Search results for: Mckinsey 7s

Facebook McKinsey 7S framework illustrates how seven individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S model, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Facebook McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Facebook McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. Facebook follows cost leadership business strategy with a particular focus on user experience. According to its mantra “1% is finished”, the social media company develops new products and services and improves its current range of products and services in a continuous manner. Additionally, important elements of Facebook Inc. business strategy include growth via acquisitions and continuous exploration of new ways of site monetization with positive implications for the bottom line. Structure. Facebook Inc. has a hybrid organizational structure that integrates important elements of hierarchical and divisional organizational structures. Elements of hierarchical structure are expressed via presence of multiple levels of management in the company, whereas elements of divisional or matrix organisational structure are evident on the formation of product-based teams on the global scale. The founder, Chairman of the Board and CEO Mark Zuckerberg is the main driving force and the ultimate operational and strategic decision maker in the company. Systems. Facebook Inc. business operations rely on a wide range of organizational systems. The ranges of systems that are the most critical for the social media company include HR system, information system, security system and others. Security system in particular is a critical success factor and it relates to both, company’s own security, as…
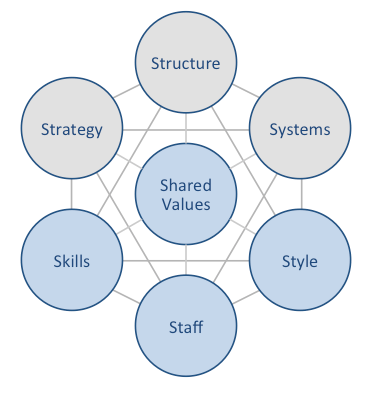
Gap Inc. McKinsey 7S model explains how seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. The essence of this model is this: there are links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Gap Inc. McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behavior with implications in their performance. Gap Inc. McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. Gap Inc. uses cost leadership business strategy for all five brands within its portfolio – Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, Athleta, and Intermix. The company offers fashion, apparel and accessories products for much cheaper prices compared to the prices of premium fashion brands such as Prada, Dolce & Gabbana and Gucci. In other words, Gap Inc. business strategy capitalizes on the willingness of consumers to express themselves via clothes, to feel stylish, ‘cool’ and trendy in the cost effective manner. Structure. Gap organizational structure is hybrid and it integrates certain elements of divisional and hierarchical organizational structures. Gap organizational structure is divided into five divisions with each division representing a separate brand and headed by a president. At the same time, the organizational structure of each division is highly hierarchical and there are multiple levels of management between the president of the division and a shop floor assistant. Systems. There is a wide range of systems such as supply-chain system, quality control system, sales system, finance system, employee selection and recruitment system and others that facilitate Gap Inc. business operations. The company subjects the level of efficiency of its system into a critical analysis in…
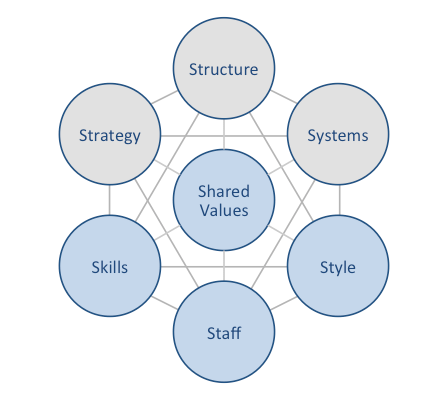
eBay McKinsey 7S framework attempts to explain the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to achieve higher effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. The framework stresses that there are strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of eBay McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. eBay McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. eBay has traditionally pursued first mover business strategy since the e-commerce site has been set up by Pierre Omidyar in 1995. Accordingly, the business has enjoyed from the first mover advantage in becoming the first and the largest online auction website with the widest range of products. However, the latest changes in eBay business strategy are associated with the shift from a primarily auction website to becoming an online retailer in general, a segment which is traditionally dominated by Amazon. It can be argued that if eBay fails to find new solid sources of competitive advantage as an online retailer, the e-commerce company will find it increasingly difficult to compete with Amazon in the new area. Structure. eBay business strategy can be characterised as a hierarchical reflecting the massive size of the business that employs 12,000 people worldwide and has more than 160 million customers.[1] Separation of PayPal from eBay in 2015 resulted in a major structural change for the business, at the same time depriving eBay a solid source of cash. The Board of Directors and the Senior Leadership Team comprise 11 members each and each member is responsible for a specific aspect or a geographical…
