by managers to collect updated and comprehensive data in order to engage in informed and effective decision making. Management Information System is a much broader concept than just handling data in a way that Management Information System stands for data analysis in accordance with a range of important factors such as organisational culture, relevant policies and procedures and wider business environment. Adoption of Management Information System principles in an appropriate manner is going to provide Company the advantages of engaging in informed planning, mini Management Information Systeming the level of information overload, and increasing the level of coordination between various departments of the company. Moreover, Management Information System can have a positive contribution on employee performance evaluation and improvement at Company and it can also serve as a valuable tool for identifying current position of the company in the marketplace and formulating growth strategies. The five important functions of management information systems have been identified by Pride et al (2009) to consist of the following points: Collecting data. The collection of data that is necessary for decision making in short-term and long-term perspectives. Storing data. Keeping the data in an effective format in order to ensure that they can be the right of data can be…

Porter’s (1985) value chain analysis illustrates the manner in which various business activities relate to the competitive advantage of firms. The model divides business activities in primary and support activities. Primary activities deal with the delivery of products in a direct manner, whereas the main aim of support activities relate to increasing the levels of effectiveness of various business processes. Primary Activities Inbound logistics include activities associated with bringing and storing of all external materials. For Illy, this comprises harvesting, parchmenting, quality control and purchasing within countries where the coffee beans are grown, shipping the beans in bags to company plant in Trieste, Italy. Expenses associated with inbound logistics account for significant amount due to the large distance between operations plant in Trieste and purchasing plants in Africa, Asia and Latin America continents and this can be specified as one of the major factors causing the levels of overall costs to increase. Within the scale of ‘Illy’s and Boos Cupcakery’ specific branch, on the other hand, inbound logistics involve the delivery of necessary products and ingredients on a daily basis, according to the order sent by the shift manager on the previous day. Operations relate to the ways in which outputs are created out of inputs. Illy operations mainly include blending, roasting and packaging coffee beans in company plant in Trieste. Basically, internal operations consist of a set of consequent processes as a result of which coffee beans in bags are turned into packaged products in paper packages and metal cans depending on the nature of each individual product. In case of ‘Illy’s and Boos Cupcakery’ in Bristol operations involve physical preparation of coffee and other beverages and food within the store. Outbound logistics activities include all activities involved in sending ready products to consumers. Illy products…
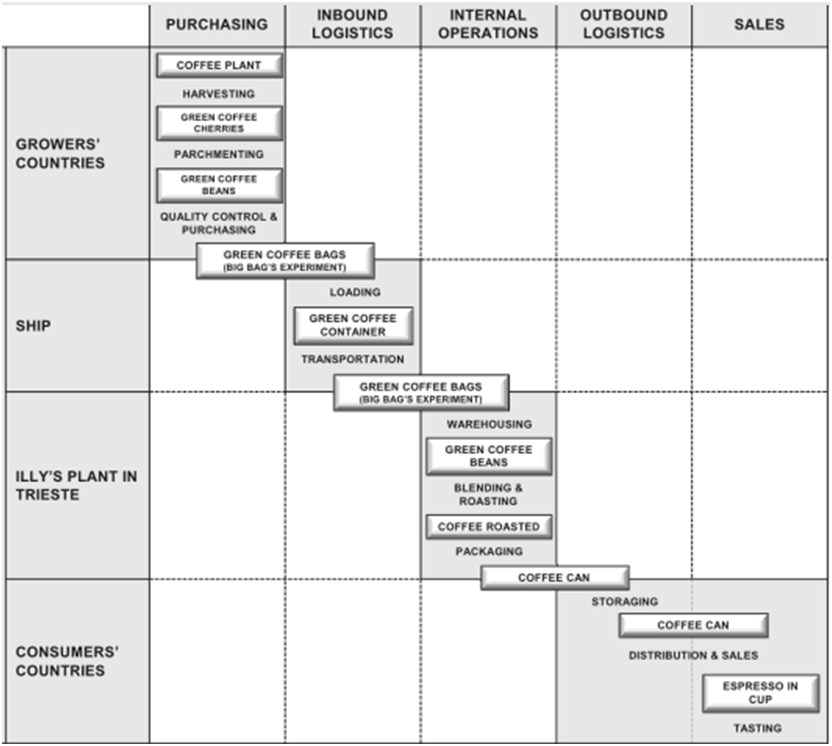
Illy is a global coffee brand that is sold in 140 countries and employs more than 800 people globally (Illy: By the Numbers, 2013). The main difference between traditional logistics and supply chain has been drawn by Agrawal and Smith (2009) in a way that supply chain is a much broader concept than logistics and it focuses on the quality of relationships between various elements within the supply chain with the aims of achieving improvements Elements of supply-chain management (SCM) have been specified by Wisner et al. (2008) as purchasing, operations, distribution, and integration. Wisner (2008) argues that effectiveness in one particular element does not compensate shortcomings in other elements, and thus businesses need to strive to strive to obtain competitive advantages each of these elements. Three major tendencies impacting SCM have been specified by (Muller, 2011). Firstly, increasing numbers of businesses are acquiring their resources from other countries. Secondly, timeframe associated with the delivery of resources and the quality of resources is playing increasing role for firms in terms of obtaining competitive advantage. Thirdly, rapid technological developments among a range of other factors are causing uncertainties in the market with direct implication on SCM practices Ruston et al. (2010) advocate the adoption of strategic approach in dealing with suppliers. This viewpoint has been supported by a wide range of other authors as well, and the benefits of adopting a strategic approach with suppliers have been listed as more effective quality control based on trust (Leeman, 2010) and achieving greater level of supplier cooperation in times of economic difficulties (Agrawal and Smith, 2009). Basu and Wright (2012) further expand this point and argue that adoption of strategic approach in dealing with suppliers based on ethical practices can have highly positive implications on business brand image if these relationships are communicated…

