Posts by John Dudovskiy
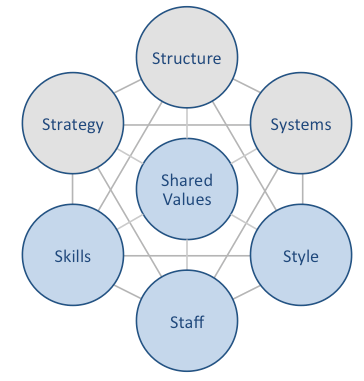
Xiaomi McKinsey 7S model illustrates the ways in which seven elements of businesses can be aligned so that overall effectiveness can be increased. According to the framework strategy, structure and systems are hard elements, whereas shared values, skills, style and staff are considered as soft elements. McKinsey 7S model stresses the presence of strong links between elements in a way that a change in one element causes changes in others. As it is illustrated in figure below, shared values are positioned at the core of Xiaomi McKinsey 7S model, since shared values guide employee behaviour with implications in their performance. Xiaomi McKinsey 7S Model Hard Elements Strategy. Xiaomi business strategy is based on cost leadership. Company’s business strategy also integrates gathering and utilising a large fan base and aggressively increasing the ecosystem of products and services. Moreover, Xiaomi positions itself as an internet and software company rather than a hardware company. Accordingly, the sales of hardware are perceived as a means to deliver software and services in the long-term perspective. Structure. Xiaomi has a matrix organizational structure. The electronics and software company has various business units that are managed independently. Xiaomi organizational structure can also be also classified as flat. Despite its large size employing more than 18000 people in 70 countries, the company has only a few layers of management. Systems. Xiaomi’s business depends on a wide range of systems such as employee recruitment and selection system, team development and orientation system and transaction processing systems. Moreover, there are critically important systems for the company such as customer relationship management system, business intelligence system, and knowledge management system. The mobile internet company aims to increase the efficiency of these and other systems via the integration of internet-based information technologies. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis…
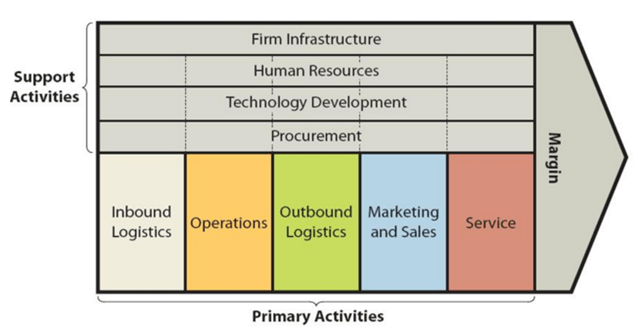
Xiaomi value chain analysis is an analytical framework that assists in identifying business activities that can create value and competitive advantage to the mobile internet company. Figure below illustrates the essence of Xiaomi value chain analysis. Xiaomi Value Chain Analysis Xiaomi Primary Activities Xiaomi Inbound logistics Xiaomi inbound logistics involves the delivery and storage activities of raw materials by the mobile internet company. Strategic relationships with Taiwan-based manufacturers of various components is one of the main sources of value for Xiaomi inbound logistics. Specifically, Xiaomi partners with Inventec and Hon Hai for assembly, Wintek and TPK for screen technology and Unicorn for PCB (printed circuit boards). Moreover, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (TSMC) is the main processor supplier for the company. Xiaomi also procures various electronic components from nearby countries. For example, MOS and batteries are mainly imported from Thailand. Xiaomi Operations Operations activities within Xiaomi value chain analysis refer to the processes of transforming raw materials into ready products. The mobile internet company has established its presence in 70 countries and regions and it is among the top 5 in 16 markets. Xiaomi manufactures locally more than 75% of smartphones it sells in India.[1] Location of manufacturing units in China and India is one of the main sources of value in Xiaomi operations. This is because the costs of human resources in these developoing countries are cheap. Along with proximity of manufacturing units to the sources of raw materials, cost-effective human resources play an instrumental role in sustaining cost advantage competitive edge of the business. Moreover, Xiaomi sophisticates its manufacturing processes in a systematic manner using advanced technologies and benefiting from technological innovations. Xiaomi Outbound Logistics Initially, Xiaomi outbound logistics practices were limited to the shipment of products directly to end-users via couriers. At that stage the company…
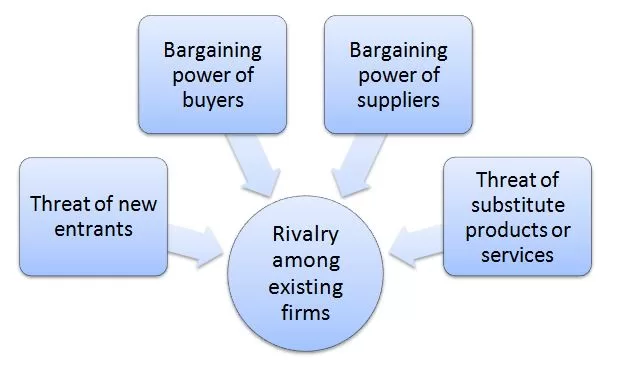
Porter’s Five Forces is an analytical framework developed by Michael Porter (1979)[1]. Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces consists of five individual forces that shape an overall extent of competition in the industry. These forces are illustrated in Figure 1 below: Figure 1 Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Threat of New Entrants in Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Threat of new entrants into the internet technology is low. There are entry barriers for potentially new market players. Economies of scale is one of the major factors and entry barrier for new companies. Xiaomi is able to offer its products for competitive prices because it purchases raw materials in bulk and benefits from the economies of scale to a large extent. Moreover, entry into the electronics and software industry requires formidable capital investments. Xiaomi was initially funded with USD41 million in 2010 and the company went through series of funding and debt financing of several billion USD to reach its current state.