Posts by John Dudovskiy
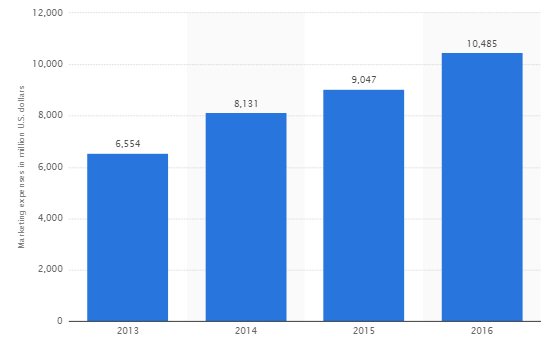
Alphabet (Google) marketing strategy integrates various online and offline marketing techniques. Alphabet’s marketing budgets and efforts mainly focus on main business – Google. It has been noted that “though you’ll never see an ad for the king of the search engines, this query behemoth employs some of the most subtle, yet fantastically impressive marketing strategies out there”[1] Beyond Google, Alphabet Inc. does not invest much resources and efforts to advertise its other projects such as Access, Calico, CapitalG, GV, Nest, Verily, Waymo, and X. This is because most of these projects are only on the stage of research and development and they do not have products and services ready to offer to the market. As it is illustrated in Figure 4 below, total annual marketing spending of the company has been consistently increasing during the past several years. Out of these amounts, for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2015 and 2016, advertising and promotional expenses totalled approximately USD3,004 million, USD3,186 million, and USD3,868 million, respectively[2]. Annual Alphabet Inc. (Google) marketing spending[3] Google marketing strategy is based on the following principles: Within the framework of marketing mix, focusing on product element to a greater extent compared to other elements. The majority of Alphabet products and services are innovative in their nature or they add innovative features to existing products and services. Targeting the broadest customer segment with multiple products and services. The company’s core business, Google offers a wide range of products and services such as Search, Android, Maps, Chrome, YouTube, Google Play, and Gmail that are used by billions of people every day worldwide. Using several elements of marketing communications mix in an integrated manner. Specifically, the internet giant uses sales promotion, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing tools to company to communicate its marketing message to…
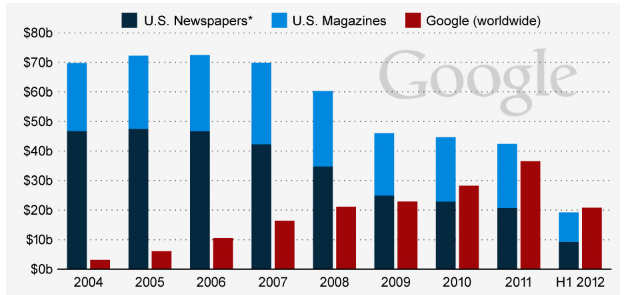
Google marketing communication mix explains the ways in which advertising, sales promotion, events and experiences, public relations and direct marketing tools are used by the company to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment. Advertising Google emerged as a popular alternative for traditional print and media advertising and changed advertising industry worldwide to a great extent. As it is illustrated in figure below, by 2012 Google was generating more advertising revenues than print media in the US as a whole. The significance and market share of Google in the global advertising industry has increased even to a greater extent during the past five years, since 2012. Accordingly, owning a more significant advertising platform than print and media advertising, Google does not use traditional print and media advertising to communicate its marketing message to the target customer segment. Revenues by print media in the US and Google (worldwide)[1] Sales Promotion Sales promotion refers to the “stimulation of sales achieved through contests, demonstrations, discounts, exhibitions or trade shows, games, giveaways, point-of-sales displays and merchandising, special offers and similar activities”[2]. Google employs sales promotion marketing techniques rarely. The most noteworthy case relates to one day sales promotion of Google Glass via online purchase for USD1,500[3] and the promotion of Android 4.4 in cooperation with candy bar KitKat, owned by Nestle International Travel Retail. Up to date Google does not use popular sales promotions techniques such as seasonal sales promotions, money off coupons, competitions, discount vouchers, free gifts or loyalty cards… Alphabet Inc. (Google) Report contains a full analysis of Google marketing communication mix and Google marketing strategy in general. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Google. Moreover, the report…

Alphabet (Google) segmentation, targeting and positioning efforts can be explained as the essence of company’s marketing efforts. Segmentation divides population into groups on the basis of specific characteristics. Targeting refers to choosing certain groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products and services. Lastly, positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Google uses the following types of positioning: Multi-segment positioning. The company offers a wide range of products and services such as Search, Android, Maps, Chrome, YouTube, Google Play, and Gmail that target multiple customer segments Standby positioning. Certain products within Alphabet portfolio such as robotics, Waymo self-driving cars, Lunar XPRIZE space exploration program, 3D mapping and