Posts Tagged ‘catering’

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following illustrates Marriott SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Diverse portfolio of brands 2. Global presence 3. Strong loyalty program 4. Asset-light business model Weaknesses 1. Labour issues 2. Brand image damaged due to data breach Opportunities 1. Targeting millennial and Gen Z segments 2. Increasing focus on alternative lodging 3. Focusing on emerging economies 4. Entering into adjacent industries Threats 1. Increased competition from alternative lodging 2. Currency fluctuations 3. Geopolitical tensions 4. Global pandemic Marriott SWOT Analysis Strengths in Marriott SWOT Analysis 1. Diverse portfolio of brands. Marriott International has 30 brands[1] in its portfolio appealing to the needs and wants of a wide range of customer segments. The company has something to offer every type of traveller, from budget-minded backpackers to luxury-seeking executives. This diversity gives the hotel chain substantial competitive advantage. Specifically, it allows the company to reach a wider range of customers. A traveller looking for a budget-friendly hotel is just as likely to book a room at a Fairfield Inn by Marriott as a traveller looking for a luxury hotel is to book a room at a Ritz-Carlton. 2. Global presence. Marriott is the largest hotel chain in the world and operates properties in 138 countries and territories[2]. Such a global presence gives the company a number of advantages. For example, global presence gives the company a competitive advantage over smaller hotel chains. Smaller hotel chains typically do not have the resources to expand into new markets and build new hotels. Marriott’s global presence allows the company to quickly and easily expand into new markets and compete with local hotel chains. Second, the hotel chain’s global presence allows it to leverage its brand recognition. Marriott is one of the most…
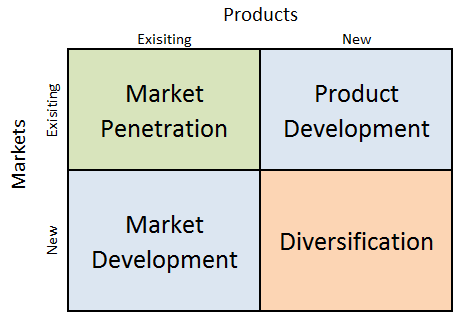
Marriott Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the international hotel chain to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Marriott Ansoff Growth Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Marriott International uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products and services to existing markets in increased quantities. Market penetration is one of the main growth strategies for Marriott. The company uses this strategy through competitive pricing for some of the brands within its portfolio, promotional discounts, targeted marketing and other means. Moreover, Marriott Bonvoy loyalty program plays in instrumental role in increasing the effectiveness of market penetration. 2. Product development. This growth strategy involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Marriott has a strong track record of developing and launching new brands and hotel concepts that meet the evolving needs of its customers. For example, the company launched several new brands in recent years, such as Moxy Hotels, AC Hotels by Marriott, and Autograph Collection, as well as, new hotel concepts such as Tribute Portfolio and Element Hotels. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. An extensive focus on market development business strategy has allowed Marriott International to become the largest hotel chain in the world operating in 138 countries and territories under 30 brand names.[1] 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets and this is considered to be the riskiest strategy. Marriott uses diversification sparingly, preferring to stick to its core hotel business. The rare cases of diversification for the hotel chain include entering into vacation rentals, timeshares and operating…

Marriott organizational culture integrates the following five key elements: 1. People-first approach. Putting people first is Marriott’s top priority. The company believes that by taking care of its employees, they will in turn take care of customers. This commitment is evident in Marriott’s many employee-focused programs and initiatives, such as its tuition reimbursement program, its employee assistance program, and its diversity and inclusion initiatives. 2. Pursuing excellence. Pursing excellence is another core value that is integrated within Marriott organizational culture. The company sets high standards for its employees and encourages them to continuously strive to improve. This commitment to excellence is reflected in hotel chains many awards and accolades. These include recognition as one of Fortune’s 100 Best Companies to Work For and one of Ethisphere’s World’s Most Ethical Companies. 3. Acting with integrity. The largest hotel chain in the world expects its employees to be honest, ethical, and fair in all their dealings. This commitment to integrity is reflected in Marriott’s code of conduct and its many policies and procedures designed to promote ethical behaviour. 4. Serving the world. Marriott International declares its commitment to making a positive difference in the world. The company supports a variety of charitable organizations and encourages its employees to volunteer in their communities. Marriott also has a number of sustainability initiatives in place, such as its commitment to reducing its environmental impact and its investment in renewable energy. 5. Embracing change. The company understands that change is essential in the hospitality industry, which is constantly evolving. Marriott is committed to staying ahead of the curve and adapting to the changing needs of its customers. This commitment is evident in the company’s willingness to invest in new technologies and its focus on innovation. Marriott International Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Marriott organizational…