[2] It may not be easy for new market entrants to secure funding at such a scale to enter the industry. Additional range of factors that decrease the threat of new entrants to the industry include access to distribution channels and likely retaliation from existing market players such as Apple, Samsung, Xiaomi and Huawei. Bargaining Power of Buyers in Xiaomi Porter’s Five Forces Analysis Bargaining power of buyers in technology and the mobile internet industry is significant. This is caused by primarily high level of competition in the global marketplace. Nevertheless, companies try to reduce buyer bargaining power through developing their ecosystem. For example, “all products belonging to Apple ecosystem are highly compatible with each-other and the purchase of one product belonging to the brand’s portfolio often leads to the purchase of other products. Gradually, it will come to the point that consumers…

Xiaomi marketing communication mix explains the extent of usage of individual elements of marketing communication channels by the mobile internet company. Generally, elements of the marketing communication mix consist of print and media advertising, sales promotions, events and experiences, public relations, direct marketing and personal selling. Xiaomi Print and Media Advertising “Xiaomi once touted its avoidance of advertising as one of the keys to its early success—saving money on commercials helped keep the overall price of the phones lower. Instead, it relied on its upper executives and its “fans” to spread the word and attract new customers through social media.”[1] However, due to increasing competition from its local rivals Oppo and Vivo, The mobile internet company had no choice but to engage in certain forms of traditional advertising such as posters and newspaper advertising. Nevertheless, viral marketing remains as the most important form of marketing for Xiaomi. The internet technology company also uses celebrity endorsement from the likes of top Hong Kong actor-singer, Tony Leung, a 54-year-old best-known to English-speaking audiences for movies like “In the Mood for Love” and “Lust, Caution.”[2] Xiaomi Sales Promotions Xiaomi uses the following sales promotions techniques: Flash sales. Flash sales refer to sales of products and services online at a heavily discounted price for a short period of time. Xiaomi uses flash sales extensively, especially in India. Customer Loyalty Scheme. Reward Mi is a customer loyalty program that rewards loyal customers with exclusive benefits such as priority passes a.k.a F-codes and discount coupons which can be redeemed on selected products across Mi Store.[3] Seasonal sales promotions. The electronics and software company announces sales promotions on notable occasions as Christmas day and anniversaries of notable days for the company. Point of sale materials. The company uses point of sale materials such as posters and…

Xiaomi segmentation, targeting and positioning is needed to indentify the target customer segment for the company and to develop products and services that are attractive to this segment. Segmentation involves dividing population into groups according to certain characteristics, whereas targeting implies choosing specific groups identified as a result of segmentation to sell products. Positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Xiaomi uses mono-segment and imitative types of positioning. The internet technology company uses mono-segment positioning, appealing to the needs of a single customer segment. Specifically, Xiaomi targets a customer segment that want to use smartphones and other technology products, but have limited budget to make such a purchase. Xiaomi also uses imitative type of positioning by closely imitating the products of market leaders such as Apple and Samsung. The electronics and software company has even earned the nickname “Apple of the East” due to its close imitation of Apple products and Apple product presentation. The following table illustrates Xiaomi segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmentation criteria Xiaomi target customer segment Geographic Region 70 countries and regions globally Density Urban and rural Demographic Age 18 – 65 Gender Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage young, single people not living at home Newly Married Couples young, no children Full Nest I youngest child under six Full Nest II youngest child six or over Full Nest III older married couples with dependent children Empty Nest I older married couples, no children living with them Empty Nest II older married couples, retired, no children living at home Solitary Survivor I in labour force Solitary Survivor II retired Occupation Students, employees, professionals Behavioural Degree of loyalty ‘Hard core loyals’ ‘Soft core loyals’ ‘Switchers’ Benefits sought Cost attractiveness Personality Easygoing, determined and ambitious personality types User status non-users, potential…