others may not have a clear target customer segment at this stage. Nevertheless, these products and projects are awaiting changes in the market for the demand to emerge. Imitative positioning. Google has used imitative positioning in a few instances. The launch of Chrome browser to imitate then-market leader Internet Explorer and the launch of G+ social networking site to imitate Facebook can be mentioned to illustrate this point. The following table illustrates Google segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Google target customer segment Geographic Region Global scale Density Urban and rural Demographic Age Anyone older than 12 years old Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labour force Solitary Survivor II retired…

Alphabet (Google) marketing mix, also referred to as Alphabet (Google) 7Ps of marketing comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product. Alphabet Inc. is a holding company and its portfolio comprises nine companies. Products and services offered by these companies are illustrated in table below: Company Products and services Google Search, Android, Maps, Chrome, YouTube, Google Play, and Gmail Waymo Self-driving cars Verily Miniaturized CGM, Smart Lens Program, Debug, Retinal Imaging etc. Calico Research and development projects focused on ageing Nest Indoor and outdoor cameras, learning thermostats, and smoke alarms Access High-speed fiber internet access across the U.S X Projects associated with “moonshot” technologies Capital G Equity investment fund GV Venture capital Companies in Alphabet portfolio and products and services offered by them It is important to note that although Alphabet product portfolio is vast and diverse, Google remains as its core business accounting for 88% of total revenues in 2016 through advertising[1] Place. Being an e-commerce and internet company, Google relies on online sales channel for the sales of its products and services. In 2015 the company opened its first physical store and up to date, there are only a few Google physical stores in various formats in North America and the UK. Google’s first physical store in London, is a “shop in a shop” located inside the Currys PC World store on Tottenham Court. “In addition to showcasing Google merchandise—Chromebooks, Chromecasts, Android phones, and so on—the space includes a “Doodle Wall” for customers to scribble on with digital spray paint, a “Chromecast Pod” for movie viewing, and a “Portal” for touring the planet via Google Earth.”[2] It has to be noted that place element of the marketing mix does not relate to certain companies belonging to Alphabet portfolio…

Founded by Stanford University students Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1998, Google dominates almost all of its markets and the company is well-known for its culture of creativity and innovative approach to develop new products and services. Google offers a wide range of interrelated internet-based products and services that are aimed at satisfying personal and professional needs in terms of communication, recreation, organization and increasing the level of performance and effectiveness. Google Inc. was restructured in 2015 to become Alphabet Inc. “Google’s search product became a wholly owned subsidiary of a new parent company, Alphabet, with other Google projects and teams spun out into separate “Alphabet companies,” each with its own CEO.”(Price and Nudelman, 2016, online). Alphabet Inc. is a holding company with no business operations of its own. Google is the largest business within Alphabet Inc. product portfolio. The company’s product portfolio also comprises Access, Calico, CapitalG, GV, Nest, Verily, Waymo, and X. The company classifies it’s all non-Google businesses as Other Bets. In fiscal year 2016, Alphabet Inc. generated revenues of USD90.3 billion and revenue growth of 20% year over year, with constant currency revenue growth of 24% year over year. Google segment generated revenues of USD89.5 billion, with revenue growth of 20% year over year. Other Bets revenues of USD0.8 billion with revenue growth of 82% year over year. Revenues from the United States, the United Kingdom, and Rest of the world were USD42.8 billion, USD7.8 billion, and USD39.7 billion, respectively (Annual Report,2016). The company has more than 72,000 full-time employees worldwide. Google core business strategy is business diversification and introduction of new products and services in a regular manner. Google business strategy is also based on the development of a closed eco-system to motivate customers to use greater range of products and services. Customers usually…

