Search results for: Ansoff Matrix

Effective BYD leadership is one of the main factors behind the phenomenal growth of the electric automaker. In April 2022, Wang Chuanfu, founder, Chairman and President of BYD, was listed on The 50 Most Influential Business Leaders in China 2022 by Fortune. Described as “a mix of Thomas Edison and Jack Welch, the former General Electric chief” by Charlie Munger in 2008[1], Wang Chuanfu is a charismatic and passionate leader known for his long-term vision and relentless work ethic. Transformational leadership principles prevail at BYD. Wang Chuanfu’s audacious vision for a sustainable future through EV and renewable energy motivates employees and stakeholders alike. He articulates a clear picture of BYD’s potential impact on the world, transcending mere financial goals. This inspires employees to see their work as contributing to a larger purpose. It is important to note that maintaining a transformational leadership style as the company scales can be challenging. Effective communication and delegation become crucial to keep everyone aligned with the vision and empowered to act. BYD Company Limited Report contains the above analysis of BYD leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on BYD. Moreover, the report contains analyses of BYD business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of BYD marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility. [1] White, E. & Campbell, P. (2024) “Wang Chuanfu, the driving force behind BYD’s rise” Financial Times, Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/22527628-733e-4188-9678-ab3210fdb1ba

BYD business strategy consists of the following three pillars: 1. Cost leadership. Cost efficiency compared to its main competitor, Tesla is one of the key competitive advantages for BYD. Cost leadership has been a crucial component of BYD’s success, helping them establish themselves as a competitive contender in the EV market. BYD is able to maintain cost leadership business strategy in the global marketplace due to a number of factors such as lower cost of human resources in China, the extensive support by Chinese government to EV makers and an extensive vertical integration. Competitive pricing makes BYD’s EVs accessible to a wider range of consumers, particularly in cost-sensitive markets. This can drive market share gains and boost overall sales. Moreover, efficient cost management helps BYD maintain healthy profit margins even with lower prices, enhancing financial stability and fuelling further investments. 2. Extensive vertical integration. The electric automaker produces the majority of its spare parts in-house. For example, for BYD Dolphin only tyres and windows are delivered by suppliers and all other components are produced by the company itself. Vertical integration to such an extent allows the EV behemoth to maintain its cost leadership business strategy along with reducing the dependence on external vendors for spare parts. Moreover, controlling critical components minimizes dependence on external suppliers, mitigating risks of disruptions and shortages. Vertical integration also creates unique capabilities and intellectual property, setting BYD apart from competitors and bolstering brand differentiation. 3. Accelerated pace of new model development. While it takes about four years for an average automaker to develop a new car from scratch to design, for BYD it takes only 18 months. The electric automaker has adapted an accelerated pace of new model development to reflect changes in customer tastes and preferences as a cornerstone of its business…

Founded in 1995, BYD Company Limited is a leading technology company that has established itself as an industry leader in electronics, automotives, renewable energy, and rail transit. As a global leader with more than 30 industrial parks across 6 continents, BYD’s zero-emission solutions, focused on energy generation and storage, are expansive and widely applicable. The electric automaker sold 26,864 million units of cars in 2022 , generating operating revenue of RMB 424,061 million, an increase of 96.20% compared to the previous year. The company delivered a record high of 1,788,000 new energy vehicles in 2022, representing a year-on-year growth over 217.6% . The electric vehicle (EV) giant pursues a business strategy of cost leadership fuelled with extensive vertical integration and an accelerated pace of new model development. BYD organizational structure integrates the elements of matrix structure, independent brands, emphasis on R&D and regional variations. Organizational culture of the EV behemoth, on the other hand, is associated with meritocracy, focus on cost-cutting and prioritizing company values. As one of the leading rechargeable battery manufacturers in the global arena BYD possesses certain strengths such as vertical integration and cost advantage, leadership in technological capabilities and economies of scale advantage from massive manufacturing. At the same time, the company has certain weaknesses. These include overdependence on domestic market, too broad range of businesses and dependence on subsidies by Chinese government to sustain cost advantage. BYD Company Limited Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on BYD. Moreover, the report contains analyses of BYD’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and ecosystem. The report also analysis marketing strategy, ecosystem and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Executive Summary 2. Business…

