
Apple business strategy can be classified as product differentiation. Specifically, the multinational technology company differentiates its products and services on the basis of simple, yet attractive design and advanced functionality. Apple business strategy consists of the following four elements: 1. Focus on design and functionality of products. According to its business strategy, Apple has adapted advanced features and capabilities of its products and services as bases of its competitive advantage. The list of innovations introduced by Apple include, but not limited to the introduction of iPad, the first device of its kind that stored thousands of songs with a simple shuffle capabilities through songs, development Macintosh, the first computer to use a graphical user interface and the launch of iMac that “ripped up the computer design rule book, doing away with dull beige boxes and instead replacing them with fun, translucent machines in shades such as “Bondi Blue” that hinted at the aesthetic Apple would become so well-known for.”[1] The first company ever to be valued at $1 trillion systematically improves features and capabilities of its products, setting new standards for the industry at the same time. Take photos for example. Apple single-handedly advanced global photography industry with a range of innovations illustrated in table below. Innovation Year High dynamic range imaging 2010 Panorama photos 2012 True Tone flash 2013 Optical image stabilization 2015 Dual-lens camera 2016 portrait mode 2016 portrait lighting 2017 night mode 2019 LiDar scanning 2020 Photography innovations by Apple Inc. First mover advantage is another element of Apple competitive advantage. It has to be stated that Apple competitive advantage may be challenging to be sustained for long-term perspective. Specifically, the management may fail in terms of ensuring the addition of innovative features and capabilities in new versions of its products, thus compromising…

Apple Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the multinational technology company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Apple Ansoff Growth Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Apple uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. Existing market for Apple consists of its global operations divided into five operating segments: Americas, Europe, Greater China, Japan and Rest of Asian Pacific. The tech giant operates more than 518 retail stores in 25 countries and regions.[1] Apple engages in market penetration strategy via effective application of marketing strategy. Apple’s ecosystem of products and services also plays an instrumental role in pursuing market penetration strategy with high level of efficiency. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. New product development in a regular manner is one of the core growth strategies pursued by Apple. Each new product or service by Apple nicely fits within its ecosystem and serves to further strengthen the company ecosystem. Moreover, the multinational technology company regularly introduces updated versions of its existing products and services and introduces totally new products. The company’s investments on research and development for new products has increased from USD 0,78 billion in 2007 to USD 25,3 billion in 2023. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. This strategy has been adapted as the main growth strategy by Apple. Specifically, the world’s largest IT company by revenue focuses of emerging economies in Asia as attractive markets for long-term perspective. The multinational technology company appeals to local culture and sentiment when developing marketing strategies…
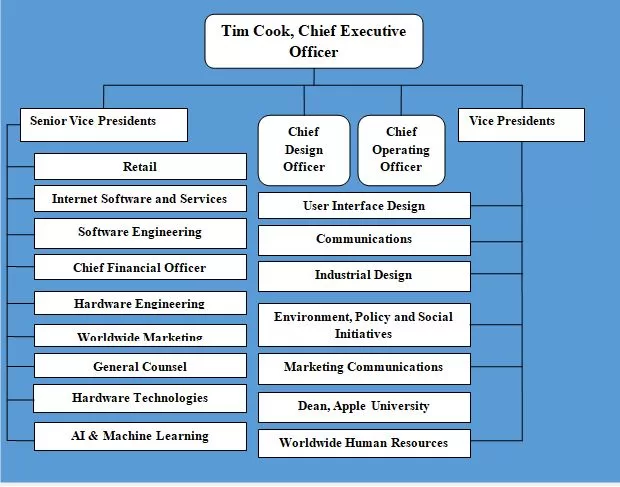
Apple organizational structure can be described as hierarchical and functional. Such a structure has been developed by its founder and former CEO late Steve Jobs in order to ensure focused realization of his innovative ideas and clear vision for the business. When Steve Jobs returned to turnaround failing Apple in 1997 the company had a typical organizational structure with many business units with their own profit and loss (P&L) responsibilities. In order to increase the coherence and fuel innovation, Jobs fired general managers of all business units (within one day) and put in place one P&L for the entire business. Apple organizational structure has been subjected to certain modifications since the leadership role was assumed by Tim Cook on August 2011. Specifically, Mr. Cook embraced the decentralization of decision making to a certain extent in order to encourage innovation and creativity at various levels. Also, Cook divided hardware function into hardware engineering and hardware technologies. As the most recent change to the corporate structure Cook added artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning as separate function areas due the increasing importance of AI and machine learning. Currently, Apple organizational structure has the format illustrated in figure below: Apple Organizational Structure Generally, Apple corporate structure has the following characteristics: 1. Hierarchical organizational structure. Although Tim Cook introduced considerable changes to Apple corporate structure since assuming the top job in 2011, the structure still remains to be highly hierarchical with many layers of management. Massive size of the company that comprises 164,000 full-time equivalent employees globally necessitates the adherence to the hierarchical organisational structure. Advantages of Apple hierarchical organizational structure include tight control possessed by senior management over all aspects of the business. Moreover, promotion opportunities motivate employees to perform well and there are clear levels of authority and responsibility. On the negative…

During Steve Jobs era that covers the period 1997 – 2011, Apple leadership was autocratic with Steve Jobs micro-managing a wide range of business operations. It has been noted that “when Steve Jobs was in charge, everything flowed through him.”[1] Apple leadership practices have changed dramatically under Tim Cook. Acknowledged as the World’s Greatest Leader by Fortune Magazine[2], Tim Cook proved to be effective from various perspectives. Moreover, Tim Cook has been praised by employees for inspirational leadership and helping his subordinates to become a better human being.[3] The multinational technology company is parting with perfectionism and autocracy elements of leadership that had prevailed under Steve Jobs. Apple leadership style integrates the following elements: 1. Democratic leadership style. In contrast to highly autocratic leadership style of Apple co-founder and late CEO Steve Jobs, the current CEO Tim Cook exercises and promotes democratic leadership. For Cook, it is important to build consensus among senior management regarding strategic decisions for the ebusiness. Moreover, since assuming the top role, Cook granted greater autonomy to new product development team, decreasing the direct participation of the CEO in new product development process. 2. “Quiet” leadership. Tim Cook has been praised for his quiet, yet effective leadership style. Nicknamed as “quiet leader” by some industry analysts[4], Cook is totally different from his charismatic predecessor, Steve Jobs. At the same time, Tim Cook is occasionally criticized by analysts and industry watchers for the lack of ambition and vigour, his predecessor Steve Jobs had. For example, according to a report by BGC financial services firm, “under Cook, Apple has been cautious about entering new product categories. The Apple Watch, launched in April 2015, is the No. 1 smartwatch, but overall sales have disappointed. Apple Music, which debuted in June 2015, has grown rapidly to 15 million subscribers, but…
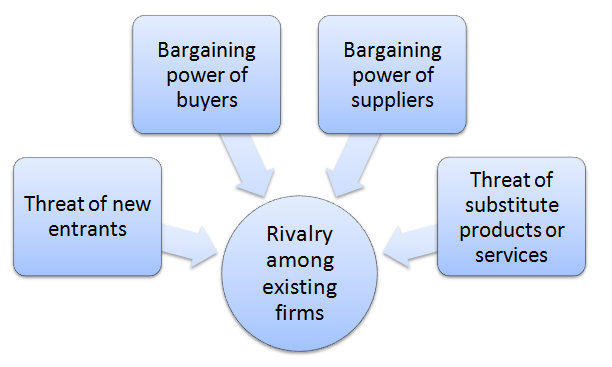
Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] represents five individual forces that shape the overall extent of competition in the industry. Apple Porter’s Five Forces are represented in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entrants in Apple Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into consumer electronics industry is not substantial. The following factors, among others, determine the threat of new entrants into the industry to compete with Apple: 1. Massive capital requirements. Manufacturing technological devices and producing operating systems require massive capital investments. As illustrated in Table 1 below, the top players in the market invest billions of dollars in R&D in order to keep the pipeline of new products and services active. New market entrants will have to produce new products and services that will have to compete with products and services of top players that invest billions of dollars every year in R&D. Rank Company R&D spending (USD) 1 Amazon 70.3 billion 2 Alphabet 38.1 billion 3 Meta Platforms 34.0 billion 4 Apple 25.3 billion 5 Microsoft 23.0 billion 6 Samsung Electronics 18.2 billion 7 Intel 17.5 billion 8 Roche 16.0 billion 9 Volkswagen 14.0 billion 10 Johnson & Johnson 14.0 billion Table 1 Top R&D spenders among technology companies in 2022 Moreover, capital is needed to obtain resources in general and to attract human resources and talented employees in particular. Accordingly, it is safe to argue that access to capital can prove to be a substantial entry barrier for new businesses. 2. Economies of scale. Economies of scale are substantial entry barrier into consumer electronics and tech industry. New players will find it difficult to compete with established global brands such as Apple, Samsung, Google and HTC that are able to gain cost advantage…
