Posts by John Dudovskiy

According to Harrison’s model of culture, Xiaomi organizational culture can be classified as power culture. Specifically, powers of decision making at the internet technology company are concentrated in the hands of founder and CEO Lei Jun. Inspirational and effective leadership style of Lei Jun justifies the necessity of power culture for Xiaomi. Xiaomi organizational culture integrates the following three key elements: 1. “Just for Funs” concept. The tagline “Just for fans” is placed at the core of Xiaomi organizational culture. Founder and CEO Lei Jun explains that “the culture of fandom is about becoming friends with our consumers.”[1] There is a story of a master’s student who spends free time doing MiUI testing and moderating a Xiaomi fan forum that nets 200,000 posts every day as a volunteer.[2] 2. Innovation and creativity. Company’s official website claims that “we are incredibly flat, open, and innovative. No never-ending meetings. No lengthy processes. We provide a friendly and collaborative environment where creativity is encouraged to flourish.”[3] In other words, Xiaomi aims to promote informal organizational culture at all levels with positive implications on employee creativity. 3. Intense working culture. Xiaomi organizational culture can be characterized as intense. This is due to cost leadership business strategy followed by the company in a way that effective application of this strategy involves deriving the maximum benefit from resources, including human resources. Departure of former Google executive Hugo Barra from the key post of Xiaomi international vice president has been said to be linked to negative elements of Xiaomi organizational culture. Specifically, Barra said he was leaving because difficulties of living in “such a singular environment” had “taken a huge toll” on his life.[4] Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business…
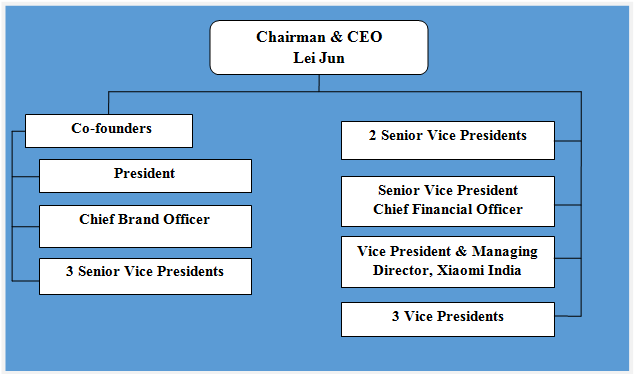
Xiaomi organizational structure can be classified as matrix. Specifically, Xiaomi organizational structure is decentralized, where different business units are managed independently. Despite the large size of the business involving presence in 70 countries with more than 18000 employees, the company has less layers of management compared to other businesses of similar sizes. Figure below illustrates Xiaomi organizational structure: Xiaomi organizational structure Matrix organizational structure allows the mobile internet company to develop its new products and services in a short duration of time. This is due to absence of bureaucracy that is associated with hierarchical organizational structures. However, disadvantages of matrix organizational structure for the business may include lack of strict control by the top management over separate business units and lack of integration between the operations of individual business units. Nevertheless, it is important for Xiaomi to maintain its flat organizational structure in order to remain flexible, so that the mobile internet company can adapt to frequent changes in the global marketplace. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi organizational structure. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis, Ansoff Matrix and McKinsey 7S Model on Xiaomi. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Xiaomi leadership, business strategy and organizational culture. The report also comprises discussions of Xiaomi marketing strategy, ecosystem and addresses issues of corporate social responsibility.