Company reports, analysis and business research methods since 2011 by John Dudovskiy Save hours of business research by using a library of thoroughly written reports and articles. See Analytical Tools Learn Writing Dissertation Business reports on world’s top companies See All Reports Why Us? All you need for your business research Trusted source of knowledge, honed by years of experience, offering unparalleled depth in business reports, analysis, and research methods since 2011. Your journey to informed decision-making starts here! Competent Researchers A team of seasoned dissertation advisers with practical business management experience. Comprehensive Reports Application of major tools SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s 5 Forces, Value Chain etc. within a single report. Dissertation Guide Comprehensive guidance from the selection of the research area to the completion of the final draft. Up-to-date Data Regularly updated articles and business reports reflect changes in the macroeconomic environment. Business Analytical Tools SWOT Analysis Ansoff Matrix PESTEL Analysis 7Ps of Marketing Segmentation, Targeting Marketing Communication Mix Porter's Five Forces Analysis Value-Chain Analysis McKinsey 7S Model SWOT Analysis A simple yet powerful framework for assessing a company's competitive position, developing business strategies, and making informed decisions. Strategic analytical tool for analyzing: Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats Learn More Ansoff Matrix A marketing planning model that helps companies to identify and evaluate their growth options and determine its product and market strategy. The model integrates four different strategy options: Market Penetration Product Development Market Development Diversification Learn More PESTEL Analysis Strategic analytical tool for assessing external factors affecting businesses. The PESTEL acronym stands for: Political Economic Social Technological Environmental Legal factors impacting companies Learn More Marketing Mix (7Ps) Comprises elements of the marketing mix. Companies manipulate each element based on their marketing and business strategy: Product Place Price Promotions Process People Physical Evidence Learn More Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP) Consequent…

Nvidia Supporting Local Communities NVIDIA employees joined the company in contributing more than USD22 million and 16,500 volunteer hours to charitable causes in fiscal year 2022.[1] The company and its employees supported 5,700 nonprofits in 50+ countries around the world. Nearly 40% of employees participated in the Foundation’s Inspire 365 efforts during FY22, bringing the unique participation rate since the initiative’s start to 68%. Nvidia and Gender Equality and Minorities As of January 30, 2022, the company’s global workforce was 80% male, 19% female, and 1% not declared and 6% of workforce in the United States was composed of Black or African American and Hispanic or Latino employees.[2] The company scored 100% on the Human Rights Campaign’s Corporate Equality Index for a seventh consecutive year Energy Consumption by Nvidia By the end of the fiscal year ending January 31, 2025, the company plans to purchase or generate enough renewable energy to match 100% of its global electricity usage for its offices and data centres Waste Reduction and Recycling by Nvidia The company diverted 56% of FY22 waste from landfill, a 12 percentage point decrease from the previous year. Bulk carton packaging uses corrugate material that is 100% recycled fibres, and the cartons maintain an overall recyclability rate of 100% Consumer packaging uses 70% recycled fibres and maintains a recyclability rate above 75%. Overall recyclability rate for all packaging is 93% Nvidia other CSR Initiatives and Charitable Donations The company donated more than USD4.6 million to date for humanitarian relief to Ukraine and its refugees.[3] Nvidia Corporation Report contains a full analysis of Nvidia corporate social responsibility including Nvidia CSR issues. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff…

Marriott Supporting Local Communities In 2022 alone, employees contributed over 1.6 million volunteer hours across the globe, focusing on environmental and social issues to positively impact their communities. The company aims to locally source 50% of produce by year-end 2025 Marriott Educating and Empowering Workers In 2022, 78% of all associates* completed career- or skillsrelated training. The largest hotel chain in the world has been listed as Fortune 100 Best Companies to Work For® Great Place to Work® in 2022 Marriott and Gender Equality and Minorities A majority of Marriott’s Board are minorities or women Listed as one of 50 Best Companies for Latinas to Work for in the U.S., LATINA Style 2022 The company aims to increase representation of people of colour in U.S. executive positions to 25% by year-end 2025. 47% of Marriott’s global executives (vice president level and above) are women 22% of Marriott’s U.S. executives (vice president level and above) are people of colour Energy Consumption by Marriott In 2022, numerous Marriott-managed hotels across the globe implemented energy efficiency projects, saving approximately 45,000 MWhs of energy. 9% Global Reduction in Energy Consumption per Square Meter of Conditioned Space from 2016 Baseline 1% of electricity consumption sourced from renewable energy in 2022 Water Consumption by Marriott The company aims to reduce water consumption per occupied room by 15% from a 2016 baseline by year-end 2025 3% Global Reduction in Water Consumption per Occupied Room from 2016 Baseline Waste Reduction and Recycling by Marriott The hotel chain aims to reduce waste-to-landfill by 45% and food waste by 50% from a 2016 baseline by year-end 2025 In Thailand, 27 Marriott hotels donated over 33,000 kg (72,000 lbs.) of food and surplus food to Scholars of Sustenance (SOS) throughout 2022. Carbon Emissions by…