The nature of leadership in private sector organisations is directly impacted by the primary purpose of such organisations and this primary purpose is profit maximisation (DuBrin, 2012). This opinion is confirmed by Goldsmith et al. (2010), who perceive profit maximisation as the main assessment criteria for private sector organisational leaders. According to Gold et al. (2010) constant search for competitive advantage can be justly specified as one of the most fundamental characteristics of leadership in private sector organisations. According to this stance, competitive advantage can be derived from a wide range of sources and business processes, and it is the responsibility of a business leader to be able to formulate the most appropriate competitive advantage, and ensure its efficient utilisation. Stanfield (2009) explore the issues of ethics for modern business leaders and conclude that the level of ethical requirements have increased for business leaders in the last several decades contributed by increasing level of scrutiny business leaders are being subjected to. Stanfield (2009) offers justification for this claim by stating that increasing role of viral media in the society makes any evidence of unethical behaviour hard to escape from. Maintaining high level of flexibility and implementing changes in relation to various business processes in a constant manner is pointed to as a significant challenge to business leaders by Kezar et al. (2011) and Kreitner and Cassidy (2012). Moreover, Kezar et al. (2011) stress the role of assertiveness and communication skills for business leaders in order to be able to implement changes in an efficient manner. The issue of talent management by business leaders comprehensively addressed by Bertocci and Bertocci (2009) reveals another important aspect of successful leadership practice. Specifically, according to Bertocci and Bertocci (2009) human resources need to be perceived as the most valuable business asset in the 21st…

Major differences between public and private sector organisations have been specified and addressed by a range of management scholars. According to Wirick (2009) the main difference between public and private sector organisations relates to forms of ownership. Specifically, public sector organisations are owned and operated by government, whereas private sector organisations are not part of the government. The form of ownership as the main distinctive point between public and private sector organisations has also been mentioned by Kassel (2010), Sims (2010) and others. Linked to the point above, aims and objectives of organisations have also been specified by authors as a major point of difference between public and private sector organisations. Kassel (2010) and Starling (2010) assert that the primary objective of organisations operating in private sector is profit maximisation. Gallos (2008) advises not to be deluded by charitable acts of private sector organisations in regards to intentions and insists that all of these acts are aimed at supporting the primary objective of private sector organisations which is profit maximisation. The aims of public sector organisations, on the other hand, involve serving the interests of taxpayers through various manners according to the type of the organisation (Sims, 2010). For example, public schools aim to provide education to citizens within a country, whereas the objectives of public health organisations involve providing quality healthcare. Importantly, the source of funding of organisations represents another point of difference between public and private sector organisations (Sabatier, 2007). Namely, public sector organisations are funded by taxpayers; therefore serve the interest of taxpayers, while private sector organisations are funded by individuals and corporate investors aiming to make a profit. References Gallos, J.V. (2008) “Business Leadership: A Jossey-Bass Reader” 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons Kassel, D.S. (2010) “Managing Public Sector Projects: A Strategic Framework for Success…

According to Grigoroudis and Siskos (2009) as taken by Oliver (1997) “satisfaction is the consumer’s fulfilment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product or service itself, provided (or is providing) a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfilment, including levels of under-or overfulfillment” (Grigoroudis and Siskos, 2009, p.4) The Business Dictionary (online, 2013) defines private sector as a part of national economy that consists of private enterprises including personal sector (households) and corporate sector (companies). The definition of the public sector is suggested by The Free Dictionary (2011) as “the part of an economy that consists of state-owned institutions, including nationalised industries and services provided by local authorities” (The Free Dictionary, online, 2011). Although the term ‘quality’ on its own is widely known and does not require further elaboration, some authors have offered their viewpoints regarding the definition of the term within the context of customer services. Specifically, it has been stated that, “quality of the delivered products or services is essential to achieving customer satisfaction. The quality concept embraces how to meet all customers’ requirements, including how they are greeted on the telephone or at the counter, the speed with which a query is responded, providing new services when required, and ensuring the delivered services satisfy the community needs” (Nagel, 2000, p.47). Introduction According to Grigoroudis and Siskos (2009) the advantages of private sector organisations over the public sector organisations include better level of the service, more information about various aspects of customer services, better management, market testing and rewarding performance. Secondary data authors (Murley, 1997) argue that a part of the issue of effective customer service provision within public sector relates to the identification of customers in public sector in the first place. Discussing police services specifically, the author reasons that “their customers…