Marriott organizational structure had to change significantly with new executive appointments early in 2023. Following the departure of company’s president Stephanie Linnartz to become president and CEO of Baltimore-based sports equipment company Under Armour, Anthony Capuano became Marriott’s President and CEO[1]. Marriott International has a hybrid organizational structure that combines elements of both a matrix and functional structure. The company’s matrix structure is evident in the combination of functional and divisional configurations. Marriott has functional divisions such as marketing, sales, and operations, but it also has divisional units organized by geographic region. This allows the largest hotel chain in the world to achieve both global uniformity and local diversification and responsiveness. Marriott Organizational Structure The matrix structure works in conjunction with a regional structure, with each region having its own functional divisions. For example, the Greater China region has its own marketing, sales, and operations divisions. This allows Marriott to tailor its operations to the specific needs of each region. Marriott’s organizational structure is also characterized by a high degree of centralization. The company’s CEO and executive team have a significant amount of authority over decision-making. This centralization allows Marriott to maintain a consistent brand image and service quality across all of its properties. Marriott International’s hybrid organizational structure has several advantages. The matrix structure allows the company to achieve both global uniformity and local diversification and responsiveness. The regional structure allows the hotel chain to tailor its operations to the specific needs of each region. The centralization of authority allows the company to maintain a consistent brand image and service quality across all of its properties. However, there are also some potential disadvantages to Marriott organizational structure. The matrix structure can be complex and time-consuming, and it can lead to conflict between functional and divisional units. The centralization…

The current CEO of Marriott International is Anthony Capuano. He has been with the company for over 25 years and has held a variety of leadership positions, including Chief Development Officer and President of Global Development. Capuano is known for his strategic thinking and his ability to build and lead high-performing teams. Marriott International‘s leadership team is also notable for its diversity. The company’s executive team includes women, people of colour, and representatives from all over the world. This diversity of experience and perspectives helps Marriott International to better understand its customers and to develop innovative products and services. In terms of leadership style, Marriott is known for its commitment to servant leadership. Servant leaders focus on serving their employees and customers, rather than the other way around. This approach has helped Marriott International to create a positive work culture and to build strong customer relationships. Marriott International has a leadership development program called Voyage. Voyage is a 12-18 month program that is available to recent university graduates and provides a combination of practical hands-on experience and leadership training. Participants in the Voyage program rotate through different departments within a Marriott hotel and receive training from experienced leaders. Upon successful completion of the program, participants are well-positioned for leadership roles within hotel chain. Furthermore, Marriott leadership practices integrate the following important elements: Focus on employee development. The largest hotel chain in the world invests heavily in employee development and training. The company believes that its employees are its most valuable asset, and it is committed to helping them succeed. Fostering the culture of innovation. Marriott encourages its employees to be innovative and to come up with new ideas. The company has a number of programs in place to support innovation, such as its “TakeCare” program, which allows employees to submit ideas for improving the company.…

