
Square Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the B2B fintech to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Square Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Square uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Square uses market penetration strategy extensively. Specifically, the payments company relies on viral marketing based on storytelling along with other marketing strategies to sell its financial products and services to small and medium businesses in North America, Canada, Japan, Australia, Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom. Furthermore, the financial services and digital payments company offers individuals on the same locations listed above the services of storing, sending, receiving, spending and investing their money. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. New product development is the main growth strategy for Square. Having entered the market only with a card reader, nowadays Square offers more than 30 distincg products and services for businesses and increasing numbers of products and services to individuals. . Each new product developed by Square further strengthens its expanding ecosystem of financial products and services. The financial services and mobile payments company is expected to further engage in product development strategy in an accelerated rate. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Square is cautious and overly selective in expanding in new markets. Moreover, there are entry barriers for the financial unicorn such as the level of financial infrastructure, regulatory barriers and the level of technological savvy for consumers. 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets…

Square organizational culture integrates the following 3 key elements: 1. Informal work environment. Work environment at Square is highly informal and this has a stark reflection the design of its offices worldwide. Moreover, “Square has designed its work spaces to be large, open and ripe for serendipitous collaboration”[1] In other words, Square organizational culture defies formality in the workplace through seemingly-casual, yet effective organization of workspaces. 2. Inclusion and diversity. Square organizational culture embraces and promotes diversity among employees at all levels. There are various employee communities in the company that cater for the interests of its members. These include Black Squares Association, Latinx, Asian Pacific Islander Squares, Veterans at Square and others. These communities are employee-run resource groups that promote universal inclusivity through networking, development opportunities, and social events.[2] In other words, people belonging to minority groups do not feel alienated when they join Square with positive implications on their work performance and overall happiness. 3. Social and economic impact. Square positions itself as a challenger to traditional banks. Specifically, the company attempts to democratise a wide range of financial services to simplify them and make these services available for small businesses for a little cost. From this point of view, the financial services and digital payments company is set to disrupt banking sector in a global scale. Such a challenger position attracts specific type of workforce, who are motivated by the perception of participating in and contributing to the worldwide change of banking services for the better. These types of highly motivated employees contribute to the formation of an advanced organizational culture at Square. Square Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Square organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces,…
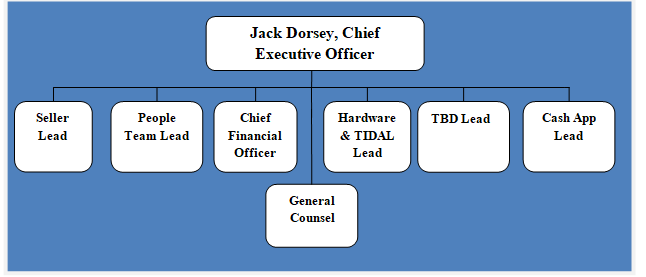
Square Inc. organizational structure can be classified as relatively flat, taking into account ever-growing size of the business. Co-founder and CEO Jack Dorsey attempts to maintain a start-up environment and culture and reduce bureaucracy in order to keep the business flexible to be able to respond to changes in the external environment. Therefore, it can be argued that Square organizational structure is designed to increase the speed of decision-making. Leads of units operate as a CEOs and they report only to Jack Dorsey. Leads oversee project leaders and project teams at Square are small groups comprising maximum 12 people of diverse backgrounds. As illustrated in figure below, Square’s cryptocurrency business unit TDB is a division separate from both, seller and cash units. One of the reasons for this separation may relate to regulatory reasons. Specifically, maintaining crypto separate from other units decreases the chances of regulatory interferences. Square organizational structure The company is increasing the range of products and services extensively. This strategy can increase complexity of the business with direct implications on Square organisational structure, despite CEOs attempts to maintain it simple. Accordingly, the senior management of the financial services platform has a challenging task of maintaining flexibility of the business amidst its exponential growth. Moreover, there are opinions among industry analysts that CEO Jack Dorsey’s ultimate plan is to make Square a holding company for autonomous fintech businesses[1]. A Tweet by Dorsey on July 2021 claiming that the payments company will create a new business line to help developers build financial services products focused on Bitcoin can be seen as a signal to support such as viewpoint. Square Inc. Report contains the above analysis of Square organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five…

Efficiency of Square leadership is one of the competitive advantages of the business. Jack Dorsey, Square co-founder, President, and Chief Executive Officer, also serves as Chief Executive Officer of Twitter, Inc. The payments company Board of Directors comprises strong business leaders such as former CFO of PayPal Roelof Botha, CEO of Shake Shack Randy Garutti and former CFO of Goldman Sachs David Viniar. Square leadership style integrates the following two principles: 1. Purpose-driven leadership. Leadership style practiced by Jack Dorsey can be classified as a purpose-driven leadership. This type of leadership can be defined as “prioritizing purpose and people over profit and greatness over growth.”[1] For Square leadership the prioritized purpose is making easier for everyone to participate in the economy. The payments company attempts to achieve this mission through developing an ecosystem of financial products and services that are greatly simplified versions of banking services. Moreover, the purpose serves as a compass for long term decision making for Square leadership team. 2. Focus on team effort and appreciation of teamwork. At Square great emphasis is placed at teamwork and decision-making at strategic level reflects inputs from teams. It has been noted that “whether he is discussing Twitter or Square, Dorsey gives most of the credit to his team.”[2] Such an approach encourages team members at all levels to feel the ownership of the company with positive implications on their work performance. Currently, Square leadership is faced with a challenge of sticking to its leadership principles and maintaining organizational culture amid an extensive growth of the business in an international scale. Taking into account successful leadership experience of Dorsey at Twitter, which is a truly global business, it can be expected that senior management at Square can deal with this challenge in an appropriate manner. Square Inc. Report contains the above…

