
Gap Inc. 7Ps of marketing consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence elements of the marketing mix Product Gap Inc. portfolio comprises five distinct brands and the table below illustrates the main categories of products sold under each brand. Brand Main products GAP all things denim, tees, button-downs, and khakis, must-have trends Banana Republic clothing, eyewear, jewelry, shoes, handbags, and fragrances with detailed craftsmanship and luxurious materials Old Navy a wide range of clothing products Athlete apparel and gear for a range of activities from yoga to strength training and running, as well as seasonal sports, including skiing and tennis Intermix Clothing, shoes, bags and accessories Gap Inc. brands and respective products Products belonging to Gap Inc. portfolio are designed and positioned as ‘cool’ and ‘trendy’ and they are used by the target customer segment to express their individuality. The company offers an extensive variety of range in terms of size, colors and design. Place The retailer uses online and offline sales channels in an integrated manner. There are 3,721 company-operated and franchise store locations within Gap Inc. portfolio and most stores are open seven days a week.[1] Customers have an opportunity to find the address of the nearest store to their location from the official website of the company. Starting from recently, the company has been attempting to increase the extent of utilization of online sales channel. In a notable move, Gap’s CEO Art Peck “told shareholders that Gap is open to selling its merchandise on Amazon or other third parties in the U.S.”[2] The company also offers online shoppers to the opportunity to purchase multiple brands within its portfolio from a single website into one shopping card. Price Gap Inc. pricing strategy integrates the combination of psychological and product line pricing techniques.…
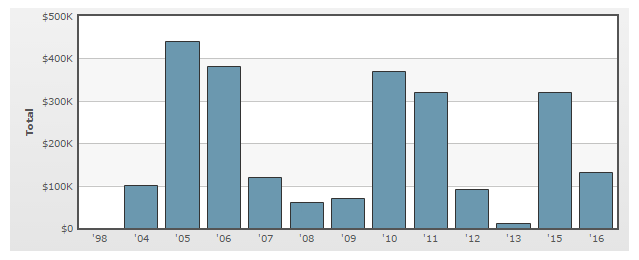
PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Gap Inc. PESTEL analysis refers to the analysis of potential impact of above external factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects of the business. Political Factors There is a set of political factors such as political stability in the market, relevance of bureaucracy and corrupt practices, the freedom of press, home market lobbying practices and others that can affect Gap Inc. in multiple levels. The company is engaged in lobbying its political interests. However, as it is illustrated in figure below, Gap Inc. annual lobbying budget is not fixed and it fluctuates significantly year by year to reflect specific political issues the business wants to address each year. Gap Inc. annual lobbying budget[1] Gap Inc. has also been involved in a political controversy and has been accused of causing racial controversy to get spectacular press coverage and social visibility. The company’s Twitter campaigns included an image of “two white girls in poses that look quite painful, next to a third white girl using a smaller black girl as an armrest”[2] The campaign caused a massive controversy and debate attracting thousands of retweets and likes, the story being covered by more than 214 news articles.[3] Another instance of Gap marketing campaign involved an image of a happy interracial family, causing debates on social media platforms about the issue of interracial marriage. Economic Factors Gap Inc. market share and revenues are affected by a great range of economic factors directly or indirectly. Changes in foreign exchange rate is one of the major economic factors that have direct implications on Gap’s financial performance. For example, the company’s net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased USD 638 million, or 4 percent, compared with fiscal 2014…

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates Gap Inc. SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. A strong portfolio of distinct brands across multiple channels 2. Global presence of the brand 3. Presence of timeless iconic products 4. Strategic supplier relationships Weaknesses 1. Declining sales and profits 2. Failure to utilize online sales channels efficiently 3. Dependency on external manufacturers 4. Loss of ‘coolness’ to a certain extent during the past five years Opportunities 1. Increasing the efficiency of online sales 2. International market expansion focusing on Asia 3. Celebrity endorsement 4. Formation of strategic alliances Threats 1. Further decline of sales and profits 2. Risks related to global sourcing and manufacturing 3. Inability of the management to turn around the business 4. Further increase in the cost of labor Gap Inc. SWOT analysis Strengths Gap Inc.’s portfolio comprises Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, Athleta, and