Fundamental Analysis of Marriott Stock Fundamental analysis refers to the practice of using financial activity to forecast stock prices. The following table illustrates main financial ratios for Marriott International: Ratio Marriott International performance Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Marriott’s P/E ratio is currently 22.4, which is slightly above the average P/E ratio of the S&P 500 index (18.6). In other words, Marriott’s stock is currently trading at a premium to the broader market Price-to-book (P/B) Marriott’s P/B ratio is currently 3.2, which is above the average P/B ratio of the S&P 500 index (2.3). This can be interpreted as Marriott’s stock is currently trading at a premium to the broader market based on its book value. Enterprise value to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EV/EBITDA) Marriott’s EV/EBITDA ratio is currently 11.5, which is in line with the average EV/EBITDA ratio of the hotel industry (11.0). This suggests that Marriott’s stock is currently trading at a fair valuation relative to its peers. Debt-to-Equity Ratio Marriott’s debt-to-equity ratio is currently 1.2, which is considered to be a healthy level of debt. In other words Marriott is well-positioned to manage its debt obligations. Return on Equity (ROE) and Return on Assets (ROA) Marriott’s ROE and ROA are both above the average ROE and ROA of the hotel industry. This suggests that Marriott is a profitable company that is generating good returns on its equity and assets. Marriott International main financial ratios Overall, Marriott’s financial ratios suggest that the company is well-managed and financially sound. Technical Analysis of Marriott Stock Technical analysis is the reliance of historical stock price activity to predict future price activity. Short-term trend The short-term trend for Marriott International is neutral. The stock is currently trading in a range between USD 198.23 and USD 206.55. A…

Marriott business strategy consists of the following 3 elements: 1. Pursuing asset-light business model. Operating in light-asset manner is one of the cornerstones of Marriott business strategy. Under this model, Marriott focuses on managing and franchising hotels, rather than owning them. This allows the hotel chain to expand rapidly and efficiently, without having to invest heavily in real estate. Light-assed strategy provides the company with a range of substantial advantages such as reduced capital investment and as a result, increased flexibility to enter into new markets and experiment with new brands. Furthermore, this strategy reduces exposure to the risk of real estate market downturns. 2. Growth through acquisitions. Marriott International has been a major user of acquisitions to fuel its growth. In 2016, it acquired Starwood Hotels & Resorts Worldwide in an USD 13.6 billion deal, which made it the world’s largest hotel company. The acquisition added nearly 1,300 hotels to Marriott’s portfolio, including brands such as Sheraton, W, and Westin. Since the Starwood acquisition, Marriott has continued to make smaller acquisitions to expand its reach into new markets and segments. For example, in 2017, it acquired Delta Hotels and Resorts, which added 38 hotels in Canada to its portfolio. In 2022, it acquired Hoteles City Express, which added 152 hotels in Mexico, Costa Rica, Colombia, and Chile. 3. Focusing on bleisure travellers. Bleisure travelling, a portmanteau of “business” and “leisure”, refers to the trend of business travellers extending their trips to include leisure activities. Marriott International is increasing its focus on bleisure travellers as part of its long-term business strategy. Up to date, this new customer segment, the business traveller who wants more choices for accommodations, that new blended traveller, and younger travellers who want more space for their travels, have been mainly served by Airbnb and…