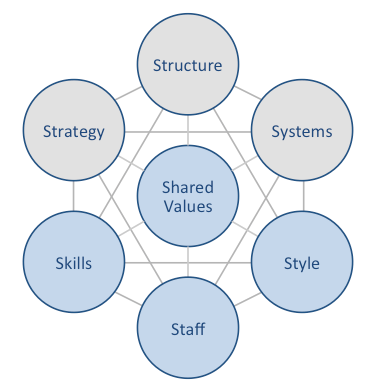
Hilton McKinsey 7S framework focuses on seven elements of a business practice that can be aligned to improve effectiveness of the company. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Hilton McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Hilton McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Hilton business strategy can be classified as service differentiation. The major points of differences of Hilton hotels from the competition include high quality of services and advanced integration of information and communication technologies into various aspects of hotel experience. Moreover, Hilton business strategy attempts to associate the experience of staying in Hilton Hotels with customer perceptions of status, achievement and recognition. Structure. Hilton organizational structure is hierarchical due to the massive size of the business that comprises 13 brands serving 140 million guests in 2015 alone (Annual Report, 2015). Moreover, Hilton organizational structure can also be described as divisional and the business is divided into three divisions: ownership, management and franchise, timeshare. Systems. Hilton Worldwide business operations rely on a wide range of systems such as customer reservations system, quality control system, employee recruitment and selection system, employee performance evaluation system and others. Since his appointment as the President and CEO in 2007, Christopher Nassetta simplified a wide range of Hilton systems to a great extent. For example, an introduction of a single company-wide system for employee performance evaluations simplified relevant processes to a great extent. Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. Report contains a detailed discussion of Hilton…
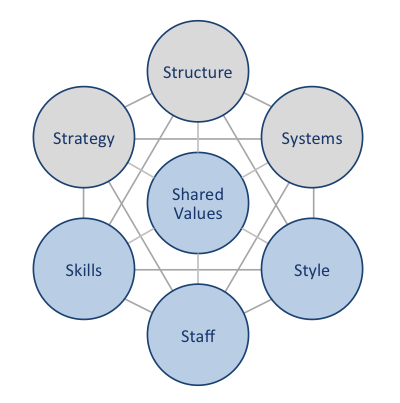
Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework explains how seven key elements of businesses can united to increase the overall effectiveness of the company. According to Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Red Bull McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. Red Bull pursues the business strategy of product differentiation. The company differentiates its energy drinks according to the perception of ‘Red Bull gives you wings’. Specifically, according to the company’s marketing message, consumption of Red Bull energy drinks result in enhanced mental and physical performance. Benefiting from first mover advantage and an extensive reliance on marketing also represent important elements of Red Bull business strategy. Structure. Red Bull organizational structure can be described as divisional and company runs two business divisions: Red Bull soft drinks and other businesses. Red Bull soft drinks division comprises Red Bull Energy drinks (regular, sugar free, zero calories and Red Bull editions) and Red Bull Simply Cola. Other business division, on the other hand, comprises motor racing, media, MVNO and fashion online retailing. Systems. Main systems that run Red Bull GmbH include information system, HR system, financial system, quality management system and others. The management attempts to achieve a close integration between individual systems within the organization in order to increase the overall effectiveness of the company… Red Bull GmbH Report contains a detailed discussion of Red Bull McKinsey 7S framework. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and on Red Bull.…
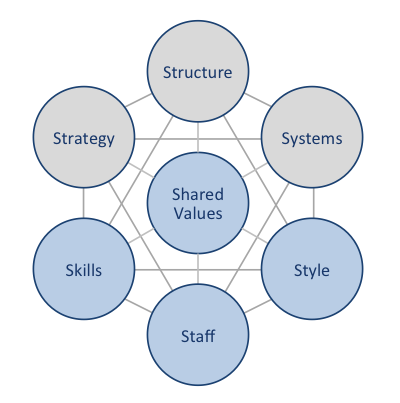