Intermix brands, addressing the needs of different customer segments within clothing and fashion industry. Gap is associated with optimistic American casual style, whereas Athleta offers performance and lifestyle apparel for the fitness-minded woman. Moreover, there is a range of Gap sub-brands such as GapKids, GapBody, GapMaternity, GapFit and babyGap that effectively appeal to the needs and preferences of relevant customer segments. Gap Inc’s current strong portfolio of distinct brands is a considerable strength from a viewpoint of appealing a wider customer segment with positive implications on the volume of revenues. Gap Inc. is a global company with almost 3,700 stores worldwide, including company-operated stores in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, France, Ireland, Japan, China and Italy, and franchise stores in Asia, Australia, Europe, Latin America, the Middle East and Africa.[1] The global presence of the brand plays an integral role in terms of market…
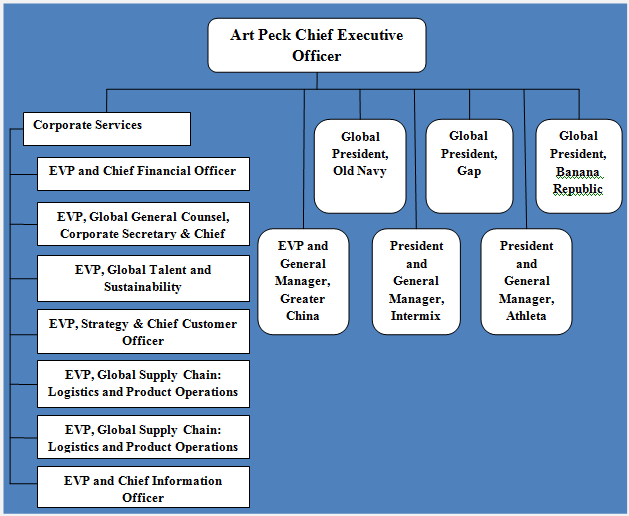
Gap Inc. organizational structure can be characterized as hybrid integrating certain elements of divisional and hierarchical organizational structures. Gap organizational structure has the following pattern: Gap Inc. organizational structure As it is illustrated in figure above, Gap organizational structure is divided into five divisions with each division representing a separate brand and headed by a president. At the same time, the organizational structure of each division is highly hierarchical and there are multiple levels of management between the president of the division and a shop floor assistant. In 2016, as a part of an initiative to address declining sales and profitability, Gap CEO Art Peck announced plans for global restructuring that includes reducing the numbers of Gap stores in the US, withdrawing the Old Navy fascia in Japan and making head office redundancies.[1] Moreover, store closures also involved Banana Republic brand bringing the total expected store closure count to 75 by the end of fiscal 2016.[2] There are also occasional brand-specific changes in organizational structures led by the presidents of respective brands. For example, a major restructuring introduced in Gap brand in 2015 included combining e-commerce and marketing organization into one unit and elimination of Creative Director role resulting in Rebekka Bay’s departure from the company.[3] Organizational structure of Gap Inc. may be subjected to further changes to a considerable extent in the foreseeable future to address serious challenges the company is facing. Specifically, net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased 4 percent to USD 15.8 billion compared with USD 16.4 billion for fiscal 2014. Gross profit for fiscal 2015 was USD 5.7 billion compared with USD 6.3 billion for fiscal 2014.[4] Accordingly, we can expect the company to engage in downsizing of management layers along with further store closures in developed countries to concentrate more in strategic developing countries such as China,…

Since founding the company with his wife Doris Fisher in 1969, Donald Fisher has been at the helm of Gap Inc. leadership serving as CEO until 1995 and Chairman of the Board until 2004, and as company director and Chairman Emeritus until his death in 2009. Millard “Mickey” Drexler served as GAP CEO from 1995 until 2002 and he is credited for transforming the company into a global brand. It has been noted that “Drexler possessed the fashion instincts that built the Gap brand and image into a destination for multiple target customer groups”.[1] Drexler was forced to resign in 2002, following the decline of sales and a loss of USD 7.7 million in 2001. Paul S. Pressler from Disney was named as the new CEO due to his reputation as operations wizard to restore discipline to the floundering company.[2] Failing to appreciate the nuances of the fashion business Pressler oversaw a further decline in sales and brand image. Currently, GAP’s senior management team is led by CEO Art Peck and he is focused on executing the company’s strategy to engage customers and maximize shareholder returns. Today, Gap leadership is faced with a serious challenge of declining sales and profitability. Net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased 4 percent to USD 15.8 billion compared with USD 16.4 billion for fiscal 2014. Gross profit for fiscal 2015 was USD 5.7 billion compared with USD 6.3 billion for fiscal 2014.[3] This is the outcome of the brand using its perception of ‘coolness’ along with a set of other issues. Despite the complexity of the current situation for Gap Inc., there are optimistic views that CEO Art Peck may be successful in turning around the business partially due to his experience of two decades in management consultancy. Moreover, Mr. Peck is credited with the…