Effectiveness of Xiaomi leadership can be considered as one of the main competitive advantages for the business. Xiaomi CEO Lei Jun is a respected businessman in China who previously led Kingsoft and founded Joyo.com that was sold to Amazon in 2014. It is said that Lei has never yelled at his staff. When he encounters a problem, he just smiles and gets down to business, and tries to find a solution. In social gatherings, Lei is always a good listener.[1] Named businessmen of the Year by Forbes in 2014 and along with Alibaba Founder Jack Ma, Lei Jun is rightly considered as the face of China Inc.[2] Xiaomi CEO is recognized as an effective charismatic leader worldwide. Along with Lei Jun, seven co-founders of the company have senior leadership roles with the titles of president and vice-presidents. Having co-founders in the senior management team is an important factor due to increased sense of ownership with positive implications on the performance of executives. Xiaomi has been dubbed as “Apple of China” for its emulation of design of Apple’s products, as well as, Lei Jun style of product announcements and his general image that resembles late Apple founder and CEO Steve Jobs. However, Lei Jun leadership style is fundamentally different from Steve Jobs leadership. Specifically, while Steve Jobs was known for his centralized and micro-managing leadership style, Xiaomi CEO has a reputation for being a good listener and takes into account views of other members of his senior management team. Xiaomi leadership challenges at present include maintaining cost leadership position amid intensifying competition from other budget internet technology brands such as Oppo and Vivo. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains a full analysis of Xiaomi leadership. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL,…
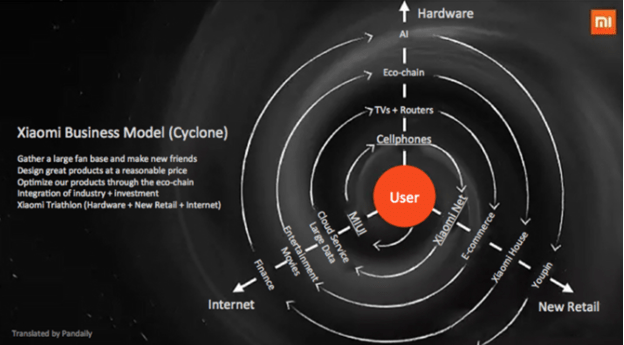
Xiaomi business strategy can be classified as cost leadership. According to its founder and CEO Lei Jun, Xiaomi was founded on the belief that “high-quality technology doesn’t need to cost a fortune.”[1] Accordingly, the company offers smartphones and other internet-technology products and services for affordable prices. On a wider perspective, Xiaomi business strategy is based on the following four pillars: 1. Gathering and utilising a large fan base. Xiaomi has a large fan base involving millions of people across the globe. Fans spend countless hours online discussing Xiaomi products on various forums, thus increasing the level of brand awareness with no extra cost for the company. The mobile internet company enjoys cult-like following, the same way as its major competitor Apple. According to its business strategy, Xiaomi fosters, develops and encourages its fans via Mi Fan Festivals that involves discounts and gifts. The motto of the company is “Just for Fans” and the company is also known to recruit its new employees among Mi Fans. 2. Designing great products at a reasonable price. Xiaomi practices ‘design as you built’ philosophy, incorporating Mi Fans feedback in a constant manner at all stages of new product development. Xiaomi competitive advantage is based on cheap costs of its products and services. In simple terms, cheap costs of Xiaomi products and services is the main reason for consumers buying those products and services. 3. Constant optimization of products through eco-chain. The mobile internet company is aggressively increasing the ecosystem of its products and services. This is another important aspect of Xiaomi business strategy. Currently, Xiaomi ecosystem comprises 55 companies including 29 companies which were incubated from the ground up by Xiaomi.[2] The ecosystem produces ever-increasing range of products ranging from smartphones to rice cookers. 4. Xiaomi Triathlon: Hardware+New Retail+Internet. As it is illustrated in…

Xiaomi Inc. is a privately owned electronics and software company founded in 2010 by serial entrepreneur Lei Jun, along with seven other co-founders. The mobile internet company has established its presence in 70 countries and regions and it is among the top 5 in 16 markets. Xiaomi currently employs about 18,000 people. In 2017 Xiaomi generated more than RMB 100 billion revenues and expected to get listed in the Fortune Global 500 list in foreseeable future. Xiaomi business strategy is based on cost advantage. Moreover, the company gathers and utilizes its large fan base in an efficient manner with positive implications on customer loyalty and the bottom line for the business. An aggressive expansion of ecosystem of products and services is also placed at the core of Xiaomi business strategy. The mobile internet company has matrix and flat organizational structure. According to framework of Ansoff Growth Matrix, Xiaomi uses all for strategies – market penetration, product development, market development and diversification, in an integrated manner. Efficient leadership by founder and CEO Lei Jun, impressive rate of growth and cost advantages compared to competition are considered as major strengths associated with Xiaomi. At the same time, the company has noteworthy weaknesses such as low profit margin, lower smartphone capabilities and functionalities compared to major competitors and difficulties of sustaining competitive advantage. Xiaomi Inc. Report contains the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s Five Forces, Value Chain analysis and McKinsey 7S Model on Xiaomi. Moreover, the report contains analyses of Xiaomi business strategy, leadership and organizational structure and its marketing strategy. The report also discusses the issues of corporate social responsibility. 1. Executive Summary 2. Business Strategy 3. Leadership 4. Organisational Structure 5. Organizational Culture 6. Xiaomi and Ansoff Matrix 7. SWOT Analysis…

