
McDonald’s marketing strategy is based on the following principles: 1. Think globally, act locally. McDonald’s is a truly global company with 40,031 restaurants in in119 countries.[1] The fast food chain is famous for standardisation of a wide range of business processes. Specifically, the company attempts to adjust its menu, as well as, restaurants settings to the tastes and preferences of local consumers. For example, it serves McSpaghetti in Philippines, Chicken Parm in Australia, Cookie and Cream Pie in Malaysia, Gracoro Burger in Japan and the list goes on. 2. Extensive focus on print and media advertising. The fast food giant focuses on print and media adverting component of marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other components. Specifically, McDonald’s advertising costs totalled USD 82.9 million, USD 329.2 million and USD 81.5 million for 2021, 2020 and 2019 respectively.[2] The marketing message attempts to associate the brand with enjoying tasty food and sharing goods moments with loved ones. 3. Targeting the widest range of customer segment. McDonald’s segmentation, targeting and positioning strategy attempts to appeal to the needs and preferences to the wide range of customers in terms of geographic location, demographic, behavioural, as well as, psychographic traits. 4. Cost leadership strategy. Within the framework of marketing communication mix (also known as 7Ps of marketing) McDonald’s prioritizes price over other elements. In fact, enjoying tasty food served in short duration of time is fast food chain’s unique selling proposition. The tasty food served by the company is often not a healthy one, but this is a separate issue impacting the brand. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. McDonald’s PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these factors on the bottom line and long-term growth prospects. Political Factors in McDonald’s PESTEL Analysis McDonald’s revenues and long-term growth prospects are affected by a number of political factors such as levels of bureaucracy and corruption, government stability and the freedom of press. Moreover, activities of trade unions and home market lobby groups can be referred to as noteworthy political factors that may affect multinational corporations. Exiting Russia On March 8, 2022 McDonald’s announced that it had temporarily closed restaurants in Russia and paused operations in the market due to Russia-Ukraine war conflict. The humanitarian crisis caused by the war in Ukraine, and the precipitating unpredictable operating environment, have led McDonald’s to conclude that continued ownership of the business in Russia is no longer tenable, nor is it consistent with McDonald’s values.[1] On May 2022 the fast food chain announced it starts the process of selling its business in Russia, meaning that the company is leaving the country permanently. Exiting one of its biggest markets where McDonald’s had more than 800 restaurants employing 62000 employees[2] due to a war conflict is a stark example for a political factor affecting the fast food chain. Trade Unions Activities of trade unions and their implications belong to the list of important political factors affecting McDonald’s. Trade unions may succeed in their demands to increase employee wages and to improve working conditions and these will have negative implications for the profitability of the business. Accordingly, the fast food giant is known worldwide for its hostility to trade unions. For example, in 2021 it was reported that McDonald’s has, for years, spied…

SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats related to organizations. The following table illustrates McDonald’s SWOT analysis: Strengths 1. Global market leadership 2. Brand value and brand awareness 3. Sustainable business model 4. High level of profitability 5. Effective utilization of digital technologies Weaknesses 1. Unhealthy food on the menu 2. Declining brand image 3. High employee turnover 4. Negative publicity 5. Low differentiation Opportunities 1. Enhancing focus on nutritional menu 2. Product differentiation 3. Improving CSR aspect of the business 4. Reviving the brand image 5. Increasing the extent of localization in international markets Threats 1. Food safety concerns 2. Fast food market saturation in developed countries 3. Lawsuits against the company 4. Currency fluctuations 5. Competition from quality burger chains McDonald’s SWOT analysis Strengths in McDonald’s SWOT Analysis 1. McDonald’s is an undisputed market leader with more than 40000 restaurants worldwide. The fast food giant has a global market share of about 43,8% and its closest competitor Yum Brands that comprises KFC, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell and The Habit Burger Grill has a market share of only 30,9% in the global fast food industry.