British Airways McKinsey 7S framework illustrates how seven individual elements of the airline business are aligned to increase the overall effectiveness of the business. McKinsey 7S divides elements into hard and soft groups. Strategy, structure and systems represent are considered as hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff represent soft elements. As it is illustrated in the figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of British Airways McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. British Airways McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. British Airways pursues the business strategy of service differentiation. Specifically, the airline differentiates its services via an extensive reliance on digitalization and information technology and a high level of customization of service provision. An aggressive international market expansion is another important element of British Airways business strategy and in 2016 alone the airline company is expected to fly to more than a dozen new routes.[1] Structure. British Airways is owned by International Airline Group (IAG), the largest airline group in Europe that also owns Iberia, Vueling and Aer Lingus. British Airways organizational structure is hierarchical reflecting the large size of the business. The new CEO Alex Cruz is expected to introduce de-layering initiatives into British Airways organizational structure as a part of his wide-scale cost-cutting measures. Systems. Apart from the standard set of organizational systems such as employee recruitment and selection system, performance appraisals system, quality control system, complaint handling system and others, British Airways also maintains a number of industry-specific systems. These include, but not limited to passenger check-in system, baggage handling system, in-flight entertainment system and others. British Airways Report contains a detailed discussion of British Airways McKinsey 7S framework. The report also illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such…

Tesco McKinsey 7S model illustrates the linkage between seven separate elements of the business to increase the overall effectiveness. According to this model, businesses have hard and soft elements and shared values as soft element are the result of interaction of all elements with direct and huge effects on employee behavior and performance. Tesco McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. Tesco pursues cost leadership business strategy according to its marketing communication message Every Little Helps. The supermarket chain has been able to sustain this strategy due to the extensive exploitation of the economies of scale and the exercise of bargaining power in dealing with suppliers to secure low purchasing costs. Currently, Tesco is dealing with a set of complex challenges such as restoring customer trust following profit accounts scandal, supplier payment delays scandal and dramatic decline of sales as a result of these incidents. Tesco strategy to deal with these issues as announced by its new CEO Dave Lewis include the reduction of capital expenditure to GBP 1 billion, replacement of the benefit pension scheme for all employees and the review of property portfolio with the aim of cost reduction. Moreover, a focus on availability, service and selectively on price emerged as a strategic priority for the new management. Structure. Tesco’s organizational structure is highly hierarchical and comprises many layers of management from store sales assistant to the CEO. The new CEO Dave Lewis eliminated the roles of deputy store managers in 2015 as part of attempts to simplify the organizational structure. There are 10 members in The Board of Directors and the company’s Executive Committee comprises 11 members. Systems. The supermarket chain relies on a wide range of systems on a daily basis to sustain its operations. New management led by CEO Dave Lewis announced plans to simplify organizational…

PepsiCo McKinsey 7S framework explains how important elements of businesses can be aligned to increase the overall effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S framework, strategy, structure and systems are hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff represent soft elements of businesses. The essence of the framework can be explained in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in Figure 1 below, shared values are positioned at the core of PepsiCo McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behavior with implications in their performance. Figure 1 McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. PepsiCo business strategy integrates the following six principles: Achieving growth through mergers and acquisitions (M&A) Forming strategic alliances in global scale Focusing on emerging markets Focusing on organizational culture Developing and promoting the idea of One PepsiCo Innovation in marketing initiatives Moreover, as it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, the level of consumption of carbonated