Xiaomi marketing mix (Xiaomi 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Xiaomi mainly focuses on hardware, software and internet services. The company’s product range is vast and includes laptops, mobile phones, tablets, smart TVs, power banks, smartwatches etc. Xiaomi also manufactures and drones, sells water purifiers, vacuum cleaners and even rice cookers. Xiaomi products such as cellphones, TVs, TV boxes, and speakers have received more than 145 industrial design awards altogether.[1] Continuous expansion of ecosystem of products and services is placed at the core of company’s business strategy. Place Xiaomi is headquartered in Beijing, China and has offices in Asia-Pacific, India, and Brazil. The mobile internet company has established its presence in 70 countries and regions and it is among the top 5 in 16 markets. These markets include Turkey, Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Indonesia, Brazil, India, and Vietnam. The mobile internet company opened its first offline retail store in February 2016 and by the end of 2017 had more than 155 stores.[2] In March 2017, the company established a new sales channel called Xiaomi kiosks to reach districts without Mi Home Stores and towns and villages with limited e-commerce access[3] Price Xiaomi pricing strategy can be described as economy pricing. Accordingly, the internet technology company sets its prices low, keeping marketing and promotional costs to a minimum. Flash sales are integral component of Xiaomi pricing strategy. The electronics and software company uses the flash sales to announce the sales of its smartphones at a greatly reduced price. Xiaomi flash sales last only for a short duration of time. For example, in India “a flash sale for the Redmi 1S model in September 2014, around 40,000 pieces were sold out in just…

Xiaomi marketing strategy has been traditionally minimalistic due to the cost leadership business strategy pursued by the company. Accordingly, the mobile internet company only engaged in social media marketing, saving on advertising costs and passing this cost advantage to customers in the forms of products with low price tags. However, “Oppo and Vivo have grown in China by using the exact tactics that Xiaomi once avoided. Both companies spend heavily on offline advertisements and celebrity endorsements, plastering billboards on subways and bus stops across China’s second- and third-tier cities.”[1] This has caused a shift in Xiaomi marketing strategy and starting from lately the internet technology company has started to use traditional marketing communications channels as well. Moreover, Xiaomi marketing strategy nowadays also includes product placements and Xiaomi holograms in fiction triller Anon (2018) can be mentioned as an example. As s privately-owned company, Xiaomi does not disclose its annual marketing budget. Xiaomi 7ps of marketing focuses on price element of the marketing mix to a greater extent compared to other elements. Accordingly, the brand’s target customer segment represents price-conscious consumers who want to own the latest smartphones with advanced functions and capabilities for affordable cost. Hunger marketing strategy is one of the integral components of Xiaomi marketing strategy. The electronics and software company appeals to emotional needs of their target customer segment by selling only limited amount of products for a limited duration of time. In other words, the company creates the shortage of supply in purpose, creating a buzz in the market and evoking desire in customers to own a MI brand smartphone. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi marketing strategy. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix…

PESTEL is a strategic analytical tool and the acronym stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. Xiaomi PESTEL analysis involves the analysis of potential impact of these external factors on the profitability and long-term growth prospects of the mobile internet company. Political Factors in Xiaomi PESTEL Analysis There is a wide range of political factors that can affect the internet technology company. These include government stability, bureaucracy, corruption, freedom of press and others. On one hand, Xiaomi has benefited from political factors in China in general and protectionism policy of Chinese government in particular. The government of China protects local technology companies such as Tencent, Baidu and Xiaomi by imposing barriers to operate in the country to their international rivals such as Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, YouTube and Google. The head of Xiaomi, along with the heads of Tencent and Baidu advice the government on international business policies.