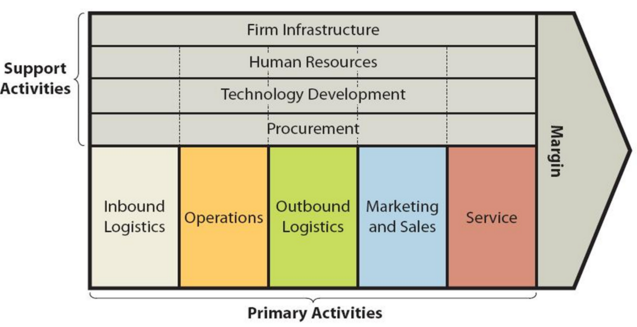
Apple value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the business. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Apple value chain analysis. Figure 1 Apple Value Chain Analysis Apple Primary Activities Apple Inbound logistics Inbound logistics primary activity refers to receiving and storing of raw materials for their consecutive use in manufacturing. Apple works with hundreds of suppliers around the globe and maintains a highly sophisticated supply-chain management as illustrated in Figure 2 below. Figure 2 Apple operations roadmap[1] Apple supply chain involves more than 3 million people working for thousands of businesses in 52 countries[2] The multinational technology company’s purchase commitments typically cover its requirements for periods up to 150 days[3]. Tim Cook is an experienced word-class supply chain professional. Steve Jobs had convinced him to join Apple as head of supply chain in 1998 when the tech giant was in trouble, risking the bankruptcy. As part of massive supply chain turnover Tim Cook cut the numbers of suppliers, reduced the number of warehouses by half and established relationships with contract manufacturers. Cook has been able to reduce Apple inventory turn over from 1 month to 2-5 days. Cook further reduced the numbers of suppliers after becoming CEO in 2011. As a result of these and other initiatives, Apple supply chain practices have become a benchmark for efficiency for global businesses. The main sources of value in Apple inbound logistics relate to the economies of scale due to the massive scope and scale of business operations as discussed below and the development of strategic relationships with suppliers. Moreover, Apple Inc. exercises an immense bargaining power in dealing with its suppliers and as a result, the company is able to secure cost advantage in the purchase of…

Apple marketing mix (Apple’s 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Element in Apple Marketing Mix (Apple 7Ps of Marketing) In 2010, before he became chief executive officer, Tim Cook claimed that Apple’s all products could fit on a single table. At that time the multinational technology company produced only 14 products.[1] It is different now. It has been noted that “no longer do the barista and the corporate executive use the same iPhone — today, there are high-end models, consumer models, and a long line of old products the company keeps around to fill every niche and price point.”[2] Today, Apple designs, manufactures and sells technological devices such as IPhone smartphones, IPad tablets, Mac desktop and portable personal computers and iPod digital music and media players. Moreover, the company generates revenues via iTunes and the iTunes Store, Mac App Store, iCloud and Apple Pay. Apple also develops iOS and OS X operating system software and a range of application software such as iLife and iWork. Lastly, Apple Corporation designs, manufactures and sells own and third-party Mac-compatible and iOS-compatible accessories, including Apple TV, headphones, cases, displays, storage devices and various other connectivity and computing products and supplies[3]. Apple also sells third-party digital content and applications through iTunes Store®, App Store®, Mac App Store, TV App Store, iBooks Store™ and Apple Music®. Table 1 below illustrates the full range of Apple products, their brief descriptions and additions in 2023: Product Categories Description Additions in 2020 iPhone A line of smartphones based on iOS operating system iPhone SE, iPhone 12, iPhone 12 Pro, iPhone 12 Pro Max, iPhone 12 mini Mac A line of personal computers based on macOS operating system 16-inch MacBook Pro, 13-inch MacBook Pro, 27-inch iMac iPad…

Apple marketing strategy is based on the founder Steve Jobs’s philosophy that customers do not always know what they want. Accordingly, instead of conducting marketing researches to identify customer needs and wants, the multinational technology company prefers to install innovative features and capabilities in their products, making customers to want Apple products. Under the leadership of Tim Cook since 2011 certain aspects of the business such as management style and company’s stance towards CSR have changed. However, the dismissal of marketing research remains to this day. Apple marketing strategy expresses the brand in minimalist, yet highly efficient ways. The world’s largest IT company by revenue is one of the first companies to successfully associate the brand image with being innovative, rebellious and non-conformist. Apple 7Ps of marketing is marked with a particular focus on the product element of the marketing mix and the company’s segmentation targeting and positioning initiatives are aimed at