Surprisingly, despite the size and scope of its business activities, Facebook Inc. does not release an annual Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) report detailing its programs and initiatives. The company has a dedicated Facebook page ‘Green on Facebook’ that regularly announces its charitable programs and CSR activities. Additionally, Facebook has a website at www.sustainability.fb.com dedicated for the same purpose. The table below illustrates the highlights from the latest report for 2015: Categories of CSR activities Facebook Performance Supporting local communities The company hosts farmers market at its Menlo Park headquarters each week providing fresh produce to the Belle Haven and East Palo Alto communities.Facebook has collaborated with Menlo Park Rotary Club to build The Belle Haven Community Garden, where families in the community now have access to 25 planting beds that are free to use.The company has sponsored solar installations on homes in Belle Haven through its partnership with Menlo Spark and Grid Alternatives. Educating and empowering workers Facebook has an employee satisfaction rating of 93 per cent due to competitive pay, informal and empowering organizational culture Labour and human rights It has been noted that “Facebook employees are often placed in roles that cater to their strengths and are encouraged to question and criticize their managers”[1] Employee health and safety Facebook strives to have maximum amount of natural light in its offices and serves local organic food in its kitchens Gender equality and minorities White males constitute 39.1 per cent of employees and black males and females represent only 1.7 per cent of employees. Also, Hispanic males and females represent only 4.3 per cent of the total workforce[2] Environment a) energy consumption b) water consumption c) Waster reduction and recycling d) CO2 emissions The company has announced that its latest data centre in Los Lunas, New Mexico will…
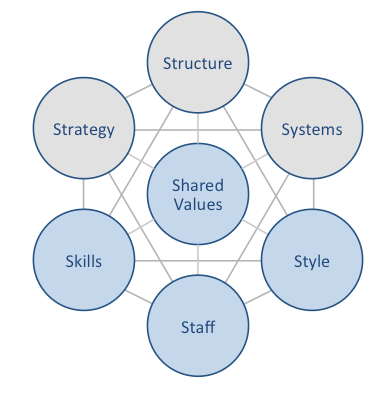
Samsung McKinsey 7S model attempts to explain how seven individual elements of the business can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to this model strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. McKinsey 7S model argues that there are strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Samsung McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Samsung McKinsey 7S model Hard Elements Strategy. Samsung business strategy is mainly based on market readership, i.e. replicating innovations made by market leaders in terms of introducing new products and/or adding innovative features to new products. Samsung’s major competitor, Apple can be specified as company Samsung mainly replicates from. Moreover, Samsung business strategy is based upon scanning and utilising opportunities in the market and new product development on a regular basis. Structure. Samsung organizational structure is divisional and the company is divided into three divisions on the basis of products: IT & Mobile Communications (IM), Consumer Electronics (CE), and Device Solutions (DS). Each division is managed separately according to unique aspects and characteristics of its products. As the outcome of review of optimal organizational structure completed on April 2017, the senior management decided not to shift to holding pattern of organizational structure. Nevertheless, Samsung organizational structure may change in medium term perspective. This is due to a series of scandals the company had to deal with recently, including the imprisonment of Jay Y. Lee, a former Samsung executive and founding family member for his role in bribery and embezzlement. Systems. Samsung’s long-term growth prospects depend on smooth running of a wide range of systems. These…

Facebook McKinsey 7S framework illustrates how seven individual elements of businesses can be aligned to increase effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S model, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. The framework stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Facebook McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Facebook McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. Facebook follows cost leadership business strategy with a particular focus on user experience. According to its mantra “1% is finished”, the social media company develops new products and services and improves its current range of products and services in a continuous manner. Additionally, important elements of Facebook Inc. business strategy include growth via acquisitions and continuous exploration of new ways of site monetization with positive implications for the bottom line. Structure. Facebook Inc. has a hybrid organizational structure that integrates important elements of hierarchical and divisional organizational structures. Elements of hierarchical structure are expressed via presence of multiple levels of management in the company, whereas elements of divisional or matrix organisational structure are evident on the formation of product-based teams on the global scale. The founder, Chairman of the Board and CEO Mark Zuckerberg is the main driving force and the ultimate operational and strategic decision maker in the company. Systems. Facebook Inc. business operations rely on a wide range of organizational systems. The ranges of systems that are the most critical for the social media company include HR system, information system, security system and others. Security system in particular is a critical success factor and it relates to both, company’s own security, as…