drinks in the US has been consistently declining for the last ten years and this tendency is expected to continue for the foreseeable future. PepsiCo strategy reflects this important tendency and accordingly, the company has been increasing its portfolio to include food and snacks product categories to decrease the dependency of the business on sodas and carbonated drinks. Figure 2 The decline of millions of liters of soda sold in the US[1] Along with strong financial performance, numerous customer awards is a convincing indicator of appropriateness and effectiveness of PepsiCo business strategy. The list of awards won during the year of 2015 alone include Innovation Supplier of the Year from 7-Eleven, Vendor of the Year from Dollar General, the Think Customer Award from CVS, Supplier of the Year from Target, and Food & Beverage Supplier of the Year from Walmart.[2] Structure. PepsiCo has…
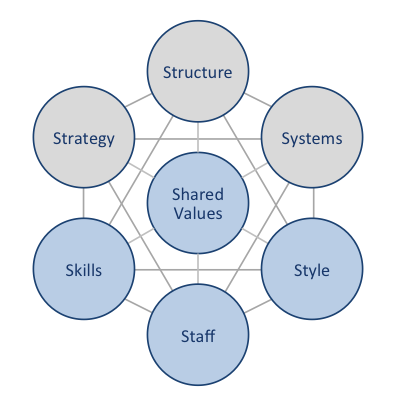
BMW McKinsey 7S framework illustrates the manners in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. McKinsey 7S framework recognizes strategy, structure and systems as hard elements, while shared values, skills, style and staff are accepted as soft elements. According to the framework, there are strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in Figure 13 below, shared values are positioned at the core of BMW McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behavior with implications in their performance. McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. BMW Group business strategy can be described as product differentiation and accordingly, the company positions itself as a premium brand in an automobile industry. BMW Group pursues differentiation business strategy with a focus on advanced technological features and capabilities and digitalization of its vehicles according to its Strategy Number One. Moreover, the company strategy attempts to associate ownership of BMW Group vehicles with personal achievement and the representation of high status. The company communicates relevant marketing messages to the target customer segment via various marketing communication channels. Structure. BMW Group organizational structure is complex due to the size of the company and the massive scope of its operations. Yet, BMW organizational structure is sophisticated enough to respond to changes in the external marketplace in a timely manner. BMW AG Supervisory Board is the highest strategic management team with members organized into four committees. These are Personnel, Audit, Nomination and Mediation committees. BMW AG Supervisory Board oversees BMW AG Board of Management headed by its Chairman Harald Krüger. Systems. These relate to daily activities and procedures engaged by BMW Group employees in order to get their job done. BMW Group integrates robotics technology, IT and online platforms within its…
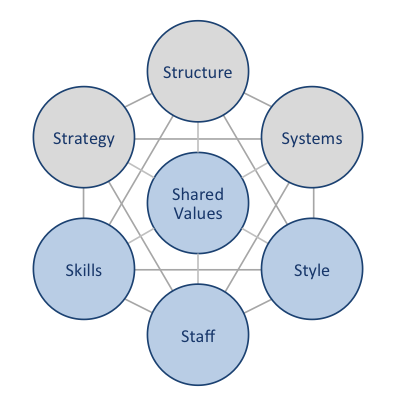
Walmart McKinsey 7S framework illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in Figure 10 below, shared values are positioned at the core of Walmart McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behavior with implications in their performance. Hard Elements Strategy. Walmart pursues cost leadership business strategy according to its brand promise of ‘everyday low prices’. The company has been able to sustain this strategy thanks to the economies of scale, exercise of its vast bargaining power to secure low prices from suppliers and paying employees low wages. Three important pillars in Walmart business strategy can be specified as – assortment, price and access. Due to its aggressive pursuit of cost leadership strategy, Walmart has attracted criticism for paying its employees low wages with a consequent negative impact on the quality of customer services. CEO Doug McMillion had to address this issue via introducing certain changes in Walmart business strategy. Specifically, in February 2015, the company announced a USD1 billion investment in U.S. hourly associates to provide higher wages, more training and increased opportunities to build a career with Walmart.[1] Structure. Traditionally, Walmart organizational structure has been highly hierarchical due to the massive size and scope its business that comprises more than 11,000 stores in 27 countries and serves nearly 260 million customers each week under 72 banners.[2] However, new CEO Doug McMillion introduced initiatives to delayer the organizational structure. Specifically, in 2015 Walmart announced that “it will eliminate a layer of management…