Square business strategy is based on the following two principles: 1. Simplifying financial transactions. Square Inc. was founded when Jim McKelvey, friend of current CEO Jack Dorsey could not sell his glass faucets and fittings because he could not accept credit card. The two co-founders saw a business opportunity in this problem and developed the first card reader, which allowed small businesses and individuals to accept credit cards. The finance sector disruptor simplified a range of other financial transactions. For example, instant payment feature on Seller account allows businesses to pay their employees the next business day. Thanks for this capability, employees do not have to wait for the paycheck for several days or even weeks, which has been the case. Furthermore, Square has also simplified the practice of investing in stocks and bitcoin commission-free for people with no prior investing experience. Customers simply open up the Cash app, decide how much they want to invest in a single stock and click purchase. Challenging the status quo in finance and simplifying financial transactions is the core business strategy for Square. 2. Developing and expanding an ecosystem of financial products and services. In its course to simplify financial products and services as discussed above, Square business strategy relies on the development and strengthening of ecosystem. Currently, the payments company is developing two ecosystems simultaneously – seller and cash. Square seller ecosystem is a cohesive commerce ecosystem that helps its sellers start, run, and grow their businesses. Cash ecosystem, on the other hand, consists of a line of products and services that help individuals to manage their money. Although the link between the two ecosystems is rather weak at this stage, the company will attempt to increase the linkage through developing financial products and services that will intersect both. Square Inc. Report contains…

Square Inc. is a global financial services and digital payments company based in San Francisco, USA. Founded by co-founder of Twitter, Jack Dorsey and Jim McKelvey in 2009, the company started with selling card readers that enabled small businesses to accept credit cards. Since that time Square has evolved into an international financial services and mobile payments platform providing an ecosystem of integrated products and services. In 2019 Square processed USD106.2 billion of Gross Payment Volume (GPV), which was generated by nearly 2.3 billion card payments from 407 million payment cards. At the end of 2019, Square point of sale ecosystem had over 180 million buyer profiles and approximately 230 million items were listed on Square by sellers. The financial unicorn generated net income of USD375.4 million in 2019, employing 3,875 people full-time. Square business strategy is based on simplification of financial transactions and the company has developed an expanding ecosystem of products and services. The finance sector disruptor has certain business advantages such as the first mover advantage and strong leadership by CEO Jack Dorsey. At the same time, there are certain weaknesses associated with Square. These include lack of global presence, high employee turnover and dependence on payment cards networks. The payments company faces a set of potential threats as well such as increasing complexity of the business, cyberattacks and emergence of new competitors. Leadership style at Square can be classified as purpose-driven leadership and the payments company has a purpose to make it easier for everyone to participate in the economy. Furthermore, Square leadership appreciates teamwork and focuses on benefiting from team effort to a great extent. Square Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S…

Uber corporate social responsibility is attracting a lot of interest among business researchers and practitioners recently. Not paying due attention to CSR aspect of the business has been traditionally one of the weaknesses associated with Uber under previous CEO and co-founder Travis Kalanick. The ride-hailing giant has even lost its license to operate in London in 2017 due to the lack of corporate social responsibility[1]. However, under the new CEO Dara Khowrowshahi the company has fully recognized the importance of conducting sustainable business and this change is communicated to internal and external stakeholders systematically. The largest mobility platform in the world has pledged to become a fully zero-emission platform by 2040, with 100% of rides taking place in zero-emission vehicles, on public transit, or with micro-mobility Uber CSR Programs and Initiatives Uber and Gender Equality and Minorities The company received the maximum score of 100% on Human Rights Campaign 2020 Corporate Equality Index 59,7% of total workforce are man and 40,3% of all workforce are women. In tech jobs, the majority 76,9% of employees are men, whereas women fill only 23,1% of tech positions Black or African American represent only 7,5% of the total workforce Water Consumption by Uber The global transportation technology company used 699,854 cubic meters of water globally in 2019 Mission Bay campus in San Francisco, USA is estimated to save round 2.5 million gallons of water through re-using the water Carbon Emissions by Uber The company has set a goal that 100% rides in US, Canadian, and European cities will be in electric vehicles (EV) by 2030. Uber Green program is being expanded make it easier for riders to choose to travel in hybrids or EVs The ride-hailing giant is committing USD 800 million in resources to help hundreds of thousands of drivers transition to EVs…