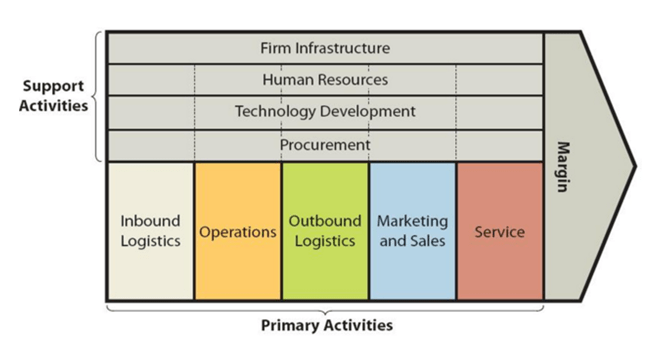
Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that can be applied to analyse business activities to be able to identify those activities that contribute most the overall competitive advantage of the business. Facebook value chain analysis provided below discusses sources of competitive advantage of the social media company by referring to its primary and support business activities. Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of value chain analysis. Figure 1 Facebook Value Chain Analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics Facebook Inc. inbound logistics refers to ways the company acquires resources and uses according to its needs. The range of resources used by the social media giant includes hardware, various types of technologies and office supplies. Generally, value chain analysis framework analyses the processes of receiving and storing raw materials until their transformation into the final goods. However, due to Facebook Inc.’s business model illustrated in Figure 6 below, tangible resources such as hardware and technology used by the company are only secondary in their nature and the primary resources used to attract the customers are intangible. Specifically, Facebook offers its customers unique intangible ‘products’ of informational nature, i.e. content. From this point of view, inbound logistics of content is highly cost-effective since the content is uploaded by users of in the forms of texts, pictures and videos without any additional costs for the business. Operations Facebook is available in more than 90 different languages, and the company has offices or data centres in more than 30 countries around the world. Moreover, there are five support offices and more than 35 sales offices located globally.[1] Approximately 84.5% of Facebook daily active users are outside the US and Canada.[2] As it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Facebook operations mainly involve the transformation of raw content into user-friendly format via profile page, timeline,…
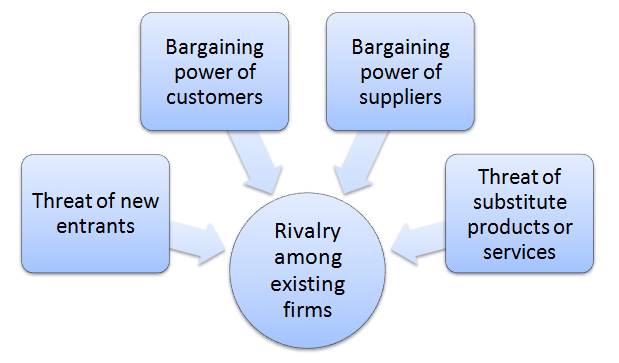
Facebook Inc. Porter’s Five Forces analytical framework assesses an overall extent of competition in the social media industry. Developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1] consists of five individual forces as illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1. Facebook Inc. Porter’s Five Forces Rivalry among existing firms in social media industry is fierce. Alphabet Inc. (Google) is the most prominent competitor for Facebook and Google Adsense and Facebook Ads are two most popular competing platforms for online advertising. Generally, the major players in the industry include Facebook, You Tube, Reddit, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, Tumblr, LinkedIn, Yahoo! Answers, Yelp and others. As it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Facebook is the most popular social networking website in the US with an approximate market share of 42.4 per cent. Most popular social networking websites in the USA (as of August 2016)[2] The rate of the industry growth is immense, diversity within the competition is vast with no switching costs for customers and this fact further intensifies the rivalry among existing market players. Moreover, “there are several regional social networks, such as Renren in China, Mixi in Japan, vKontakte in Russia, etc., and these compete with FB for users in their respective geographies. Increased regulation in certain markets such as China is more beneficial to regional players”.[3] Threat of new entrants into social media industry is significant. Although there are certain industry entry barriers such as capital requirements for marketing and expected retaliation from existing businesses, it is generally easy to built websites and mobile apps. New social media platforms based on innovative ideas and/or integrating innovative features can secure funding from investors to pose a threat to the market share of Facebook, Google+ and other established market players. Taking into account decreasing popularity of Facebook among teens,[4] it can be argued that a new social…