Gap Inc. business strategy in the global market of fashion, style and accessories can be classified as cost leadership. The retailer offers stylish and fashionable clothing items and accessories for competitive prices. In simple terms, Gap business strategy is associated with offering people the opportunities of being ‘cool’ and ‘stylish’ for affordable prices. Gap Inc. portfolio comprises Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, Athleta, and Intermix brands. Gap competitive advantage has been traditionally associated with innovative casual design of clothing items and accessories and the variety of choice that enables the opportunities for self-reflection for a wider range of customer segment. For the past few years, the fashion retailer has been facing challenges in terms of maintaining its US and global market share and ensuring the growth of revenues. During the fiscal year of 2015, Gap Inc. experienced a decline of both, sales and gross profit. Net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased 4 percent to USD 15.8 billion compared with USD 16.4 billion for fiscal 2014. Gross profit for fiscal 2015 was USD 5.7 billion compared with USD 6.3 billion for fiscal 2014.[1] Gap business strategy to deal with the issue of declining sales as announced by CEO Art Peck includes the following plans and initiatives. Focusing on its Gap’s core products that contributed to the global success of the company. Specifically, the senior management has expressed a commitment to return Gap iconic denim, including a rich assortment of on-trend silhouettes, washes and fabrications. Start selling on Amazon. The company has shun association with online retailers for more than a decade mainly because online stores are not able to convey attractive store desing and the point of purchase marketing efforts of the brand. However, in a most recent meeting with shareholders CEO Art Peck announced that “Gap is open to selling…

Gap Inc. is a global apparel retail company that owns Gap, Banana Republic, Old Navy, Athleta, and Intermix clothing, fashion and accessories brands. The first GAP store was opened in 1969 by Doris and Don Fisher and today Gap Inc. is the largest specialty apparel retailer in the North America with 3,721 company-operated and franchise store locations around the globe. The company has more than 140,000 employees worldwide (Annual Report, 2015) and its organizational structure can be characterized as hybrid integrating certain elements of divisional and hierarchical organizational structures. Gap Inc. uses cost leadership business strategy for all five brands within its portfolio offering fashion, apparel and accessories products for much cheaper prices compared to the prices of premium fashion brands. Apart from cost leadership, competitive advantages possessed by the company include a strong portfolio of distinct brands across multiple channels, a global presence of the brand and strategic relationships with its suppliers. At the same time, Gap Inc. has certain weaknesses such as declining sales and profits, failure to utilize online sales channels in an efficient manner, dependency on external manufacturers and others. The company has been struggling with declining sales and profits during the last two years. Net sales for fiscal 2015 decreased 4 percent to USD 15.8 billion compared with USD 16.4 billion for fiscal 2014. Gross profit for fiscal 2015 was USD 5.7 billion compared with USD 6.3 billion for fiscal 2014 (Annual Report, 2015). The range of initiatives introduced by CEO Art Peck to deal with this problem includes focusing on core products that contributed to the global success of the company, start selling on Amazon and engaging in international market expansion. Gap Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value…

Unlike other major corporations of similar sizes, eBay does not release an annual sustainability report. Nevertheless, information about eBay CSR efforts can be found on the company’s website. Most of eBay’s social responsibility initiatives are conducted by the EBay Foundation. Table 3 below illustrates the major points of eBay CSR programs and initiatives: Categories of CSR activities eBay Performance Supporting local communities Global Impact Team program established in 2008 attempts to engage employees in service to the communities where they live and work In the US, 35 eBay offices have GIVE teams — groups of employees who voluntarily participate in charitable events and allocating grant funds to organizations in their local communities Educating and empowering workers eBay offers a range of leadership development programs to employees at all levels. For example, eBay’s Finance Leadership Development Program (FLDP) highlights a unique employee experience. Each FLDP cohort receives extensive leadership development, coaching, and senior executive mentoring, while working on challenging assignments Labour and human rights The company has been receiving the maximum score of 100 per cent on the Human Rights Campaign’s Corporate Equality Index (CEI) every year since 2009 Employee health and safety eBay organizes an annual ‘health and safety week’ to raise awareness of health within the workplace. It includes completion of health and safety survey, attending workshop and seminars. Gender equality and minorities The launch of Women’s Initiative Network (WIN) in 2011 increased the number of women in leadership roles. 