Uber Technologies Inc. is a global transportation technology company that operates in more than 10,000 cities in approximately 71 countries. The ride-hailing giant and its subsidiaries employ approximately 22,800 people globally (Annual Report, 2020). The global transportation technology company generated revenues of USD 11,1 billion in 2020, a decline of 14% compared to the previous year. Uber incurred operating losses of USD 3.0 billion, USD 8.6 billion and USD 4.9 billion in 2018, 2019 and 2020 respectively. The largest taxi company in the world has no cars of its own. Drivers are independent contractors for the company and they use their own or rented cars to drive with Uber using Uber app. The company has effectively disrupted the taxi industry in the global scale. Uber business strategy involves increasing service range to cater for the needs of great amount of customers and focusing on high levels of user convenience. Moreover, cost-saving through technological innovation is placed at the core of Uber business strategy. The company follows growth path through acquisitions, purchasing start-ups that can contribute to its ecosystem. The ride-hailing giant had a leadership crisis in 2017. Lack of leadership skills of co-founder and the first CEO Travis Kalanick had caused the formation of a poor corporate culture. As a result the company suffered from a range of serious scandals involving discrimination, sexual harassment and even mobbing. Uber CEO was even caught on video rudely arguing with driver about declining fares (Wong, 2017). Mr. Kalanick had to step down from leadership role as demanded by investors and Expedia’ CEO Dara Khosrowshahi became a new CEO for Uber. Uber possesses considerable strengths such as the first mover advantage, global market leadership and the brand value and advanced level of user convenience. At the same time, the company has serious weaknesses such…

Samsung marketing communication mix utilises a number of marketing communication channels such as print and media advertising, sales promotion, events and experiences and public relations. Samsung Electronics uses these channels in an integrated manner as discussed below in more details. Advertising Print and media advertising is one of the core elements of the marketing mix extensively utilized by Samsung Electronics. One of the important key features of Samsung advertising strategy is that the multinational electronics company usually advertises its specific products such as Galaxy S and Note smartphones, but it does not advertise much Samsung brand in general . The most noteworthy media advertising campaigns include live commercials for Samsung Galaxy S 3 device on popular Jimmy Kimmel Live show in June 2012 and on Late Night With Jimmy Fallon on July and August of the same year. Moreover, partnership with Fox channel in the US to run four 30-second advertising clips during the National Football League, college football and World Series games in 2012 have been praised as efficient marketing campaigns.[1] Samsung print advertising in popular newspapers, magazines and journals have previously included direct attacks on its major competitors, notably Apple. For example, a print ad campaign titled ‘It doesn’t take a genius’ is a clever play of words on Apple’s emphasize on genius branding. The print ad compares major functionalities of iPhone5 and Galaxy S III and illustrating the superiority of Samsung’s product on several fronts.[2] Viral marketing is also extensively used by Samsung as one of the most effective advertising methods. For example, the latest 60-second viral marketing video titled “Anticipation” is a successful attempt to associate Samsung Galaxy S6 with excitement and a sense of achievement and recognition.[3] Sales Promotion Samsung uses sales promotions as a marketing tool more extensively compared to the majority of…