[1] Market leadership is a considerable strength for McDonald’s in terms of generating cash flow and profits for medium and long-term perspectives. 2. McDonald’s is one of the most valuable brands in the world. According to Forbes McDonald’s is No. 10 most valuable brand in the world with the brand value of USD 46,1 billion[2]. Similarly, Interbrand considers McDonald’s No.9 most valuable brand in the world with the brand value USD 45,87 billion.[3] Brand value and brand awareness are proved sources of competitive advantage. Specifically, brand value is an indicator of a high level of consumer loyalty and it offers a wide range of advantages that include negotiating power with customers…

McDonald’s Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the fast food giant to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. McDonald’s Ansoff Growth Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, McDonald’s uses three growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. Market penetration refers to selling existing products to existing markets. The fast food chain engages in market penetration growth strategy through efficient implementation of integrated marketing strategy. 2. Product development. This involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. McDonald’s introduces new items on its menu in a regular manner on par with changes in customer tastes and preferences. For example, latest additions in the menu include The Hash Brown McMuffin, The Crunchy Double, The Land, Air & Sea and The Surf + Turf. 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Market development through franchising has been one of the main growth strategies for McDonald’s since the purchase of the company by Ray Krock from the founder brothers Richard and Maurice McDonald. Thanks to successful application of this strategy, currently there are 40,031McDonald’s restaurants in119 countries.[1] 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets and this is considered to be the riskiest strategy. Up to date McDonald’s has not diversified outside of its core business of selling food through franchising and company-operating stores and generating revenues from real estate leased to franchisees. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s Ansoff Matrix. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on McDonald’s. Moreover,…
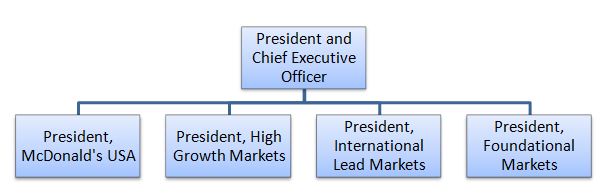
McDonald’s organizational structure can be classified as divisional. McDonald’s business operations are divided into the following four divisions according to their geographical location: United States Europe Asia/Pacific, Middle East and Africa (“APMEA”) Other countries Each division above possesses its own departments such as IT, finance, marketing and others. Massive changes in McDonald’s organizational structure introduced in 2015 increased the emphasis on the international markets clarifying the roles of executives responsible for growth in international markets. Specifically, as it is illustrated in Figure 1 below, the responsibility for overseeing international operations is distributed among three senior executives at President level. Figure 1 McDonald’s leadership structure in international markets[1] Presidents are provided autonomy in decision making to a great extent to increase sales in their respective markets. The autonomy refers to adjusting the content and delivery McDonald’s marketing message to their respective markets taking into account cross-cultural differences. Moreover, Presidents are free to introduce new items in menu reflecting tastes and preferences of local markets. Furthermore, from administrative point of view McDonald’s organizational structure involves nine senior level managers reporting to President and CEO Chris Kempczinski. These managers include Vice President and Executive Vice Presidents and each manager is responsible for a specific strategic aspect of the business. Figure 2 McDonald’s organizational structure Since becoming President and CEO in 2019 Mr. Chris Kempczinski did not introduce any massive changes in McDonald’s corporate structure. However, he may restructure the business to a certain extent to reflect changes in the external environment. Specifically, COVID 19 pandemic revealed the importance of delivery and McDonald’s may change its corporate structure to ensure greater focus on making deliveries to homes and offices. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks…