Uber is working towards developing its own ecosystem in order to increase customer loyalty with positive implications on company’s revenues. The development of Uber ecosystem has integrated the following key milestones: 1. Request API The development of Request API (application programming interface) has been viewed by industry analysis as the first step towards developing the ecosystem. It has been noted that “Request API gives third party developers the ability to integrate their application into Uber. So if you’re an airline or a restaurant booking application, you can create a situation whereby your flight delay was automatically notified to your Uber driver so that your pickup is correctly rescheduled.”[1] 2. Uber Eats The launch of food delivery service by the company as UberFRESH in 2015, later renamed as UberEAT in 2015 was an important move for the ride-hailing giant to expand beyond ridesharing. This is a major difference between Uber and its main rival Lyft. Specifically, when Lyft was concentrating solely on taxi services and ride-sharing for a long time before doing anything else; Uber senior management sought to differentiate the business using the same platform early on with positive implications on its ecosystem. 3. Uber Feed The update of app on November 2016 paved a way for further development of Uber ecosystem. Nowadays, Uber app learns from routines of users and scrapes their calendars for the address of their meetings across the town.[2] Particularly, Uber Feed is an important feature and it intends to gain customers attention during the ride. Uber Feed presents a stack of services Uber thinks customers might find useful during their trip. Customers can swipe left on Uber Eats to see which restaurants can deliver to their house in synch with their arrival time. Alternatively, if customers are running late to their destination, they can use…
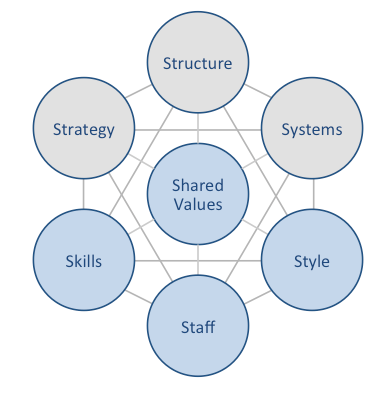
Uber McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Uber McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications on their performance. McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements Strategy Uber pursues cost leadership business strategy. The ride-hailing giant gains cost advantage thanks to internet-based nature of its business model that disrupted traditional taxi industry in the global scale. The international transportation technology company increases range of its services regularly to cater for the needs of greater numbers of customers. Moreover, Uber business strategy places a great emphasis on a high level of user convenience. Growing the business through acquiring adjacent businesses is another important aspect of Uber business strategy. Structure Uber organizational structure can be classified as hierarchical. Accordingly, the company is disadvantaged by the shortcomings of hierarchical structure such as ineffective communication across various departments, rivalry between departments that may compromise long-term growth prospects and high level of bureaucracy. Following the failed IPO in 2019, the CEO Mr. Khosrowshahi changed Uber organizational structure to increase his role in operational day-to-day management. As part of these changes, the positions of chief operating officer (COO) and chief marketing officer (CMO) were also eliminated. Systems Systems within McKinsey 7S model refer to daily activities and procedures that Uber staff use to provide ride-haling services to millions of customers worldwide. There is a wide range of various systems that are important for Uber’s long-term…
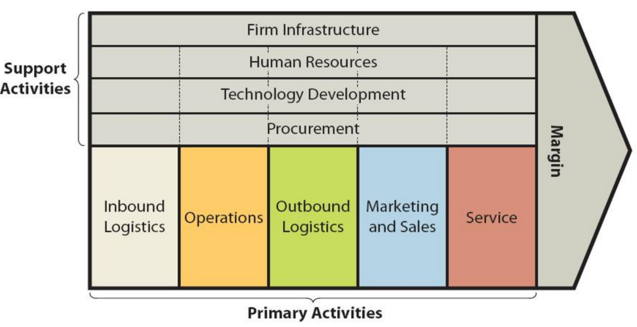
Uber Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that helps to identify the sources of value and competitive advantage for the global transportation technology company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Uber value chain analysis. Uber Value Chain Analysis Uber Primary Activities Uber Inbound logistics Generally, inbound logistics involves receiving and storing raw materials. Uber, the largest taxi technology company in the world, does not own the vehicles it uses to serve customers. The vehicles are owned or rented by Uber drivers, who are not employees, but independent contractors. Uber drivers need to possess smartphones to use Uber app software. Uber users, i.e. customers also must have access to a smartphone or mobile website to be able to use the service. Accordingly, value addition in Uber inbound logistics relates to internet-based nature of business operations and the business model of the company. Specifically, thanks to its business model, despite the large size of the business, Uber inbound logistics is only limited to mainly hardware and office equipment needed to sustain the business. The global transportation technology company does not need to procure any raw material for provide its services. Uber Operations Uber operations are highly sophisticated and customer-centric thanks to its app equipped with advanced functions and capabilities. Therefore, it can be argued that Uber app is one of the main sources of value in Uber operations. Uber operates in approximately 10000 cities worldwide. Business operations are divided into four reportable segments: 1. Mobility. In Mobility segment Uber operations consist of connecting consumers with independent providers of ride services. The usage of Uber mobility services involves the following stages: a) Requesting the ride. Customers can use Uber app to tap each ride option to see wait time, driver’s rating, and price. Customers can enter their pickup location and…