Key Components of Marriott ecosystem include the following: – Properties. Marriott has a portfolio of over 8,000 hotels in 138 countries and territories. This includes a variety of brands, from luxury to budget-friendly, to meet the needs of all types of travellers. – Loyalty programs. The hotel chain has three loyalty programs – Marriott Bonvoy, Ritz-Carlton Rewards, and Starwood Preferred Guest. These programs offer members exclusive benefits, such as free nights, room upgrades, and early check-in and check-out. – Technology platform. The largest hotel chain in the world has a robust technology platform that powers its website, mobile app, and loyalty programs. The company also uses technology to improve the guest experience, such as with contactless check-in and mobile keys. – Partners. The company has a wide range of partners, including airlines, car rental companies, and credit card companies. These partnerships allow Marriott to offer its guests a one-stop shop for their travel needs. Marriott’s ecosystem is designed to provide guests with a seamless and personalized experience. For example, when a guest books a hotel room on the Marriott website, they can also book a flight and a rental car. They can also use their Marriott Bonvoy points to pay for their hotel stay, flights, and car rental. Marriott’s loyalty programs also play an important role in its ecosystem. By rewarding guests for their loyalty, Marriott encourages them to stay at Marriott hotels and use Marriott partners. This helps Marriott to build long-term relationships with its guests. The Marriott International ecosystem benefits both Marriott and its guests. For Marriott, the ecosystem helps to increase revenue and improve customer loyalty. The hotel chain is able to generate additional revenue from its partners, such as airlines and car rental companies. The company is also able to improve customer loyalty by providing guests with a seamless and personalized experience. For guests, the ecosystem provides a number of benefits such as convenience, savings…
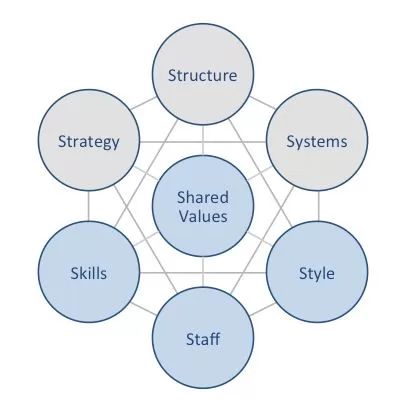
Marriott McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness for the largest hotel chain in the world. According to this framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Marriott McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in Marriott McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Marriott International’s business strategy is focused on providing high-quality hospitality services to a wide range of customers. The company has a portfolio of over 30 brands, ranging from budget-friendly to luxury, to appeal to different needs and budgets.[1] The hotel chain pursues asset-light business model and growth through acquisitions business strategy. Moreover, Marriott has been focusing on bleisure travellers as part of its business strategy. Structure Marriott International has a decentralized organizational structure, with each brand operating as its own business unit. This allows the company to tailor its offerings and services to the specific needs of each market. Marriott also has a strong focus on operational excellence, with a number of systems and processes in place to ensure that its hotels are run efficiently and effectively. Systems Marriott International has a number of systems in place to support its business operations, including a reservation system, a loyalty program, and a property management system. The company is also investing heavily in new technologies, such as mobile check-in and self-service kiosks. Marriott International Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Marriott McKinsey 7S Model.…
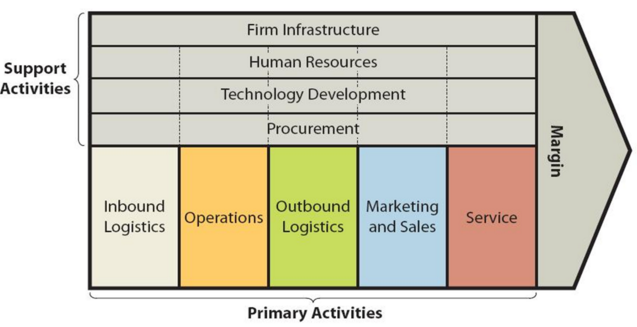