[1] This grants technology companies enviable opportunities to influence local political factors that affect their businesses to a certain extent. Xiaomi has even set up its Communist Party Committee in 2015[2] as a display of its support for the ruling government. On the other hand, while political factors benefit Xiaomi in its home market in China, the company is usually negatively affected from political factors outside of China. For example, the Taiwanese government has investigated Xiaomi on a cyber security threat in 2014 causing certain damage to the brand image of the company. There is a popular concern that the investigation was politically motivated because “China and Taiwan have been historical foes since defeated Nationalists fled to the island after losing a civil war to China’s Communists in 1949”.[3] Economic Factors in Xiaomi PESTEL Analysis Economic factors affecting the internet technology company are diverse. These include macroeconomic climate in the country,…

In business context, SWOT acronym stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats associated with the company. The following table illustrates Xiaomi SWOT analysis Strengths 1. Efficient leadership by Lei Jun 2. Impressive growth rate 3. Cost advantage 4. Brand value estimated at USD 100 billion[1] Weaknesses 1. Low profit margin 2. Lower smartphone capabilities and functionalities compared to major competitors such as Apple and Samsung 3. Competitive advantage difficult to sustain 4. Lack of experience in the global marketplace Opportunities 1. Increasing presence in cloud segment 2. Formation of strategic collaborations 3. Focusing on marketing strategy 4. Achieving a disruptive innovation in the industry as a result of research and development Threats 1. Market saturation in smartphone industry 2. Increase in the costs of resources 3. Issues with product functionality 4. Emergence of CSR-related scandals Xiaomi SWOT analysis Strengths in Xiaomi SWOT Analysis `1. Xiaomi co-founder and CEO Lei Jun is an effective business leader named “Businessman of the Year” 2014 by Forbes Asia. Dubbed the ‘new Steve Jobs’, Lei Jun is perceived as the face of China Inc, along with Alibaba Founder Jack Ma.[2] Moreover, it is said that Lei has never yelled at his staff. When he encounters a problem, he just smiles and gets down to business, and tries to find a solution. In social gatherings, Lei is always a good listener.[3] Efficient and visionary leadership style is one of the major factors behind the phenomenal growth of the internet technology company. 2. The electronics and software company has enjoyed an impressive growth rate since its foundation in 2011. In Q4 2017, Xiaomi became the world’s No.4 in terms of quantity of shipments. Despite the decline of 6,3% in the global smartphone market, Xiaomi managed to maintain a year-on-year growth of 96.9%, the only brand demonstrating continuous…
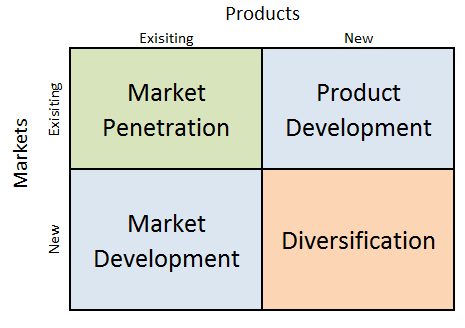
Xiaomi Ansoff Matrix is a marketing planning model that helps the mobile internet company to determine its product and market strategy. Ansoff Matrix illustrates four different strategy options available for businesses. These are market penetration, product development, market development and diversification. Xiaomi Ansoff Matrix Within the scope of Ansoff Matrix, Xiaomi uses all four growth strategies in an integrated manner: 1. Market penetration. When using market penetration, companies focus on selling existing products to existing customers. Xiaomi successfully uses market penetration strategy in its home market in China. According to Q1, 2018 smartphone sales results in China, Mi smartphones ranked third with the local market share of 12,8% after Huawei (20,8%), Oppo (18,5%), iPhone (18,2%) and Vivo (14,6%). 2. Product development. This strategy option involves developing new products to sell to existing markets. Xiaomi has ever-increasing product portfolio ranging from smartphones to water purifiers and tooth brushes. Product development strategy is likely to be continued by Xiaomi. This is because Xiaomi positions itself as a “company that provides innovation to everyone at every level — from smartphones and technology to IoT connected smart products to the basic everyday tools like power banks, backpacks and pens”.[1] 3. Market development. Market development strategy is associated with finding new markets for existing products. Xiaomi started market development in 2014, only four years after the company was founded. In mid-2013, the company hired Hugo Barra away from Google and Android to work on international expansion.[2] Since that time, the electronics and software company has established its presence in rapidly developing markets such as India, Singapore and Russia. The mobile internet company also has plans to enter US market.[3] 4. Diversification. Diversification involves developing new products to sell to new markets. Xiaomi is engaged in an aggressive diversification strategy. Xiaomi ecosystem is vast and comprises 55 companies,…
