Posts by John Dudovskiy

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates eBay SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. First mover advantage 2. Sophisticated infrastructure and the global scale of operations 3. Brand value 4. Organizational culture of experimentation and entrepreneurship Weaknesses 1. Dependence on products and services controlled by competitors 2. Complexity of business model 3. Lack of clear business strategy and competitive advantage 4. Absence of own distribution network Opportunities 1. Making a disruptive innovation in online retail industry 2. Engaging in business diversification 3. Formation of strategic alliances 4. Engaging in acquisitions Threats 1. Inability to compete with Amazon as online retailer 2. Breach of security 3. Crash of the website 4. Patent infringement and other lawsuits against the company eBay SWOT analysis Strengths First mover advantage has been traditionally a major strength for eBay. Apart from being the first platform in the world for online auctions, eBay has a first mover advantage in a range of areas such as Seller Performance Standards, eTRS, Verified Rights Owner Program and Feedback Forum. Particularly, the first mover advantage in online auctions has enabled the company to become a multi-billion company within a matter of a few years and ensured market leadership of the business. eBay has a highly sophisticated infrastructure that enables global scale of operations without any disruptions. At any given time it has more than 800 million live listings and in 2015, about 59 per cent of transactions between users on Marketplace and StubHub platforms take took place outside of the US[1]. The presence of such an advanced global infrastructure can play an instrumental role in terms of achieving global market penetration of new products and services in an effective manner. Interbrand and Forbes estimate eBay brand value as USD 13.9 billion and USD…
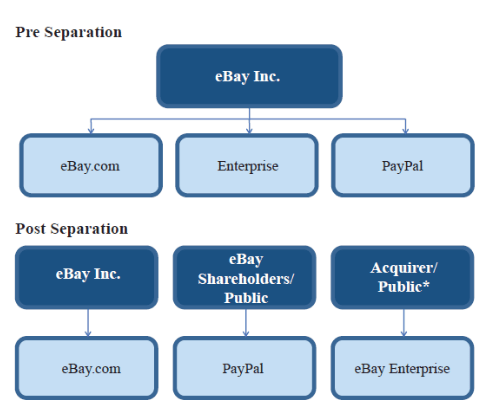
eBay organizational structure is hierarchical due to the massive size of the company that employs nearly 12,000 people worldwide. In 2015, a major restructuring was introduced to the company by separating PayPal from eBay Inc. The figure below illustrates changes to eBay organizational structure as a result of PayPal’s separation. eBay Organizational Structure eBay Board of Directors comprises 11 members and Thomas J. Tierney is the Chairman of the Board. David Wenig leads eBay executive team as President and CEO and is closely assisted by other leaders in the following positions: President, StubHub SVP, Chief Technology Officer SVP, General Counsel VP of Global Operations SVP, eBay North America SVP, eBay Asia Pacific SVP, Chief Product Officer SVP, Chief Financial Officer SVP, Chief Communications Officer SVP, eBay Europe SVP, Chief People Officer eBay Inc. Report comprises a comprehensive analysis of eBay. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on eBay. Moreover, the report contains analyses of eBay’s marketing strategy and discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility.