A company is not just a member of a single industry but it is a part of an ecosystem that crosses a wide range of industries. Despite the coffee chain being in the business for more than five decades, Starbucks ecosystem is still in the early stages of its development. When a company has an advanced ecosystem its products and services are highly compatible with each other and customers will miss out on a wide range of benefits and functionalities if they want to break out of the ecosystem. Think Apple or Microsoft. Starbucks has not been able to develop an effective business ecosystem until now partially due to the nature of products and services the company offers. In other words, the global coffeehouse chain offers limited range of products and services it has not been successful in creating compatibility and dependence between products and services. Recognising the importance of having an ecosystem, Starbucks came up with the idea for digital ecosystem in 2020 as part of measures to deal with COVID-19 crisis. Specifically, Seattle-based international coffee chain is attempting to create digital third place, shifting its third place – a place away from home and work value offering to a digital environment.[1] Development of an effective ecosystem comprises the following four stages – pioneering, expansion, authority, renewal or death. [2] These stages relate to Starbucks ecosystem in the following manner: 1. Pioneering stage. The initial stage is associated with the formation of ecosystem. Starbucks ecosystem at this early stage involves initiating global digital community – a community defined by collaboration, experiences, and shared ownership – all centred around Starbucks coffee. 2. Expansion stage. At this stage ecosystem extends to achieve maximum market coverage and critical mass. The world’s largest coffeehouse chain can extend its relevance to integrate art,…
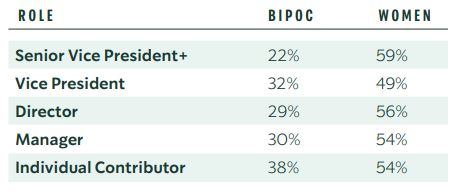
Starbucks CSR programs and initiatives are led by Michael Kobori, chief sustainability officer for the world’s largest coffeehouse chain. CSR initiatives for Starbucks cover wide range of business aspects and employee relationships such as supporting local communities, educating and empowering workers, gender equality and minorities, energy and water consumption, waste reduction etc. CSR Programs and Initiatives Starbucks Supporting Local Communities Starbucks Community Store program aims to assist local non-profit organizations in their efforts to provide education and training to achieve poverty eradication for the young segment of population. The company plans to open 100 Community Stores by the end of 2025. Starbucks has cooperated with non-profit organizations, community leaders and organizational stakeholders to provide more than 520,000 hours of volunteering service around the globe.[1] The global coffeehouse chain runs FoodShare food donation program in all company operated stores in US and Canada. 10.4 million and 1.2 million meals were donated in US and Canada respectively in FY21. Starbucks Educating and Empowering Workers Starbucks College Achievement Plan is an education program that allows employees to obtain online degrees from Arizona State University. Approximately 2500 employees earned their degrees via this program in FY21 alone It has been noted that “at the height of the global financial crisis, when other companies were cutting HR costs wherever they could, Starbucks invested in staff training, including coffee tastings and courses that ultimately qualified for credit at higher education institutions”[2] In FY21 the company oversaw more than 136000 course enrolments in Starbucks Coffee Academy and more than 55,000 course completions since launch. Starbucks and Gender Equality and Minorities At present about 40% of Starbucks US employees are minorities and 65% are women. Among vice presidents, 48% are women and 15% are minorities. The global coffeehouse chain aims to achieve at least 30% BIPOC…
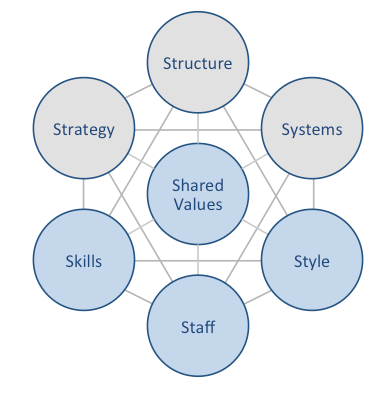
Starbucks McKinsey 7S model is used to highlight the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to this model, strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements. At the same time, shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements. Specifically, a change in one element causes changes in other elements. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Starbucks McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements in McKinsey 7S Model Strategy Starbucks business strategy is based on product differentiation with the focus on the quality of products and services. Moreover, the coffee chain giant effectively positions Starbucks stores as a ‘third place’ away from home and work, where customers can meet friends, relatives or spent time alone. Currently Seattle-based international coffee chain is positioning itself as a digital third place as well. Technological innovations and intensive integration of technology into various business processes in general and ordering process in particular represent another important aspect of Starbucks business strategy. The launch of Mobile Order & Pay feature, which allows customers to buy without getting in line, the launch of voice ordering app and “sending text message notifications to customers in the Seattle area when their mobile orders are ready”[1] can be mentioned to illustrate this point. Structure Starbucks Corporation has a hybrid organizational structure which combines geographic, brand-based and functional hierarchy structures. Operations are divided into North America (USA and Canada) and International (China, Japan, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa, Latin America and Caribbean) divisions. Brand-based divisions, on the other hand, consist of Starbucks, Teavana®, La Boulange®,, Evolution Fresh™, Seattle’s…