McDonald’s leadership team is headed by the President and CEO, who is aided by nine senior managers, each overseeing a specific aspect of the business. [1] The previous President and CEO Mr. Steve Easterbrook took the helm in 2015 and he was widely considered as an effective leader until he was fired for having consent sexual relationships with subordinate employees. During his leadership tenure Mr. Easterbrook was credited with turning around the company and reviving its falling stock price. Most prominent changes introduced by Easterbrook include reducing costs, introducing touch-screen ordering and establishing all-day breakfast. The new President and CEO Chris Kempczinski has also proved to be effective business leader. Under the new leadership McDonald’s has emerged as a clear winner during the pandemic. Mr. Kempczinski has channelled his energy and focus on digital, drive thru and delivery to adjust the business model to the pandemic environment. McDonald’s leadership is currently faced with a serious challenge. In recent years the fast food chain has faced many lawsuits and claims involving sexual harassment and racial discrimination. The former President and CEO Mr. Easterbrook being found violating company code of conduct is the evidence of severity of the issue. One of the important tasks for the new leader Mr. Kempczinski is to create a corporate culture where sexual harassment and racial discrimination is not tolerated in practice. McDonald’s Corporation Report contains the above analysis of McDonald’s leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on McDonald’s. Moreover, the report contains analyses of McDonald’s business strategy, organizational structure and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of McDonald’s marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility. [1] Annual Report…

McDonald’s business strategy utilizes a combination of cost leadership and international market expansion strategies. Franchising form of new market entry is utilized within McDonald’s business strategy to a great extent. The fast food chain has one of the largest property portfolios on the world and it is a giant real estate company. McDonald’s generates only a fraction of its profit from food and drinks sold by franchisees and the majority of income is generated by renting leased property to franchisees with a considerable mark-up. Moreover, product and service standardization lies in the cornerstone of McDonald’s business strategy. McDonald’s restaurants offer substantially uniform menu that comprises hamburgers and cheeseburgers, Big Mac, Quarter Pounder with Cheese, Filet-O-Fish, several chicken sandwiches, Chicken McNuggets, wraps, french fries, salads, oatmeal, shakes, McFlurry desserts, sundaes, soft serve cones, pies, soft drinks, coffee, McCafé beverages and other beverages.[1] It is important to note that along with maintaining product and service standardization, McDonald’s takes into account local tastes and preferences, when developing its menu and engaging in marketing efforts. McDonald’s competitive advantage is based on the following points: Cheat prices is McDonald’s main competitive advantage. The company is engaged in an extensive utilization of economies of scale to achieve the cost advantage. True to ‘fast food’ format of its restaurants, McDonald’s is famous for the speed of customer service without compromising the quality of the service. Universality of the taste to a great extent represents another base of McDonald’s competitive advantage. Big Mac tastes the same almost all over the world due to the use of the same ingredients in the same quantities and application of the standardized ways of cooking around the globe. Such a consistence in taste has positive implications on consumer loyalty. In late 2020, under the leadership of new President and CEO Mr. Chris…

McDonald’s Corporation is a global fast food chain that serves more than 70 million customers in 119 countries employing about 200,000 people. McDonald’s operates two types of restaurants – company-owned and franchised restaurants with about 93% of restaurants belonging to the latter category (Annual Report, 2021) McDonald’s had disappointing financial results in 2014 with a sales growth of only 1% and a decline of operating income of 8%. Steve Easterbrook, McDonald’s Chief Brand Officer was promoted as the new CEO and President effective from March 1, 2015 to turn around the business. The list of major changes introduced by Steve Easterbrook includes reducing the use of antibiotics in chicken and massively restructuring the corporation, along with introducing changes in the menu. The turnaround efforts of the new CEO Steve Easterbrook proved to be effective with the company shares hitting record by the third quarter of 2015. However, Mr. Easterbrook was fired in 2019 due to breaching McDonald’s employee code of conduct through engaging in consent sexual relationship with