eBay leadership at the most senior position has been assumed by only four people since its establishment in 1995 by 28-year-old Pierre Omidyar. By June 1996 the company had USD10,000 in monthly revenues and its first employee and it secured a multi-million dollar round of venture capital funding the next year.[1] Aware of his entrepreneurial and leadership limits, Omidyar brought in Meg Whitman who oversaw IPO, international expansion, numerous acquisitions including PayPal, and several well-publicized site crashes. Meg Whitman stepped down as eBay CEO and President to run for the office of the Governor of California in 2008 and eBay leadership was assumed by John Donahoe. During the times he was in charge, Donahoe was seen as effective leader and turnaround manager. He was against the split of PayPal from eBay and unable to prevent the split, Donahoe had to step down on July 2015. It has been noted that “the changes implemented during John Donahoe’s tenure have proven to be controversial as shifts in rules and fees structures and an increased orientation toward high-volume, fixed-price retail channel selling have alienated portions of eBay’s traditional community even as the competitive landscape around eBay stiffens”[2] Today, Devin Wenig is the President and CEO of eBay Inc. and the executive leadership team comprises 13 members. There are 11 members in the Board of Directors comprises 11 members, including eBay founder Pierre Omidyar. The role of the Chairman of the Board is currently held by Thomas J. Tierney. Currently, eBay leadership is faced with a challenge of declining business growth. During 2015 – 2016 holiday season “sales grew an estimated 4.8 percent, which is way below the 13.3 percent typical for ecommerce companies”[3] The leadership of Devin Wenig can be criticized for the lack of clear strategy and competitive advantage for eBay. Plans…

eBay has been continuously reinventing itself since its founding in 1995 and its strategy places a great emphasis on the first mover advantage. eBay business strategy can be described as service differentiation with the focus on user experience of both, buyers and sellers. Specifically, the most recent changes include “improving the site’s search capabilities making finding items more structured. Instead of listing all available items when a product is searched, there will now be categories such as “best value,” “brand new” and others.”[1] Generally, for the past few years eBay business strategy has been marked with a shift from a listings-based format toward a product-based format. The pursuit of this business strategy has involved a collection of product-related data from sellers to enhance user experience with the ultimate aim of building machine learning capabilities to process a global, accessible catalogue of things. In other words, eBay business strategy is attempting to shift the role and image of the company from e-commerce facilitator to an online retailer. While this decision by CEO and President Devin Wenig may reflect the overall tendency in the global market, eBay may find it increasingly difficult to compete with Amazon, taking into account Amazon’s high level of cost-effectiveness and competence in the delivery of goods. eBay business strategy for a medium term perspective also includes improving its ranking in Google search results via employing a structured data. It is important to note that the business strategy of service differentiation requires systematic financial investments in research and development. From this point of view, it can be argued that eBay may find it difficult to pursue this strategy in the future, since after the separation from PayPal in 2015, eBay lost a solid source of cash flow and a powerful growth engine. eBay Inc. Report contains more detailed…

eBay Inc. is a US-based e-commerce company and global corporation that provides consumer-to-consumer and business-to-consumer online sales platform. Founded in 1995 by Pierre Omidyar, nowadays eBay employs nearly 12,000 people worldwide, including 6200 employees in the USA. More than 160 million people buy from eBay annually and the company generated the revenues of more than USD 8.6 billion in 2015 alone. eBay’s mission statement is ‘to be the world’s favourite destination for discovering great value and unique selection’. eBay business strategy focuses on benefiting from the first mover advantage via introducing innovative services and regularly adding new features and capabilities to existing services with the aim of enhancing user experience. The senior management led by CEO and President Devin Wenig has made a strategic decision to transfer the business from an online auction to become the largest online retailer, an area which is currently dominated by Amazon. The e-commerce company has certain weaknesses that include dependence of the business on a range of products and services controlled by competitors such as Google, an overall complexity of the business model and an absence of eBay’s own distribution network to compete with Amazon. eBay Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on eBay. Moreover, the report contains analyses of eBay’s business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and its marketing strategy. The report also discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Introduction 2. Business Strategy 3. Leadership 4. Organizational Structure 5. SWOT Analysis 5.1 Strengths 5.2 Weaknesses 5.3 Opportunities 5.4 Threats 6. PESTEL Analysis 6.1 Political Factors 6.2 Economic Factors 6.3 Social Factors 6.4 Technological Factors 6.5 Environmental Factors 6.6 Legal Factors 7. Marketing Strategy 7.1 7Ps of Marketing 7.2 Segmentation,…