29% of eBay leadership positions are held by women and women represent 42 per cent of total workforce. The company publicly advocate for equal rights for same-sex couples Environment a) energy consumption b) water consumption c) recycling d) CO2 emissions eBay used 716,353 MWh of energy in 2014 alone. In 2013, the company has announced its commitments to…
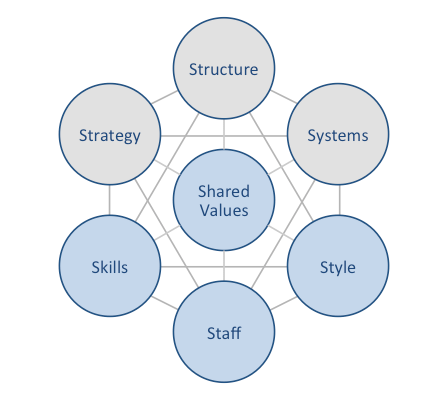
eBay McKinsey 7S framework attempts to explain the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned to achieve higher effectiveness. According to McKinsey 7S strategy, structure and systems represent hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are soft elements. The framework stresses that there are strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of eBay McKinsey 7S framework, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. eBay McKinsey 7S Framework Hard Elements Strategy. eBay has traditionally pursued first mover business strategy since the e-commerce site has been set up by Pierre Omidyar in 1995. Accordingly, the business has enjoyed from the first mover advantage in becoming the first and the largest online auction website with the widest range of products. However, the latest changes in eBay business strategy are associated with the shift from a primarily auction website to becoming an online retailer in general, a segment which is traditionally dominated by Amazon. It can be argued that if eBay fails to find new solid sources of competitive advantage as an online retailer, the e-commerce company will find it increasingly difficult to compete with Amazon in the new area. Structure. eBay business strategy can be characterised as a hierarchical reflecting the massive size of the business that employs 12,000 people worldwide and has more than 160 million customers.[1] Separation of PayPal from eBay in 2015 resulted in a major structural change for the business, at the same time depriving eBay a solid source of cash. The Board of Directors and the Senior Leadership Team comprise 11 members each and each member is responsible for a specific aspect or a geographical…
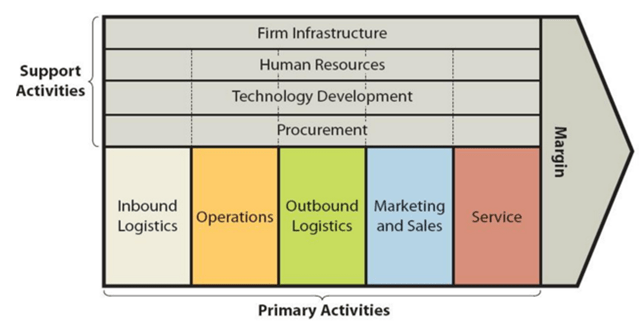
Value chain analysis is a strategic analytical tool that that is used to identify business activities important to create value and competitive advantage to the business. The figure below illustrates the essence of eBay value chain analysis. eBay Value chain analysis Primary Activities Inbound logistics eBay inbound logistics refers to ways in which the company acquires and stores raw material to be used for the business. This includes but not limited to the purchase of servers, other hardware products and a wide range of technological items along with office suppliers and other items. Due to the massive scope and scale of eBay business operations, the economies of scale can be specified as the major source of value in inbound logistics primary activities. Moreover, fostering strategic relationships with suppliers is another key source of value in eBay’s inbound logistics. Operations eBay operations revolve around technology-enabled commerce. The full range of eBay technologies and services are divided into the following three platforms: Marketplace refers to an online marketplace available at www.ebay.com. This platform has more than 800 million listings at any given time[1] StubHub represents a platform to purchase tickets to the games, concerts and theatre shows and to sell tickets. Classifieds platforms include a collection of brands such as Mobile.de, Kijiji, Gumtree, Marktplaats, eBay Classifieds and others. Ebay classifieds are offered in more than 1500 cities globally. The full range of eBay business operations include the following processes: Seller registering on eBay website Buyers bidding for a specific product offered by the seller A successful bid by a specific Buyer (or purchasing via ‘Buy It Now’) Buyer paying to the bank via PayPal or other payment methods Bank notifying eBay about Buyer’s purchase eBay notifying Seller about the payment by Buyer The delivery (shipment) of the product by the Seller…