Samsung segmentation, targeting and positioning involves a set of activities performed in a sequence. These activities constitute the essence of Samsung marketing strategy. Segmentation involves dividing population into different groups on the basis of their common characteristics. Targeting is associated with selecting specific group(s) as consumers of products and services. Lastly, positioning refers to the selection of the marketing mix the most suitable for the target customer segment. Samsung uses the following types of positioning: Multi-segment positioning. Samsung targets more than one segments at the same time through offering several packages of products and services. For example, there are several variations of Samsung SMART Signage professional displays with different sizes, screen resolutions and functionalities and ultimately with different price tags. Thus, Samsung appeals to the needs and wants of consumers with varying financial capabilities. Imitative positioning. Samsung is known to imitative its main competitor Apple in product in design, functionalities, as well, as marketing strategy. Anticipatory positioning. Certain Samsung products such as mobile image sensors currently have low turnover. However, these product have been developed with the anticipation that the turnover will increase in the future. The following table illustrates Samsung segmentation, targeting and positioning: Type of segmentation Segmen-tation criteria Samsung target customer segment Samsung IT & Mobile Communications Samsung Consumer Electronics Samsung Device Solutions Geog-raphic Region 80 countries worldwide 80 countries worldwide 80 countries worldwide Density Urban/rural Urban/rural Urban/rural Demo-graphic Age 18-65 25-65 25-60 Gender Males & Females Males & Females Males & Females Life-cycle stage Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Full Nest III Empty Nest I Empty Nest II Solitary Survivor I Solitary Survivor II Bachelor Stage Newly Married Couples Full Nest I Full Nest II Full Nest III Empty Nest I Empty Nest II Bachelor Stage Newly Married…

Samsung marketing mix (Samsung 7Ps of marketing) comprises elements of the marketing mix that consists of product, place, price, promotion, process, people and physical evidence. Product Samsung Electronics products are designed in 6 global design centres and manufactured in 53 global production bases. There are 34 R&D centres worldwide that engage in new product development. As illustrated in table below, Samsung products can be divided into three divisions and there are more than one product categories under each division. Product division Product categories Consumer electronics Visual display business Digital appliances business Printing solutions business Health and medical equipments business IT & Mobile Communications Networks business Mobile communications business Device solutions Memory business System LSI business Samsung product divisions and categories Samsung products have won a number of awards and recognitions such as Best Product Award in 8 categories by BLI Summer Pick Award and Gold Award in Design by iF Design in 2015. Place. There are 53 Samsung international sales bases and the multinational electronics company uses the following sales channels: Sales and service dealers. This sales channel is associated with corporate sales. Modern retail outlets owned by the company. These are highly attractive stores with customer service representatives, as well as, employees known as Galaxy Consultants. In 2015, there were Galaxy Consultants at 158 stores under Samsung’s direct management in Korea.[1] The company has plans to expand Galaxy Consultants program beyond Korea. Distributors. Samsung has regional, territory and country distributors. Depending on the territory, size and experience of distributors, Samsung can grant distributorship rights of a single product category or all Samsung products. Online sales. Customers can choose and order Samsung products through official website of the company. Price Samsung pricing strategy can be described as the combination of the following pricing strategies depending on the product range, the…

Samsung organizational culture has been traditionally seniority-oriented reflecting the national culture of its home country South Korea. Positive aspects of such a culture may include higher levels of employee loyalty and faster speed of decision making. On the negative side, however, seniority-oriented organizational culture does not encourage junior employees to communicate their ideas and propose initiative to their superiors. Such ideas and initiatives may prove to be insightful and play an instrumental role in new product development or adding innovative features and capabilities to existing products. Taking into account critical role of innovations and creativity in electronics industry, it can be argued that negative aspects of seniority-oriented corporate culture outweigh its positive aspects for Samsung. The company is aware of this and in 2016, the senior management announced plans to reform Samsung organizational culture. These reforms included simplification of job rankings from the previous seven stages to four stages and employees calling each other by their name with the suffix “-nim,” which shows respect in Korean, instead of calling them by their job titles, such as manager or director.[1] Moreover, culture-related changes vowed by the company included holding more online internal discussions and reducing extraneous meetings, reducing overtime and encouraging employees to spend their weekends with family or pursuing professional education opportunities.[2] However, the implementation of cultural changes announced above a year ago, now seems questionable. This is because Jay Y. Lee, former Samsung executive and de facto head of the Samsung conglomerate who announced these cultural changes was jailed for five years for offering bribes to former president of South Korea and other officials, as well as, for other crimes.[3] Samsung Group Report contains a full analysis of Samsung organizational culture. The report illustrates the application of the major analytical strategic frameworks in business studies such as SWOT, PESTEL, Porter’s…