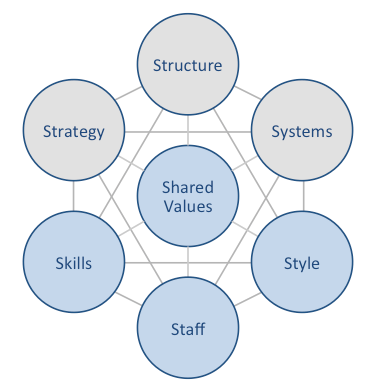
Hilton McKinsey 7S framework focuses on seven elements of a business practice that can be aligned to improve effectiveness of the company. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Hilton McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Hilton McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Hilton business strategy can be classified as service differentiation. The major points of differences of Hilton hotels from the competition include high quality of services and advanced integration of information and communication technologies into various aspects of hotel experience. Moreover, Hilton business strategy attempts to associate the experience of staying in Hilton Hotels with customer perceptions of status, achievement and recognition. Structure. Hilton organizational structure is hierarchical due to the massive size of the business that comprises 13 brands serving 140 million guests in 2015 alone (Annual Report, 2015). Moreover, Hilton organizational structure can also be described as divisional and the business is divided into three divisions: ownership, management and franchise, timeshare. Systems. Hilton Worldwide business operations rely on a wide range of systems such as customer reservations system, quality control system, employee recruitment and selection system, employee performance evaluation system and others. Since his appointment as the President and CEO in 2007, Christopher Nassetta simplified a wide range of Hilton systems to a great extent. For example, an introduction of a single company-wide system for employee performance evaluations simplified relevant processes to a great extent. Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains a detailed discussion of Hilton…
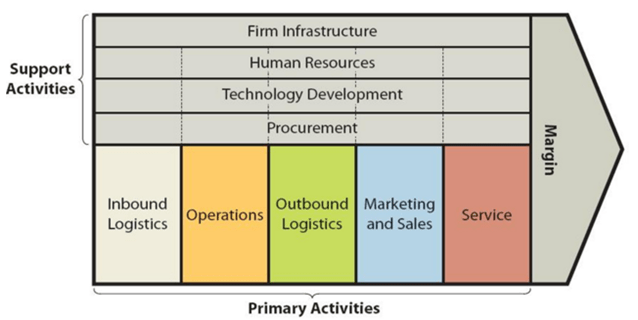
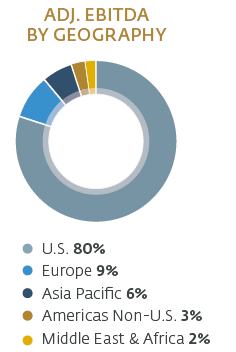
Hilton value chain analysis identifies business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. The framework of value chain analysis divides business activities into two categories: primary and support activities. The figure below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis: Hilton Value Chain Analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics Hilton inbound logistics represents a highly sophisticated system that ensures smooth operations in 572 hotels and resorts in 85 countries around the world.[1] Hilton’s “procurement group aggregates buying into national contracts for its various brands, and enables local providers where it makes sense to do so”[2] Hilton’s supply chain management and inbound logistics is unique in a way that the company makes deals directly with suppliers, then negotiates markups with the distributors that handle warehousing and delivery. This practice is an important source of value for the business since it enables the control of the whole supply chain. Operations Hilton Worldwide operates its business via the following three segments: Ownership segment. This segment consists of 146 hotels with 59,463 rooms which are owned or leased by Hilton Worldwide. Management and franchise segment consists of 4,419 hotels with 691,887 rooms. These are owned by third parties and managed by Hilton Worldwide. The company also licences its brand to franchises. As of December 2015, Hilton Worldwide franchised 3,875 hotels with 533,039 rooms. Timeshare segment consists of 45 properties comprising 7,152 units. This segment is engaged in marketing and selling timeshare intervals, operating timeshare resorts and timeshare membership clubs and providing consumer financing. Hilton operations are divided into four geographical segments: Americas Europe Middle East and Africa Asia Pacific The main sources of value in Hilton’s business operations include the highest level of standard of service, a high level of service personalization and integration of information and communication technologies into the various…
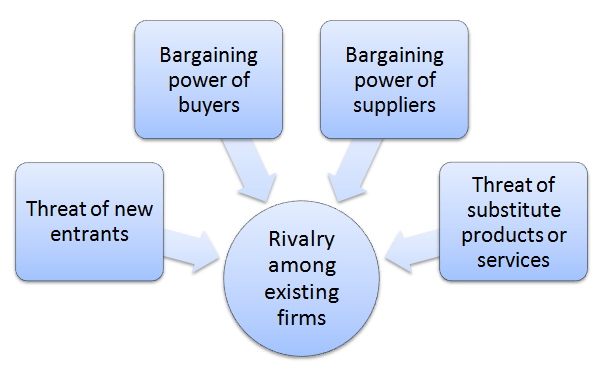
The analytical framework of Porter’s Five Forces developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] explains five separate forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1. Hilton Porter’s Five Forces Rivalry among existing firms in premium segment hotel industry is fierce. Hilton Hotels and Resorts competes with Marriott, Sheraton, Hyatt Regency, Radisson Blu, Renaissance, Westin, Sofitel and other premium segment hotel chains in the global marketplace. As a result of massive investments into various aspects of the service provision during the past few years, Hilton enjoyed greater income growths compared to the competition. Specifically, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Net Income in the 1 quarter 2016 grew year on year by 106.67 %, faster