targeting users of premium products. Moreover, marketing communication mix of Apple Inc. places greater emphasis on print and media advertising and personal selling in Apple Stores and the company rarely uses sales promotions as part of its marketing strategy. Generally, Apple marketing strategy integrates the following: 1. Focusing on attractive value proposition. Apple’s value proposition is “beautiful design that works right out of the box with ever-smaller packaging”[1] The world’s largest IT company by revenue has been able to avoid price wars with competitors by emphasizing its unique value proposition in its marketing communication messages. Apple is a unique company in a way that it is a design firm, a media platform, a publishing company, a software powerhouse and a computer manufacturer – all at the same time. Such a position allows the company to communicate its value proposition to target customer segment in a cost-effective manner.…

Apple marketing communication mix explains the company’s stance towards individual elements of the marketing communication mix such as print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling. The main aim behind Apple marketing communications mix is to communicate the marketing message of the brand to the target customer segment through elements listed above. Apple is effective in using elements of the marketing communication mix in an integrated manner to ensure the consistency of the marketing message. Apple Print and Media Advertising Since its foundation more than 40 years ago Apple has been using print and media advertising extensively to promote the brand in general and new products in particular. Some of the ads by the tech giant have become truly iconic raising the bar for advertisement globally. The following is the list of the most memorable print and media advertising campaigns launched by Apple: “1984” campaign directed by Ridley Scott and first shown during 1984 Super Bowl is widely considered as one of the most successful marketing campaigns of all times “The Quadra Revolution” is 1991 campaign that was a successful attempt by the tech giant to further itself ahead of the competition at the beginning of the digital age of 90s “Misunderstood”, a Christmas ad of 2013 won Emmy Award for the year’s most “Outstanding Commercial.” “40 Years in 40 Seconds” is a viral video that chronicles 40 years of the company in 40 seconds “Meu Bloco na Rua” (2017) is the latest ad released in Brazil for the Rio Carnival, highlighting the iPhone 7 Plus’ new portrait photography mode Apple also uses celebrity endorsements in print and media advertising extensively. In the past Apple’s ‘Think Different’ print and media advertising materials featured the images of innovators and pioneers in different areas…

Apple segmentation, targeting and positioning represents the core of its marketing efforts. Segmentation, targeting and positioning is needed because no company or product can be all things to all people. Apple segmentation targeting and positioning initiatives include the following stages: 1. Segmenting the market. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics. Specifically, customers can be segmented on the basis of their place of living, demographic variables, behavioural traits, psychographic characteristics and other variables. Market segments need to be measurable, accessible, sustainable and actionable in order to be used for marketing purposes. 2. Targeting selected segment(s). This stage involves identifying segments that are most attractive for the business. In other words, targeting implies choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products to. The multinational technology company positions itself as a premium brand offering products and services with advanced functions and capabilities for additional costs. Accordingly, Apple target customer segment comprise well-off individuals who are willing to pay extra for technology products and services with advanced design, functions and capabilities. A common set of characteristics shared by Apple target customer segment include appreciating design, quality and performance of technology products and services over their prices. 3. Positioning the offering. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix that is the most suitable for the target customer segment. It is the final process, where companies attempt to associate their products and services with needs and wants of selected customer segment. Apple targets its customer segment by tailoring products, services and overall business approach to appeal to the members of segment to a maximum extent. Under the leadership of late Steve Jobs, Apple mainly used mono-segment type of positioning, appealing to the needs and wants of a single customer segment. However, after Tim Cook became CEO,…