Value chain analysis is an analytical tool that helps to find business activities that can create the most value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure below illustrates the essence of Marriott value chain analysis. Marriott Value Chain Analysis Marriott Primary Activities Marriott Inbound logistics The inbound logistics activities for Marriott International involve the procurement, transportation, and storage of the goods and services that the company needs to operate its hotels and resorts. These activities are essential to the company’s ability to provide its guests with a high-quality experience. Marriott International procures a wide range of goods and services from suppliers such as food and beverage, linen, furniture, toiletries and other supplies. The largest hotel chain in the world has a strong supplier network and is able to negotiate competitive prices. The company also has a team of experienced procurement professionals who are responsible for managing the inbound logistics process. Marriott Operations Marriott’s operations can be divided into four key areas: 1. Hotels. Marriott operates and franchises hotels under its various brands. It also manages hotels on behalf of other owners. 2. Vacation ownership. Marriott operates a vacation ownership program called Marriott Vacation Club International. This program allows members to purchase vacation points that can be used to stay at Marriott-affiliated vacation resorts. 3. Timeshare exchange. Marriott operates Interval International, a timeshare exchange program that allows members to swap their timeshare weeks for stays at other resorts. 4. Food and beverage. Marriott operates restaurants and bars in many of its hotels. It also provides catering services. Marriott Outbound Logistics Generally, outbound logistics within value chain analysis refer to all the activities involved in delivering the finished product or service to the customer. This includes warehousing, order fulfilment, transportation, and delivery. For Marriott International outbound logistics activities include the following:…
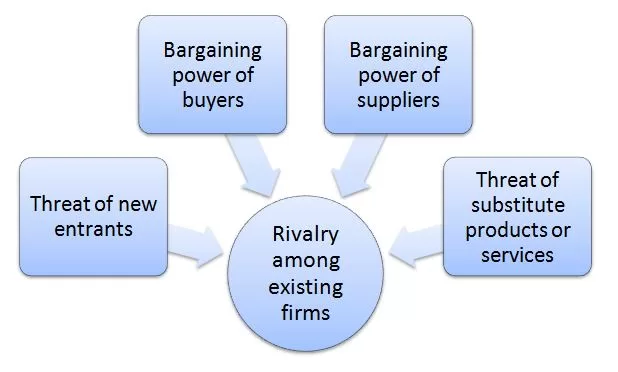
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in figure below: Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Marriott Porter’s Five Forces Analysis The threat of new entrants into the global hotel industry is moderate. There are a number of factors that make it difficult for new entrants to enter the hotel industry. These include high capital requirements, the importance of brand recognition, lack of access to distribution channels and the importance of economies of scale. Capital requirements The hotel industry is highly capital-intensive. New entrants need to have a significant amount of capital to invest in building or acquiring hotels. According to data from hospitality consulting firm HVS, ground up construction of a full-service hotel typically costs USD 323,500 per room in the US.[2] The similar pattern is echoed in many other markets as well. Accordingly, capital requirements are a significant entry barrier for new players into the hotel industry. Brand recognition Established hotel brands such as Marriott, Hilton, IHG Hotels & Resorts, Hyatt and Wyndham Hotels & Resorts have a significant advantage over new entrants. These companies have been developing and promoting their brands for decades and accordingly, have a strong reputation and customer loyalty. Moreover, effective branding enables established market players to command premium prices, further solidifying their position. New entrants, on the other hand, will have no visible brand, making it difficult for them to successes in the market. Distribution channels Distribution channels for hotels include direct channels, such as their own websites and reservation call centres, and indirect channels, such as online travel agencies (OTAs), global distribution systems (GDSs), and tour operators. Established hotel brands such as Marriott have well-established distribution channels.…