female employees. New President and CEO Mr. Chris Kempczinski has proved to be effective so far, with McDonald’s emerging from COVID-19 pandemic stronger than before. In 2021, global comparable sales increased 17.0%, primarily due to strong sales performance across all segments from continued execution of the Accelerating the Arches strategy, as well as recovery from the impact of COVID-19 in the prior year. In 2021 consolidated revenues increased 21% (18% in constant currencies) to USD23.2 billion. At the same time, the fast food giant has certain weaknesses as well. These include the menu still consisting of primarily unhealthy food and the declining brand image of McDonald’s. Furthermore, the fast food chain has very high employee turnover and the company has attracted increasing negative publicity in the past few years. McDonald’s Corporation Report…
Since Amazon went public in 1997, the e-commerce giant has been repeatedly criticized for its lack of commitment on corporate social responsibility aspect of the business. Moreover, Amazon’s first sustainability executive Kara Hartnett Hurst was appointed only in August 2014 , a stark proof that CSR aspect of the business has not been paid due attention to for a long period of time. CSR Programs and Initiatives Amazon Supporting Local Communities In 2020, the e-commerce giant created the Amazon Relief Fund, with a USD25 million initial contribution, focused on supporting its independent delivery service partners and other stakeholders to deal with the negative impact of coronavirus developments on the business. Amazon’s Device Donation Program facilitates the donation of electronic devices and gift cards to schools located near Amazon fulfilment centres throughout the US The company hosts ‘Girls Who Code’ events occasionally to help get more girls interested in coding The e-commerce giant supports local and national nonprofits with cash and product donations. Amazon Educating and Empowering Workers Amazon Career Choice Program pre-pays 95% of tuition for employees to take courses for in-demand fields, such as airplane mechanic or nursing, regardless of whether the skills are relevant to a career at Amazon. Up to date the program has been attended by more than 10000 employees worldwide. Amazon Virtual Contact Centre, allows Amazon’s customer service employees to work from home. The program “Pay to Quit” offers USD 5000 to warehouse workers who quit to encourage employees to take a moment and think about what they really want.[1] Upskilling 2025 is USD 1,2 billion investment project to provide free skills training to U.S. employees. Employee Health and Safety at Amazon Amazon employs 6200 safety professionals worldwide In 2020 due to the risk of COVID-19 coronavirus, the company recommended all of global…
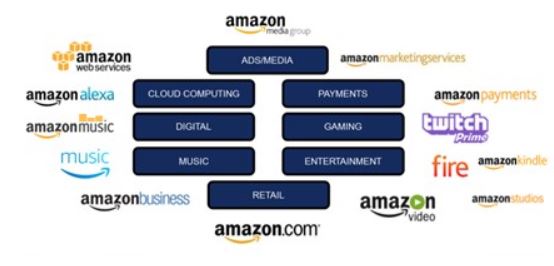
Amazon ecosystem of products and services is vast and it comprises retail, transportation, B2B distribution, payments, entertainment, cloud computing, and other segments. Started only as an online bookstore in 1995 by Jeff Bezos, Amazon has become the e-commerce and cloud computing tech giant consistently increasing the ecosystem of its products and services. The e-commerce giant is competent in focusing on what customers need, designing in-house innovative technology solutions and then commercialising these solutions. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a stark example for this. This is how Amazon ecosystem has evolved. Increasing range of products and services Today, Amazon is a “retailer, a technology company, an entertainment destination, a growing advertising platform, even a delivery company with its own fleet of planes”.[1] Importantly, consumption of one type of Amazon products and services encourages the usage of other products and services offered by the company and that is the primary aim of developing an ecosystem. This can be illustrated using Alexa virtual assistant as an example. Amazon smart security camera that is compatible with the Echo smart speakers allows users to stream live video from the camera on the Echo Show or through the Alexa smartphone app. Moreover, Amazon smart glass is based on Alexa voice assistant and can be used only if the device is linked to a user’s smartphone.[2] Figure 1 below illustrates the essence of Amazon ecosystem. Figure 1 Amazon Ecosystem[3] Each of Amazon business segment illustrated in Figure 1 above plays certain role in consumption of other types of products and services belonging to the ecosystem. Let’s take Amazon Kindle for example. As it is illustrated in Figure 2 below, Amazon Fire platform can be used to consume a wide range of products and services belonging to Amazon portfolio. Moreover, Fire platform can also be used…