than average growth of its competitors. Figure 2. Income growth differences between Hilton Worldwide and its competitors[1] Bargaining power of Hilton suppliers is low. Hilton Worldwide purchases from more than 4000 suppliers globally [2] and the bargaining power of most suppliers is low due to the lack of uniqueness of products and services supplied. Moreover, the importance of order volume for Hilton suppliers is paramount and there is no supplier switching costs for Hilton on most cases. Hilton runs Supplier Diversity Program that ensures purchasing from, and the development of, socially diverse suppliers. Accordingly, the program provides an additional competitive ground for socially diverse suppliers compared to other supplier groups. Threat of substitute products or services in hotel industry is not significant. Direct substitutes for staying in Hilton hotels includes people staying in the homes of friends and relatives and people renting apartments for short periods of time. However, arrangement of these options can be time-consuming and associated with a great deal of hassle. Hotel industry is also faced with…

Hilton marketing communication mix integrates print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing as discussed below in more details. Advertising Hilton engages in print and media advertising to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment. Hilton marketing message stresses the highest standard of service provision, a high level of integration of information technology in order to maximise service personalization and the perception of status, achievement and recognition. This marketing message is communicated through a set of specific elements of advertising promotional strategy such as advertisements in newspapers and magazines popular with senior level management professionals such as Forbes, Fortune, The Economist, and Financial Times. Moreover, the communication of Hilton Hotels & Resorts marketing message is also facilitated through broadcast advertisements in selected television channels. ‘Stop Clicking Around’ is one of the recent large-scale marketing campaigns that “challenges the common misconception that third-party Web sites always offer the best prices on hotel rooms”[1]. Sales Promotion Sales promotion relates to attempts by a business to persuade potential customers to purchase products or services through introducing various incentives. Sales promotion is popular in hotel industry and this specific element of promotion mix is used by Hilton Hotels & Resorts in an intensive manner. Specifically, Hilton uses the following forms of sales promotions: HHonors loyalty programs offer discounted prices, digital check-in, free internet access, late check-out and others. Currently, there are more than 50 million Hilton HHonors members worldwide.[2] Discount vouchers are available in official website of the company and a wide range of discount websites. Hilton Hotels & Resorts gains practical advantages from using sales promotion in the forms of increasing the level of revenues and achieving utilisation of their rooms at a greater extend. However, it is important to note that by introducing…
SWOT is an acronym that stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to businesses. The following table illustrates Hilton SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Extensive experience and a vast scope of the business 2. Effective customer retention schemes 3. strong property portfolio 4. Strong and effective leadership by Christopher Nassetta 5. A high level of service customatisation achieved via technological integration Weaknesses 1. Overdependence on the US market 2. High levels of debts 3. Little global market share, despite the large portfolio of brands 4. Lack of flexibility due to its large size Opportunities 1. Further International market expansion 2. Formation of strategic alliances 3. Focusing on research and development 4. Establishing presence in the mid-level budget hotel sector Threats 1. Threat of terrorism and political instability 2. Adverse changes in macroeconomic climate 3. Ethics-related issuesin Hilton hotels 4. Loss of key talent and key personnel Hilton SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Hilton Worldwide comprises 13 brands including well-known brands such as Hilton Hotels and Resorts, Waldorf Astoria, Conrad, Double Tree, Embassy Suites and others. Hilton Worldwide served more than 140 million guests in more than 100 countries and territories in 2015 alone.[1] Due to the large scope of its business operations, the company benefits from the economies of scale to a considerable extent, creating the potential for further growth of the business. 2. Hilton offers one of the best customer loyalty schemes in the industry represented by Hilton HHonors program. Wide range of benefits offered by the program includes discounted prices, digital check-in, free internet access, late check-out and others. These benefits are greatly appreciated by customers and there are more than 50 million Hilton HHonors members worldwide.[2] 3. Hilton Worldwide owns 4610 properties around the globe.[3] An extensive property ownership is a major strengths from the financial point…
